Full Answer
What are the solutions to negative externalities?
Remedies for Negative Externalities One of the solutions to negative externalities is to impose taxes to change people’s behavior. The taxes can be imposed to reduce the harmful effects of certain externalities such as air pollution, smoking, and drinking alcohol.
What is an example of an externality?
Because externalities that occur in market transactions affect other parties beyond those involved, they are sometimes called spillovers .Externalities can be negative or positive. The club example from above is that of a negative externality. The club imposed a cost on you, an external agent to the market interaction.
What are the ways in which government can promote externalities?
A government may impose taxes on goods or services that create externalities. The taxes would discourage activities that impose costs on unrelated parties. 3. Subsidies A government can also provide subsidies to stimulate certain activities. The subsidies are commonly used to increase the consumption of goods with positive externalities.
What is the internalization of the externalities?
The “internalization” of the externalities is the process of adopting policies that would limit the effect of the externalities on unrelated parties. Generally, the internalization is achieved through government intervention. Possible solutions include the following: 1.

When do we need to consider external costs and benefits?
External costs and benefits occur when producing or consuming a good or service imposes a cost/benefit upon a third party. When we account for external costs and benefits, the following definitions apply:
What is the effect of a market exchange on a third party who is outside or “external” to?
The effect of a market exchange on a third party who is outside or “external” to the exchange is called an externality. Because externalities that occur in market transactions affect other parties beyond those involved, they are sometimes called spillovers .Externalities can be negative or positive.
How to determine if a Pareto improvement is realized?
To determine whether this is a Potential Pareto Improvement, we need to find out whether the gains from the winners exceed the losses to others. In our example, the gain by external agents is indeed larger than the loss to private agents (d+e > e). Therefore, in theory, we could take e from the external agents and give it to the private agents and make them equally as well off as they were at the market equilibrium. External agents would still be better off by d. Thus, a Potential Pareto Improvement has been realized.
What does it mean to leave the market unregulated?
This means that there is an opportunity for government intervention to make society better off.
Is pollution a negative externality?
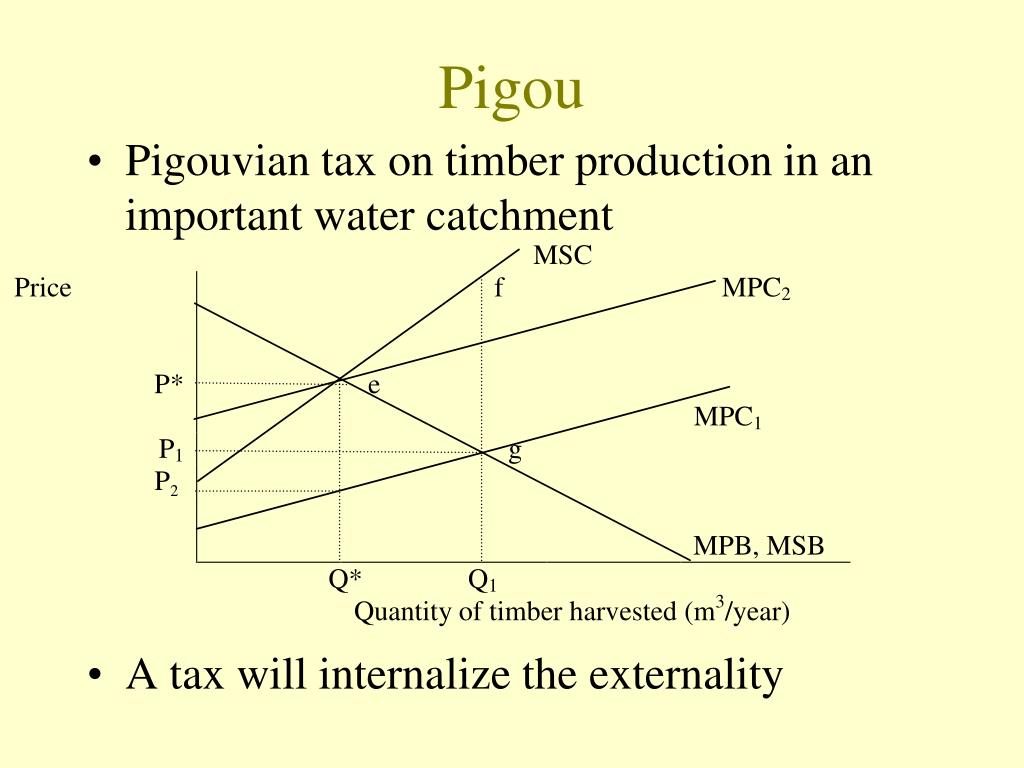
Much of the work we will do is with negative externalities. As we will see in the next section, pollution is modelled as a negative externality. Economists illustrate the social costs of production with a demand and supply diagram. For example, consider Figure 5.1a, which shows a negative externality. Notice that there are external costs but no external benefits. Graphically, this means that the marginal social cost (MSC) curve lies above the marginal private cost (MPC) curve by an amount equal to the marginal external cost (MEC) and the marginal private benefit (MPB) and marginal social benefit (MSB) are equivalent.
How to overcome externalities?
Taxes are one solution to overcoming externalities. To help reduce the negative effects of certain externalities such as pollution, governments can impose a tax on the goods causing the externalities. The tax, called a Pigovian tax —named after economist Arthur C. Pigou, sometimes called a Pigouvian tax—is considered to be equal to the value of the negative externality. This tax is meant to discourage activities that impose a net cost to an unrelated third party. That means that the imposition of this type of tax will reduce the market outcome of the externality to an amount that is considered efficient.
What Is an Externality?
