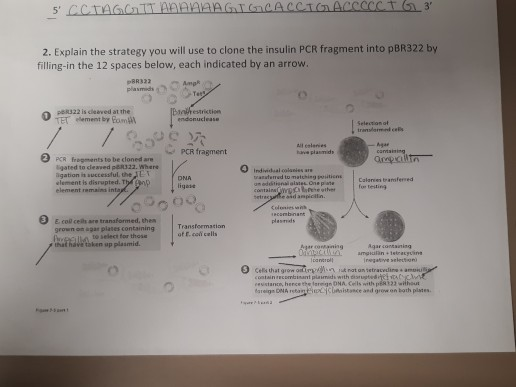
How do you clone a PCR?
- Run PCR and purify the PCR product: Run PCR to amplify your insert DNA.
- Digest your DNA:
- Isolate your insert and vector by gel purification:
- Ligate your insert into your vector:
- Transformation:
- Isolate the Finished Plasmid:
- Verify your Plasmid by Sequencing:
What is the primary method of PCR cloning?
It allows for the cloning of DNA fragments that are not available in large amounts. Typically, a PCR reaction is performed to amplify the sequence of interest, and then it is joined to the vector via a blunt or single-base overhang ligation prior to transformation. Early PCR cloning often used Taq DNA Polymerase to amplify the gene. This results in a PCR product with a single template …
What is the fastest way to clone DNA?
Experimental Procedure. Run PCR and purify the PCR product: Run PCR to amplify your insert DNA. It is important to use a high fidelity taq polymerase to minimize mutations. Digest your DNA: Isolate your insert and vector by gel purification: Ligate your insert into your vector: Transformation:
How to get rid of PCR primers before Cloning?
How do you clone a PCR? Run PCR and purify the PCR product: Run PCR to amplify your insert DNA. Digest your DNA: Isolate your insert and vector by gel purification: Ligate your insert into your vector: Transformation: Isolate the Finished Plasmid: Verify your Plasmid by Sequencing:
How do I amplify the insert DNA in PCR?
1) Make up the appropriate amount of 5xPCR master mix. You will need 20ul for each clone. Stock Resultant PCR Buffer... 2) Fill enough 0.2ml strip-tubes or PCR plates with 80ul of water to accommodate all your colonies. Pick a white colony... 3) Add 20ul of master mix to each tube. Pre-heat to 94C ...

What is the easiest way to clone PCR products?
TA cloning and blunt-end cloning represent two of the simplest PCR cloning methods. Their choice depends upon the nature of the vector and the type of PCR enzymes used in cloning. TA cloning employs a thermostable Taq DNA polymerase capable of amplifying short DNA sequences.
How can a PCR product be cloned into a plasmid?
In its simplest form, PCR based cloning is about making a copy of a piece of DNA and at the same time adding restriction sites to the ends of that piece of DNA so that it can be easily cloned into a plasmid of interest.Mar 29, 2016
Can PCR DNA be cloned?
PCR cloning is a rapid method for cloning genes, and is often used for projects that require higher throughput than traditional cloning methods can accommodate. It allows for the cloning of DNA fragments that are not available in large amounts.
What are the 4 steps of cloning?
In the classical restriction enzyme digestion and ligation cloning protocols, cloning of any DNA fragment essentially involves four steps:isolation of the DNA of interest (or target DNA),ligation,transfection (or transformation), and.a screening/selection procedure.Dec 5, 2014
How is PCR different from cloning?
There are several fundamental differences between these two methods. Molecular cloning replicates DNA within in a living cell, while PCR replicates DNA in an in vitro solution, free of living cells. Molecular cloning involves cutting and pasting the sequences, while PCR amplifies DNA by copying an existing sequence.Jun 22, 2020
Is PCR needed for cloning?
PCR cloning is a rapid method for cloning genes, and is often used for projects that require higher throughput than traditional cloning methods can accommodate. It allows for the cloning of DNA fragments that are not available in large amounts.
How do you clone a gene?
The basic steps in gene cloning are:DNA. ... Bacterial plasmids are cut with the same restriction enzyme.The gene-sized DNA and cut. ... The recombinant plasmids are transferred into bacteria using electroporation or heat shock.The bacteria is plated out and allowed to grow into colonies. ... The.
What are the cloning methods?
There are three different types of artificial cloning: gene cloning, reproductive cloning and therapeutic cloning. Gene cloning produces copies of genes or segments of DNA. Reproductive cloning produces copies of whole animals.Aug 15, 2020
How do you clone a gene from cDNA?
Complementary DNA (cDNA) cloning is termed for the gene cloning (cloning of DNA fragments) obtained from cDNA. The principle of cDNA cloning is that it involves the copying of mRNA transcripts into DNA, which are then inserted into bacterial plasmids and then placed into bacteria by transformation.Jul 18, 2020
What are the 7 steps of cloning?
