What is electricity?
- Electricity is the presence or flow of charged particles.
- An electric current is the flow of electrons around a circuit.
- Static electricity is the build up of electrons on an insulator.
Full Answer
What does the Bible say about electricity?
Bible verses about Electricity. 1 Corinthians 15:1-58 ESV / 6 helpful votes Helpful Not Helpful. Now I would remind you, brothers, of the gospel I preached to you, which you received, in which you stand, and by which you are being saved, if you hold fast to the word I preached to you—unless you believed in vain.
What is electricity and what does it contain?
Electricity is the flow of electrons. All matter is made up of atoms, and an atom has a center, called a nucleus. The nucleus contains positively charged particles called protons and uncharged particles called neutrons. The nucleus of an atom is surrounded by negatively charged particles called electrons.
What is electricity and how is it generated?
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric power from sources of primary energy.For utilities in the electric power industry, it is the stage prior to its delivery (transmission, distribution, etc.) to end users or its storage (using, for example, the pumped-storage method).
What are the basics of electricity?
Voltage, Current, Resistance, and Ohm's Law
- Electricity Basics. When beginning to explore the world of electricity and electronics, it is vital to start by understanding the basics of voltage, current, and resistance.
- Electrical Charge. Electricity is the movement of electrons. ...
- Voltage. What is Voltage? ...
- Current. ...
- Resistance. ...
- Ohm's Law. ...
- An Ohm's Law Experiment. ...
- Resources and Going Further. ...
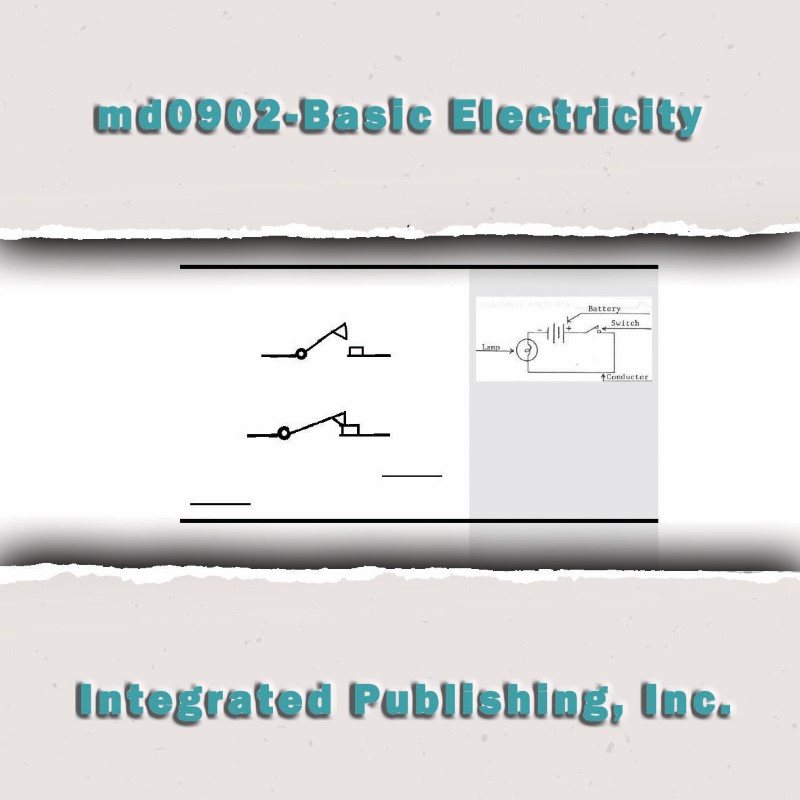
How do you define electricity '?
electricity, phenomenon associated with stationary or moving electric charges. Electric charge is a fundamental property of matter and is borne by elementary particles. In electricity the particle involved is the electron, which carries a charge designated, by convention, as negative.
Which best defines electricity?
Electricity is the presence and flow of electric charge. Using electricity we can transfer energy in ways that allow us to do simple chores. Its best-known form is the flow of electrons through conductors such as copper wires.
How is electricity defined for kids?
2:065:25Introduction to Electricity- video for kids - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipNow let's remember the definition of electricity electricity is a type of energy that can build upMoreNow let's remember the definition of electricity electricity is a type of energy that can build up in one place or flow from one place to another place. There are two types of electricity static.
What is the definition of electricity and an example?
Electricity is defined as the effects of an electric charge. An example of electricity is the force that powers a light bulb. An example of electricity is lightning. An example of electricity is static electricity, the buildup of electric charges on an object's surface.
What is electricity definition for class 10?
Electricity is defined as the rate of flow of charges in a conductor.
What is electricity in TLE?
TLE-ELECTRICITY. *ELECTRICITY – basic form of energy, flow of electrons in a conductor. -THE ELECTRON THEORY- *PROTONS – positively charge.
What is electricity definition for Class 2?
Electricity is an energy. This energy can be used to power electrical items such as toasters, kettles, cookers, televisions and computer tablets. Electrical energy is caused by electrons (the particles in atoms) moving about to make a current.
What is electricity 4th grade?
0:132:364th Grade - Science - Electrical Circuits and Conductivity - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipYou use every day comes from power plants. Inside of the power plants large generators or motorsMoreYou use every day comes from power plants. Inside of the power plants large generators or motors turn mechanical energy into electrical energy the electrical charge of energy moves in currents.
What is electricity for 5th grade?
0:053:405th Grade - GA Science - Electricity - Topic Overview - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipLike shocking your friends and lightning which are both static electricity. Or it can be built up orMoreLike shocking your friends and lightning which are both static electricity. Or it can be built up or charged.
Who gave meaning to electricity?
Most people give credit to Benjamin Franklin for discovering electricity. Benjamin Franklin had one of the greatest scientific minds of his time.
What is the sentence of electricity?
Electricity lights our houses and drives our machinery. Electricity is one of the greatest wonders of modern science. Mills and factories cannot work without the electricity.
What is the power available to push electricity around a circuit?
The volt (V) is the power available to push electricity around a circuit. Think of it like the water pressure in a pipe: the more voltage you have, the more quickly electricity flows through a circuit. Resistance, to take the analogy further, would be pipe size and is measured in ohms (r).
What is a battery?
A battery is a collection of cells, like the batteries in cars and laptops. A battery is an electrochemical source of electricity, meaning we get the electricity from a chemical reaction taking place inside the battery.
What are the different ways electricity is harnessed?
So, let's take a closer look at some of the different ways electricity is harnessed. 1. Batteries and Circuits. What we think of as batteries, like the ones we use in flashlights and remote controls, are actually cells. A battery is a collection of cells, like the batteries in cars and laptops.
How does AC technology work?
Instead of directly flowing through wire to the source, like water in a hos e, in alternating current electricity, the electrons rapidly alternate their direction of flow. The AC technology allowed electricity to be carried much further than a mile and maintain its power.
What is the difference between a conductor and an insulator?
Conductors, like Franklin's metal lightning rods, easily carry electric currents, while insulators, like rubber, wood, or cloth, stop the flow of electricity. Besides measuring electricity's current, we also measure its voltage, watts, and resistance. The volt (V) is the power available to push electricity around a circuit.
What were the main sources of electricity during the Industrial Revolution?
2. Steam Turbines and Power Stations. Soon, cells and batteries weren't enough, and we sought out larger sources of electric power. Steam turbines, developed in the 1880s, helped to spur the Industrial Revolution, while inventors like Thomas Edison perfected light bulbs for use in the home.
When did scientists get into studying electricity?
In the 1700s , scientists got super into studying electricity. This was before light bulbs, televisions, and all the other useful applications of electricity we have now. Scientists just really wanted to understand what they could about electricity, like Franklin with his lightning experiment in 1752.
What is electricity used for?
Everyday, we use electricity to do many functions for us -- from lighting and heating/cooling our homes, to being the power source for televisions and computers. Electricity is a controllable and convenient form of energy used in the applications of heat, light and power.
How do we get electricity?
We get electricity, which is a secondary energy source , from the conversion of other sources of energy, like coal, natural gas, oil, nuclear power and other natural sources, which are called primary sources. Many cities and towns were built alongside waterfalls (a primary source of mechanical energy) that turned water wheels to perform work.
How is electricity produced in the United States?
Most of the electricity in the United States is produced in steam turbines. A turbine converts the kinetic energy of a moving fluid (liquid or gas) to mechanical energy. Steam turbines have a series of blades mounted on a shaft against which steam is forced, thus rotating the shaft connected to the generator.
What is the energy of an atom?
What Is Electricity? Electricity is a form of energy. Electricity is the flow of electrons. All matter is made up of atoms, and an atom has a center, called a nucleus. The nucleus contains positively charged particles called protons and uncharged particles called neutrons. The nucleus of an atom is surrounded by negatively charged particles called ...
What happens when electrons are lost?
When electrons are "lost" from an atom, the free movement of these electrons constitutes an electric current. Electricity is a basic part of nature and it is one of our most widely used forms of energy. We get electricity, which is a secondary energy source, from the conversion of other sources of energy, like coal, natural gas, oil, ...