An externality is a cost or benefit caused by a producer that is not financially incurred or received by that producer. An externality can be both positive or negative and can stem from either the production or consumption of a good or service. The costs and benefits can be both private—to an individual or an organization—or social, meaning it can affect society as a whole.
Why do economists consider technical externalities to be market deficiencies?
Many economists consider technical externalities to be market deficiencies, and this is the reason people advocate for government intervention to curb negative externalities through taxation and regulation. Externalities were once the responsibility of local governments and those affected by them.
What are externalities in nature?
Externalities by nature are generally environmental, such as natural resources or public health. For example, a negative externality is a business that causes pollution that diminishes the property values or health of people in the surrounding area.
How do subsidies overcome negative externalities?
Subsidies can also overcome negative externalities by encouraging the consumption of a positive externality.
What is positive externality?
A positive externality includes actions that reduce transmission of disease or avoids the use of lawn treatments that runoff to rivers and thus contribute to excess plant growth in lakes. Externalities are different from donations of parkland or open-source software.
Is externality positive or negative?
An externality can be both positive or negative and can stem from either the production or consumption of a good or service. The costs and benefits can be both private—to an individual or an organization—or social, meaning it can affect society as a whole.
What are the methods used to measure externalities?
For measuring externalities, economists may use quantitative methods (cost of damages, cost of control), qualitative methods (qualitative treatment) or hybrid methods (weighting and ranking).
How to measure positive externality?
The positive externality is then measured as the deadweight loss area above the individual MC curve and below the society MB curve constrained by the vertical line going through an equilibrium quantity for the person. For the negative externality, the same measurement technique applies except that the society MC curve is bigger than the individual MC curve.
What are the two quantitative methods used by economists to assess externalities?
The two prominent quantitative methods used by economists to assess externalities are cost of damages and cost of control. For example, in the case of an oil spill, the cost of damages method puts a number to the cost of cleanup necessary to clear the pollution and restore the habitat to its original state.
What is qualitative treatment?
The qualitative method of assessing externalities widely used by environmentalists is called qualitative treatment. This method does not put any numbers behind externalities, but rather states the level of impact that a particular event has on the environment, such as no impact, moderate impact, or a significant impact.
Is externality hard to estimate?
Estimating externalities in practice is much harder than in theory since marginal cost and marginal benefit curves are not fully observed very often and since the process of estimating can be met with challenging statistical issues. Sometimes, the full extent of the externalities' effect is not known. The two prominent quantitative methods used by economists to assess externalities are cost of damages and cost of control.
What are negative externalities?
Negative consumption externalities arise during consumption and result in a situation where the social cost of consuming the good or service is more than the private benefit. Private benefits refer to the positive factors rewarded to the producer or the consumer involved in a transaction. Social costs are negative factors impacting third parties. For example, when a person consumes alcohol and becomes drunk, he/she causes social disorder, disturbing the peace of non-drinkers.
What are negative externalities in manufacturing?
Negative production externalities occur when the production process results in a harmful effect on unrelated third parties. For example, manufacturing plants cause noise and atmospheric pollution during the manufacturing process.
How do negative externalities affect public resources?
Negative externalities commonly affect public resources where it is difficult to hold parties accountable such as in a case of environmental pollution. Producers or consumers may create a negative externality without worrying about lawsuits or fines.
What is an ordinary transaction?
An ordinary transaction involves two parties, i.e., a consumer and the producer, who are referred to as the first and second parties in the transaction. Any other party that is not related to the transaction is referred to as a third party.
What is externality in marketing?
Mike Moffatt. Updated April 10, 2019. An externality is the effect of a purchase or decision on a person group who did not have a choice in the event and whose interests were not taken into account. Externalities, then, are spillover effects that fall on parties not otherwise involved in a market as a producer or a consumer of a good or service. ...
What are some examples of negative externalities?
A classic example of a negative externality is pollution. An enterprise that emits pollution while producing a product certainly benefits the owner of the operation, who is making money off the production.
What are externalities of production?
Externalities of production happen when producing a product confers a cost or benefit to a person or group who has nothing to do with the production process. So, as noted in the pollution example, the pollutants produced by a company are a negative externality of production.
Is pollution a negative externality?
It affects others who had no choice in the matter and were probably not taken into account in production decisions and is thus a negative externality.
Is riding a bike to work a positive externality?
Positive externalities come in many forms. Commuting to work by bicycle involves the positive externality of combatting pollution. The commuter, of course, gets a health-related benefit of the bike trip, but the effect this has on traffic congestion and reduced pollution released into the environment because of taking one car off the road is a positive externality of riding a bike to work. The environment and community were not involved in the decision to commute by bike, but both see benefits from that decision.
What Is An Externality?
Understanding Externalities
- Externalities occur in an economy when the production or consumption of a specific good or service impacts a third party that is not directly related to the production or consumption of that good or service. Almost all externalities are considered to be technical externalities. Technical externalities have an impact on the consumption and production opportunities of unrelated thir…
Overcoming Externalities
- There are solutions that exist to overcome the negative effects of externalities. These can include those from both the public and private sectors. Taxes are one solution to overcoming externalities. To help reduce the negative effects of certain externalities such as pollution, governments can impose a tax on the goods causing the externalities. T...
Measuring Externalities in Theory
Measuring Externalities in Reality
- For measuring externalities, economists may use quantitative methods (cost of damages, cost of control), qualitative methods (qualitative treatment) or hybrid methods (weighting and ranking).
The Bottom Line
- There are advantages and disadvantages to using any method. Quantitative methods, for instance, are convenient since they put an estimated number on externality, but a lack of data is the biggest impediment to using quantitative methods. Qualitative methods, on the other hand, are highly flexible and adaptive, but they suffer from the subjectivity of a decision-maker who m…