In standard molecular cloning experiments, the cloning of any DNA fragment essentially involves seven steps: (1) Choice of host organism and cloning vector, (2) Preparation of vector DNA, (3) Preparation of DNA to be cloned, (4) Creation of recombinant DNA, (5) Introduction of recombinant DNA into host organism, (6) ...
How do you clone?
To make a clone, scientists transfer the DNA from an animal's somatic cell into an egg cell that has had its nucleus and DNA removed. The egg develops into an embryo that contains the same genes as the cell donor. Then the embryo is implanted into an adult female's uterus to grow.Jul 8, 2019
How do you clone a human step by step?
0:122:09Scientists Take Step Towards Human Cloning - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThey start by taking a human egg take out the nucleus. And then they take a skin cell from a patientMoreThey start by taking a human egg take out the nucleus. And then they take a skin cell from a patient. Take the skin cell and put it into this D nucleated egg the skin cell that's been transferred.
Run PCR and Purify The PCR Product
Run PCR to amplify your insert DNA. It is important to use a high fidelity taq polymerase to minimize mutations. The fidelity of the polymerase bec...
Isolate Your Insert and Vector by Gel Purification
Run your digest DNA on an agarose gel and conduct a gel purification to isolate the DNA. When running a gel for purification purposes it is importa...
Ligate Your Insert Into Your Vector
Conduct a DNA Ligation to fuse your insert to your recipient plasmid. We recommend around 100ng of total DNA in a standard ligation reaction. You i...
Isolate The Finished Plasmid
Finally, you will need to pick individual bacterial colonies and check them for successful ligations. Pick 3-10 colonies depending on the number of...
Verify Your Plasmid by Sequencing
PCR based cloning carries a much higher risk for mutation than restriction enzyme based cloning. DNA replication by PCR has error rates that range...
Summary
PCR based cloning is incredibly versatile and allows for nearly any piece of DNA to be placed into a backbone vector of choice with minimal limitations.
Background
In its simplest form, PCR based cloning is about making a copy of a piece of DNA and at the same time adding restriction sites to the ends of that piece of DNA so that it can be easily cloned into a plasmid of interest.
Experimental Procedure
Run PCR to amplify your insert DNA. It is important to use a high fidelity taq polymerase to minimize mutations. The fidelity of the polymerase becomes more important the longer the expected PCR product is.
Run the PCR reaction
Run PCR to amplify your insert DNA. It is important to use a high fidelity polymerase to minimize mutations. The fidelity of the polymerase becomes more important the longer the expected PCR product is.
Isolate the PCR product
Isolate your PCR product from the rest of the PCR reaction using a kit, such as the QIAquick PCR Purification Kit. The PCR product is now ready for restriction digestion. As such, the later steps in this process are the same as those discussed in our restriction cloning post.
Leave a Comment
For more details on how we collect, store, and protect your information, we invite you to read our Transparency and Privacy Policy.
Designing colony PCR primers
The first and perhaps most important step to colony PCR is designing primers. There are 3 strategies for primer design: 1) insert-specific primers, 2) backbone-specific primers, and 3) orientation-specific primers.
PCR set-up
Setting up colony PCR reactions is nearly identical to preparing a standard PCR reaction: combine template, primers, polymerase, and dNTPs and then incubate with a standard PCR thermocycling program. One key difference is the plasmid DNA must be released from the bacteria in order to serve as PCR template.
Analyzing PCR product size on a gel
Now that your PCR is complete, it’s time to run the products on an agarose gel to determine their size. Make sure to use an appropriate molecular weight standard for reference and to add a loading dye with glycerol to your samples before pipetting them onto the gel.
Verifying the insert sequence with Sanger Sequencing
After identifying a few positive clones, the last step is to mini-prep these clones and submit the plasmids for Sanger sequencing. Sequencing allows you to confirm the sequence of the insert, insert orientation, and the sequences of the junctions between the plasmid and insert DNA.
Tips and tricks from the bench
Don't pick too large of a colony. Too many bacteria can inhibit your PCR reaction or cause non-specific products to show up on your gel.
Gene Cloning with Plasmids: Summary
We all know that DNA is the basic building block of biology. So, how can we make use of DNA to change cell biology? Well, today’s blog post will focus on “gene cloning” — making plasmids (circular DNA strands) so that we can introduce them into bacteria using our previous bacterial transformation method.
Be Careful Designing Plasmid Primers for Gene Cloning
Based on the above image, you can tell that if an enzyme’s restriction site is inside your gene of interest, you cannot use that restriction enzyme because you’ll cut your gene. Also, you’ll be putting this gene into a new plasmid. Make sure that the restriction enzyme you use is compatible with the “multiple cloning site” within this new plasmid.
Gene cloning with PCR
With the primer already designed, we are ready to clone our gene. The rest of the steps in the gene cloning process are:
