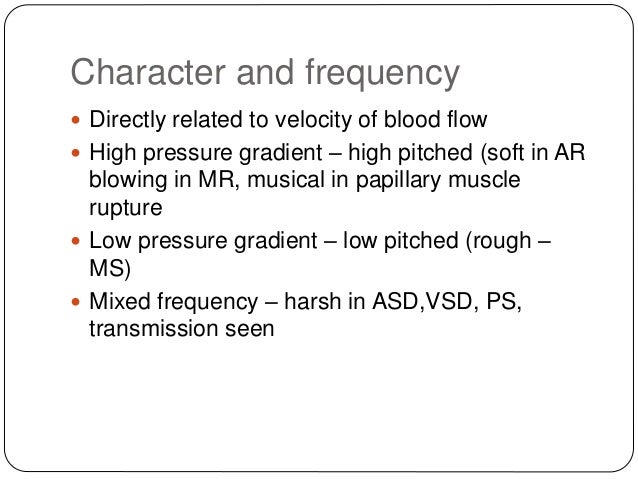
Describing Murmurs
- Timing. The timing of a murmur is crucial to accurate diagnosis. ...
- Grading. Systolic murmurs are graded on a scale of 6. ...
- Shape. The shape of a murmur describes the change of intensity throughout the cardiac cycle. ...
- Pitch. ...
- Location. ...
- Radiation. ...
How can one identify a murmur?
To check whether the murmur is innocent or abnormal, your doctor will consider the following:
- How loud is it? This is rated on a scale from 1 to 6, with 6 being the loudest.
- Where in your heart is it? And can it be heard in your neck or back?
- What pitch is it? Is it high-, medium- or low-pitched?
- What affects the sound? Does exercising or changing body position affect the sound?
- When does it occur, and for how long? ...
What is the difference between a murmur and a bruit?
As nouns the difference between murmur and bruit is that murmur is (countable) low or indistinct sounds or speech while bruit is brute, beast. As a verb murmur is .
How dangerous is a heart murmur?
The good news is that many heart murmurs aren’t dangerous. In fact, many heart murmurs go away on their own over a few months or years. Whether you need treatment for your heart murmur will depend on what type of murmur you have.
Is it possible to hear a murmur?
It is absolutely possible to hear a murmur without a stethoscope. If it wasn't audible before and now it is, get it checked out. You don't want to wait until you sound like a washing machine to look into it. Jerry is right in that a click is generally more specific to valve probs. The mechanical valves certainly go click with every beat.

What are the characteristics of a heart murmur?
Murmurs have seven main characteristics. These include timing, shape, location, radiation, intensity, pitch and quality. Timing refers to whether the murmur is a systolic, diastolic, or continuous murmur. Shape refers to the intensity over time.
How do you identify a murmur?
Echocardiogram. This is the main test used to determine the cause of a heart murmur. An echocardiogram uses sound waves to create pictures of the beating heart. It shows how blood flows through the heart and heart valves.
How do you describe heart sounds?
In a healthy adult, the heart makes two sounds, commonly described as 'lub' and 'dub. ' The third and fourth sounds may be heard in some healthy people, but can indicate impairment of the heart function. S1 and S2 are high-pitched and S3 and S4 are low-pitched sounds.
What does murmuring sound like?
The familiar 'lub-dub' sound of the heartbeat is caused by the rhythmic closing of the heart valves as blood is pumped in and out of the chambers. A heart murmur is a whooshing, humming or rasping sound between the heartbeat sounds.
What are the four types of heart murmurs?
What Are the Different Types of Murmurs?Systolic murmur. A heart murmur that occurs during a heart muscle contraction. ... Diastolic murmur. A heart murmur that occurs during heart muscle relaxation between beats. ... Continuous murmur. A heart murmur that occurs throughout the cardiac cycle.
What is the most common heart murmur?
The most common type of heart murmur is called functional or innocent. An innocent heart murmur is the sound of blood moving through a healthy heart in a normal way.
What are 3 abnormal heart sounds?
