Here are a few steps that will help you to use a radiation converter to change between radiation units:
- Select the radiation unit you want to convert.
- Enter the value of the radiation unit you selected. If you are going to convert the absorbed dose, enter the value in...
- The calculator will automatically convert the entered value into different units of measure...
Full Answer
What are the units of measurement for radiation?
- R adioactivity refers to the amount of ionizing radiation released by a material. ...
- E xposure describes the amount of radiation traveling through the air. ...
- A bsorbed dose describes the amount of radiation absorbed by an object or person (that is, the amount of energy that radioactive sources deposit in materials through which they pass). ...
What units are used to measure nuclear radiation?
Measuring Radiation. There are four different but interrelated units for measuring radioactivity, exposure, absorbed dose, and dose equivalent. These can be remembered by the mnemonic R-E-A-D, as follows, with both common (British, e.g., Ci) and international (metric, e.g., Bq) units in use:. Radioactivity refers to the amount of ionizing radiation released by a material.
How do you measure radiation?
Method 3 Method 3 of 3: Calculating Radiation Dose Download Article
- Estimate your annual dose with an online calculator. You can get a rough estimate of your annual radiation exposure without using any devices.
- Identify radiation dose with a device that measures Grays or sieverts. ...
- Set your device to detect a particular type of radiation, if necessary. ...
- Move the meter over the object or person slowly. ...
What is the SI unit of radiation?
What is SI unit of radiation? The radiation dose absorbed by a person (that is, the amount of energy deposited in human tissue by radiation) is measured using the conventional unit rad or the SI unit gray (Gy). The biological risk of exposure to radiation is measured using the conventional unit rem or the SI unit sievert (Sv).
How are radiation units measured?
The radiation dose absorbed by a person (that is, the amount of energy deposited in human tissue by radiation) is measured using the conventional unit rad or the SI unit gray (Gy). The biological risk of exposure to radiation is measured using the conventional unit rem or the SI unit sievert (Sv).
What is a unit of radiation?
A material's radioactivity is measured in becquerels (Bq, international unit) and curies (Ci, U.S. unit). Because a curie is a large unit, radioactivity results are usually shown in picocuries (pCi). A picocurie is one trillionth of a curie. The higher the number, the more radiation released by the material.
How much is 10 mSv?
The unit equivalences between the systems are 1 Sv = 100 rem, or 1 rem = 10 mSv.
How can units be converted?
A conversion factor is a number used to change one set of units to another, by multiplying or dividing. When a conversion is necessary, the appropriate conversion factor to an equal value must be used. For example, to convert inches to feet, the appropriate conversion value is 12 inches equal 1 foot.
How do you read radiation levels?
The level of radiation is expressed as an amount of radiation (in a unit called Sieverts) per hour of exposure. So if the Geiger counter reads 0.22 microSieverts per hour (as it does in the photo above), that means I received . 22 microSieverts of radiation while having my hour-long breakfast in Kiev.
How do I convert mGy to mSv?
The unit milligray (mGy) is used for other types of radiation doses, but for this discussion the only one we need to know is absorbed dose. For x rays, gamma rays, and beta radiation, the conversion factor between absorbed dose in mGy and equivalent dose in mSv is one (1). So, in this case, we can say mGy equals mSv.
How much radiation is in a MRI?
Because radiation is not used, there is no risk of exposure to radiation during an MRI procedure. However, due to the use of the strong magnet, MRI cannot be performed on patients with: Implanted pacemakers.
How much is 0.1 mSv?
Like other sources of background radiation, the amount of radon exposure varies widely depending on where you live. To put it simply, the amount of radiation from one adult chest x-ray (0.1 mSv) is about the same as 10 days of natural background radiation that we are all exposed to as part of our daily living.
How much radiation is safe for humans?
The ICRP recommends that any exposure above the natural background radiation should be kept as low as reasonably achievable, but below the individual dose limits. The individual dose limit for radiation workers averaged over 5 years is 100 mSv, and for members of the general public, is 1 mSv per year.
Why do we convert units?
Help to show another person the exact amount you have. Assist in solving a mathematical problem, especially in chemistry, where you can follow the units to get to the answer. Show which measurement system the person is using (i.e. metric or standard)
What is unit conversion table?
Unit Conversion Table/a>...Length Unit Conversion1 millimeter0.001 meter1 kilometer1000 meters1 inch2.54 × 10−2 meters1 foot0.3048 meters8 more rows•Nov 26, 2020
How do you convert one step units?
0:035:00Convert Units - One Step Conversion - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipBy 12 which is 4 point 7 5 feet. And what we've done here is converted 57 inches in defeat 4.75 feetMoreBy 12 which is 4 point 7 5 feet. And what we've done here is converted 57 inches in defeat 4.75 feet we did this by dividing out units by placing them in the opposite. Part of the fraction.
Conversion settings explained
First of all, you don't have to change any settings to use the converter. It's absolutely optional.
Number of significat figures
Do you want rounded off figures or scientifically precise ones? For everyday conversions we recommend choosing 3 or 4 significant digits. If you want maximum precision, set the number to 9
Digit groups separator
Choose how you want to have your digit groups separated in long numbers:
Exposure to ionizing radiation
Found an error? Want to suggest more conversions? Contact us on Facebook.
Acute radiation syndrome
If the figure next to the symptome is 1 or more, there's a good chance the corresponding radiation dose could cause it. The data was taken from Wikipedia.
Could not find your unit?
Hope you have made all your conversions and enjoyed Convert-me.Com. Come visit us again soon!