How many watts is a kilowatt hour?
A kilowatt represents 1,000 watts. A kilowatt-hour (kWh) is equal to the energy of 1,000 watts working for one hour. The amount of electricity a power plant generates or a customer uses over a period of time is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh).
How does water produce electricity?
The water falls through a pipe called a penstock and applies pressure against the turbine blades to drive the generator to produce electricity. In the second system, called run-of-river, the force of the river current (rather than falling water) applies pressure to the turbine blades to produce electricity.
How does electricity work in a circuit?
In a circuit, electric charges are the blood and the wires are the arteries and veins. Electric charges have a certain amount of energy.
What are the two types of electricity?
The moving electrons make up what we call electricity. There are two kinds of electricity: static and current. Static electricity is what makes your hair stand up when you rub a balloon against it or gives you a shock from your doorknob. In static electricity, electrons are moved around mechanically (i.e. by someone rubbing two things together).
What is lightning caused by?
Lightning is the result of static electricity. In a thunderstorm, negatively charged particles can build up in a cloud. Electrons repel each other; they really don’t like each other and want to get as far away from each other as possible. The farthest they can get away from each other is if they go into the ground because it’s ...
What does the + sign mean in a circuit?
The electrons in a circuit have to be pushed by something, like a battery. If you look at one end of a battery, there is a + sign, this where the extra positive charges are. At the other end, where there’s a – sign, there are extra negative charges (electrons).
How many volts does a flashlight have?
A flashlight battery has about 1 ½ Volts and your wall socket has about 120 Volts. The electrons moving through a circuit are called a current. You can get an electric shock when a big current – lots of electrons – flows through your body. The electrons in a circuit have to be pushed by something, like a battery.
Who invented electricity?
Scientists and inventors have worked to decipher the principles of electricity since the 1600s. Benjamin Franklin, Thomas Edison, and Nikola Tesla made notable contributions to our understanding and use of electricity. Benjamin Franklin demonstrated that lightning is electricity.
Is electricity a secondary source?
Electricity is a secondary energy source. Electricity is the flow of electrical power or charge. Electricity is both a basic part of nature and one of the most widely used forms of energy.
How do we make electricity?
First we will review the ingredients we need to make electricity: 1 The definition of electricity is the flow of charge. Usually our charges will be carried by free-flowing electrons. 2 Negatively-charged electrons are loosely held to atoms of conductive materials. With a little push we can free electrons from atoms and get them to flow in a generally uniform direction. 3 A closed circuit of conductive material provides a path for electrons to continuously flow. 4 The charges are propelled by an electric field. We need a source of electric potential (voltage), which pushes electrons from a point of low potential energy to higher potential energy.
What are the two forms of electricity?
Before we get much further, let's discuss the two forms electricity can take: static or current. In working with electronics, current electricity will be much more common, but static electricity is important to understand as well.
Why do electrons carry negative charges?
Electrons in atoms can act as our charge carrier, because every electron carries a negative charge. If we can free an electron from an atom and force it to move, we can create electricity.
What is the flow of current in a circuit?
In order to flow, current electricity requires a circuit: a closed, never-ending loop of conductive material. A circuit could be as simple as a conductive wire connected end-to-end, but useful circuits usually contain a mix of wire and other components which control the flow of electricity. The only rule when it comes to making circuits is they can't have any insulating gaps in them.
What are the elements that make up electricity?
Atoms exist in over a hundred different forms as chemical elements like hydrogen, carbon, oxygen, and copper.
What is the energy that is stored in a circuit?
The stored energy of a circuit is called electric potential energy .
When does static electricity exist?
Static electricity exists when there is a build-up of opposite charges on objects separated by an insulator. Static (as in "at rest") electricity exists until the two groups of opposite charges can find a path between each other to balance the system out.
What is the unit of electric current?
The SI unit of electric current is Amperes . An electric generator is a device for converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. The process is based on the relationship between magnetism and electricity. When a wire or any other electrically conductive material moves across a magnetic field, an electric current occurs in the wire.
What is the unit of power of a wire?
Electricity is measured in units of power called watts. It was named to honor James Watt, the inventor of the steam engine. A kilowatt represents 1,000 watts.
How many watts is a kilowatt hour?
A kilowatt represents 1,000 watts. A kilowatt-hour (kWh) is equal to the energy of 1,000 watts working for one hour. The force applied to electrons to push them through the conducting wire is known as voltage, and the rate of flow of the electrons is known as current.