Abnormal Heart Sounds and Murmurs - 62S1 (e.g., mitral stenosis, atrial fibrillation)S2 (e.g., hypertension, aortic stenosis)S3 (e.g., heart failure)S4 (e.g., hypertension)Abnormal splitting (e.g., atrial septal defect)
How would you describe a heart sound in nursing?
The S 1 heart sound represents the mitral and tricuspid valves closing before the contraction of the ventricle. S 1 is auscultated as “lub.” The S 2 heart sound signifies aortic and pulmonic valve closure after the ventricles have emptied. S 2 is auscultated as “dub” (see Picturing heart sounds).
How do you document cardiac sounds?
Palpation – Place your hand on the patient's chest so that it covers the heart, feeling for the point of maximum impulse. Auscultation – Auscultate for heart sounds, noting the sounds at different points in the cardiac cycle. Listen for extra heart sounds, gallops, murmurs, or rubs.
What is a synonym for murmur?
synonyms for murmurbuzz.hum.muttering.rumble.whisper.babble.buzzing.drone.More items...
What does an innocent murmur sound like?
It is usually the sound of the blood negotiating its way around the tight bends inside a young child's heart and resembles a “whooshing” or “swishing” noise.
Where do you hear a murmur?
Mitral murmursMitral murmurs are best heard at the apex and radiate to the axilla.Mitral sounds can be accentuated with the patient in the left lateral position.Hence, to listen to a mitral murmur, first listen to the apex, then listen round to the mid-axillary line at the same level. ... Note the timing of any murmur.More items...•
How should you determine whether a murmur is systolic or diastolic?
Systolic murmurs occur between the first heart sound (S1) and the second heart sound (S2). Diastolic murmurs occur between S2 and S1. In addition, timing is used to describe when murmurs occur within systole or diastole.
How do you hear a murmur?
Mitral murmurs are best heard at the apex and radiate to the axilla. Mitral sounds can be accentuated with the patient in the left lateral position. Hence, to listen to a mitral murmur, first listen to the apex, then listen round to the mid-axillary line at the same level.
How do you tell the difference between a systolic and diastolic murmur?
What is the difference between a diastolic and systolic murmur? A diastolic murmur occurs when your heart relaxes between heartbeats. Diastolic murmurs are often harder to hear than systolic murmurs. A systolic heart murmur occurs when your heart muscle contracts.
Where do you Auscultate for a murmur?
1. Auscultate the heart at various sitesAt the apex.At the base (the part of the heart between the apex and the sternum)In the aortic and pulmonary areas to the right and left of the sternum, respectively.
Murmur Characteristics
Area of maximal intensity like aortic, tricuspid,pulmonary area, mitral area.
Differential Diagnosis of Continuous murmur and Holosystolic Murmur
These are the murmurs which change their character or intensity from time to time, e.g.,
What is the sound of a heart murmur?
Heart murmur. A heart murmur is a swishing sound heard when there is turbulent or abnormal blood flow across the heart valve.
Can a murmur be present without a heart condition?
Murmurs can be present without any medical or heart conditions. Two common examples include:
How do you know if you have a heart murmur?
An abnormal heart murmur may cause the following signs and symptoms, depending on the cause of the murmur: Skin that appears blue, especially on your fingertips and lips. Swelling or sudden weight gain. Shortness of breath.
What is the sound of a heart murmur?
Heart murmurs are sounds — such as whooshing or swishing — made by turbulent blood in or near your heart. Your doctor can hear these sounds with a stethoscope. A normal heartbeat makes two sounds like "lubb-dupp" (sometimes described as "lub-DUP") when your heart valves are closing.
What is a shunt in the heart?
Cardiac shunts. Cardiac shunts occur when there's an abnormal blood flow between the heart chambers or blood vessels , which may lead to a heart murmur.
Why do older people have abnormal heart murmurs?
In older children and adults, causes of abnormal heart murmurs include infections and conditions that damage the structures of the heart. For example:
Why do children murmur?
In children, abnormal murmurs are usually caused by structural problems of the heart (congenital heart defects). Common congenital defects that cause heart murmurs include: Holes in the heart. Known as septal defects, holes in the heart may or may not be serious, depending on the size of the hole and its location. Cardiac shunts.
Can a heart murmur go away?