What is Radiation
Radioactivity is a natural property of certain substances. There are natural and artificial sources of radiation.
Absorbed dose units
When ionizing radiation hits biological tissue, the tissue absorbs it. The absorbed energy with the mass of biological tissue is called the absorbed dose. We express it in gray units (Gy).
Equivalent dose units
An equivalent dose of physical size records the biological effect of radioactive radiation. Dose equivalent characterizes the absorbed dose that the body absorbs, taking into account the biological effects.
Effective dose units
The sum of all the doses of organs and tissues is the effective dose. You express it in sievert.
Effects of Radiation on the Body
Biological action is the effect of radiation on the human body and other living beings. In particular, it can lead to immediate damage (acute radiation damage). Cause damage that becomes visible only after years ( late damage ). They cause genetic damage (hereditary damage) that occurs only in offspring. One of the genetic diseases is cholesterol.
International System of Units (SI) Unit and Common Unit
The International System of Units, abbreviated SI (from French: Système International d’Unités), is based on the International System of Quantities (ISQ). This metric system of units, introduced in 1960, is the most widespread system of units for physical quantities worldwide today.
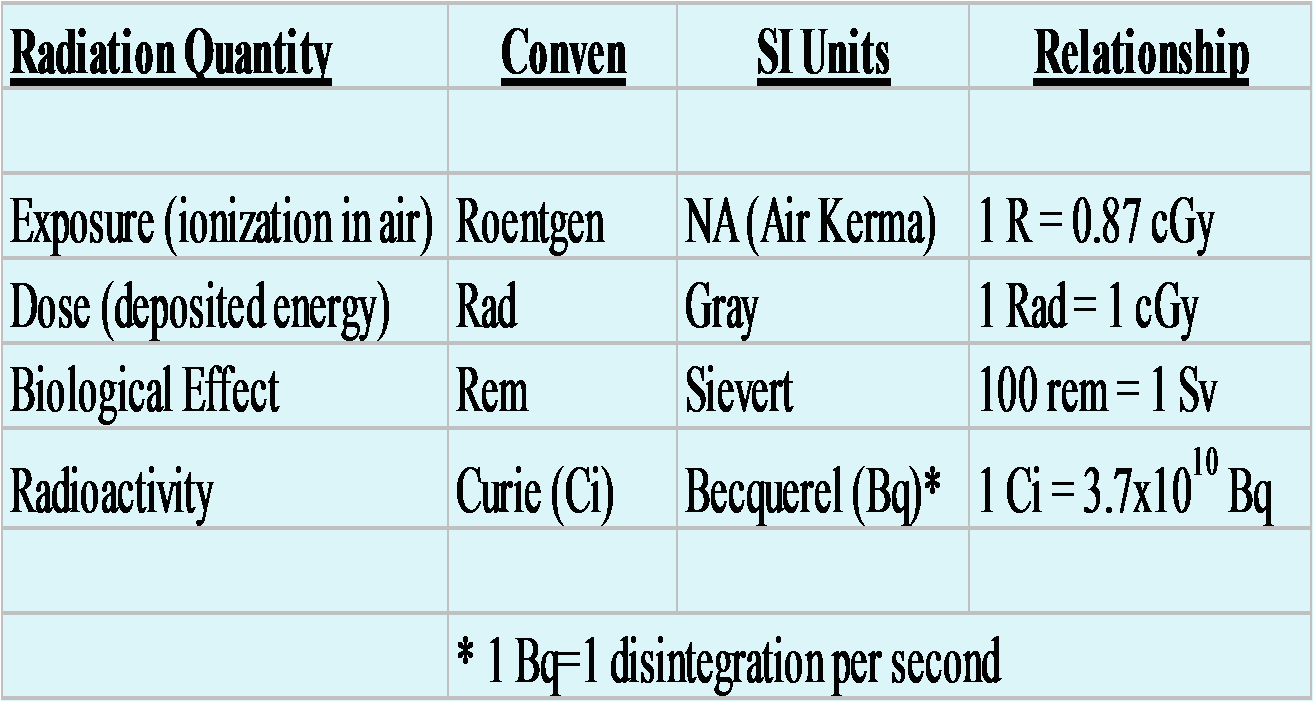
Conversion Equivalence Table
In the next table, you can find conversions between different units for radiation:
What is the unit of radiation absorbed?
The units for absorbed dose are the radiation absorbed dose ( rad) and gray ( Gy ). D ose equivalent (or effective dose) combines the amount of radiation absorbed and the medical effects of that type of radiation. For beta and gamma radiation, the dose equivalent is the same as the absorbed dose. By contrast, the dose equivalent is larger than ...
How many units are there for radioactivity?
There are four different but interrelated units for measuring radioactivity, exposure, absorbed dose, and dose equivalent. These can be remembered by the mnemonic R-E-A-D, as follows, with both common (British, e.g., Ci) and international (metric, e.g., Bq) units in use:
What is the unit of measurement for radiation exposure?
Many radiation monitors measure exposure. The units for exposure are the roentgen ( R) and coulomb/kilogram (C/kg).
What is the unit of measure for radioactivity?
The units of measure for radioactivity are the curie ( Ci) and becquerel ( Bq ).
Is the dose equivalent the same as the absorbed dose?
For beta and gamma radiation, the dose equivalent is the same as the absorbed dose. By contrast, the dose equivalent is larger than the absorbed dose for alpha and neutron radiation, because these types of radiation are more damaging to the human body.