While there's not much you can do to prevent a heart murmur, it is reassuring to know that heart murmurs are not a disease and are often harmless. For children, many murmurs go away on their own as children grow. For adults, murmurs may disappear as the underlying condition causing them improves.
Is a heart murmur a sign of heart disease?
An innocent heart murmur is not a sign of heart disease and doesn't need treatment. Abnormal heart murmurs require follow-up testing to determine the cause. Treatment is directed at the cause of your abnormal heart murmur.
What is the sound of a heart murmur?
A heart murmur is a blowing, whooshing, or rasping sound heard during a heartbeat. The sound is caused by turbulent (rough) blood flow through the heart valves or near the heart.
What is a murmur grade?
Grade I can barely be heard. An example of a murmur description is a "grade II/VI murmur.". (This means the murmur is grade 2 on a scale of 1 to 6). In addition, a murmur is described by the stage of the heartbeat when the murmur is heard. A heart murmur may be described as systolic or diastolic. (Systole is when the heart is squeezing out blood ...
What causes a murmur in the heart?
These abnormal murmurs can be caused by: Problems of the aortic valve ( aortic regurgitation, aortic stenosis) Problems of the mitral valve ( chronic or acute mitral regurgitation, mitral stenosis) Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
How many chambers does the heart have?
The heart has 4 chambers: Two upper chambers (atria) Two lower chambers (ventricles) The heart has valves that close with each heartbeat, causing blood to flow in only one direction. The valves are located between the chambers. Watch this video about: Heartbeat. Murmurs can happen for many reasons, such as:
Do heart murmurs need treatment?
Expand Section. Many heart murmurs are harmless. These types of murmurs are called innocent murmurs. They will not cause any symptoms or problems. Innocent murmurs DO NOT need treatment. Other heart murmurs may indicate an abnormality in the heart.
Do children have murmurs?
Children often have murmurs as a normal part of development. These murmurs DO NOT need treatment. They may include:
What is a murmur that increases in intensity?
Crescendo: a murmur which increases in intensity
Why does Austin Flint murmur?
Austin Flint murmurs may be mistaken for mitral stenosis. Atrial septal defect . This congenital defect is located between the left and right atria, which allows blood to flow freely.
Where is aortic regurgitation heard?
Aortic regurgitation, also known as aortic insufficiency, is a decrescendo blowing diastolic murmur heard best at the left lower sternal border, heard when blood flows retrograde into the left ventricle. This is most commonly seen in aortic root dilation and as sequelae of aortic stenosis. Innocent or Flow Murmur.
Is murmur a pathologic process?
The development of murmurs is highly dependent on the etiology and is not always associated with a pathologic process[2][3] ; benign murmurs are common in children and during pregnancy[4]. Murmurs develop from a multitude of mechanisms.
Where is the murmur in the heart?
It will be grade 1-3, midsystolic, and low-pitched (which is why you use the bell). This murmur is best heard at the left lower sternal border and can radiate to the cardiac apex . This murmur will most often be found in childhood to early adolescents.
Why does a murmur sound loud?
If the murmur is stenotic, think of HARSH/RUMBLE SOUNDS. This is due to abnormal forward flow through stenotic valves, which should otherwise be open. Stenotic lesions lead to PRESSURE OVERLOAD.
Where are the Valves and Where Do I Listen?
So, one of the first things we need to know is where to listen on the chest wall and what valve that area corresponds with. The five main areas are:
How does standing quickly affect heart murmur sounds?
Standing quickly! How does this affect heart murmur sounds? When abruptly standing , this decreases preload and has the same effect as the Valsalva maneuver .
What increases the heart murmur?
In general, there are several different positions that will increase or decrease heart murmur sounds. The hand grip maneuver will increase the afterload, which will ultimately increase the murmurs:
Which position will accentuate mitral murmurs?
The left lateral decubitus position will accentuate mitral murmurs, such as:
Does laying supine make a murmur worse?
Since this is largely due to abnormal flow of blood through the heart, position will make this murmur better or worse. Classically laying supine will worsen innocent murmurs whereas Valsalva will improve the heart sound associated with innocent murmurs.