What is the basic refrigeration cycle?
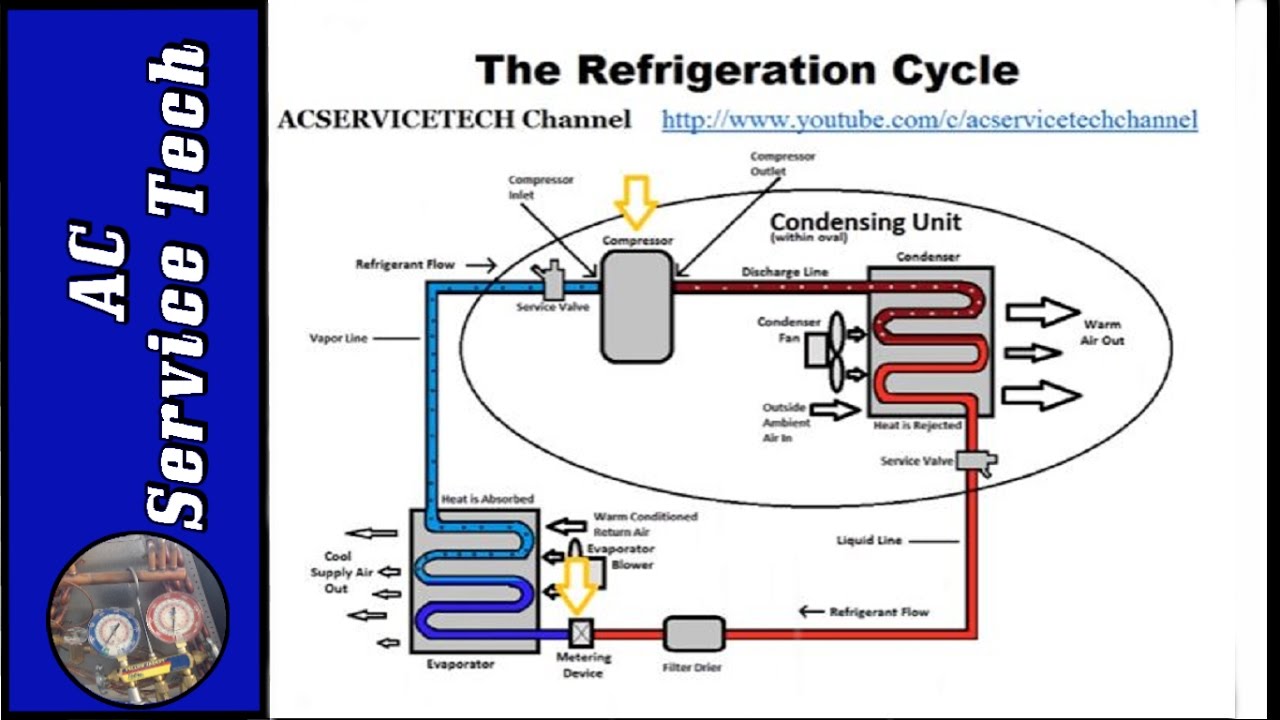
Working Principle Scheme of Refrigeration Cycle
- Refrigerant is pumped in the refrigeration cycle or circuit.
- It is circulated through refrigerant pipes or tubing.
- It has a very low boiling point & it starts evaporating at normal conditions.
- Refrigerant presents in the evaporator, takes up the heat from adjacent air for evaporation.
- Refrigerant changed its phase from liquid to vapor.
What is the refrigeration cycle theory?
The refrigeration cycle is based on the long known physical principle that a liquid expanding into a gas extracts heat from the surrounding substance or area. (You can test this principle by simply wetting your finger and holding it up. It immediately begins to feel cooler than the others, particularly if exposed to some air movement.
How does basic refrigeration cycle work?
The Refrigeration Cycle – Complete:
- SUPERHEAT – Is an amount of heat added to refrigerant vapour beyond its boiling point. This ensures the refrigerant is in a gas state with no liquid present.
- SATURATED – Is when the refrigerant is a vapour with both liquid & gas present.
- SUBCOOLING – Is an amount of heat removed from the refrigerant below its condensing point. ...
What is the cycle of refrigeration?
The refrigeration cycle is a thermodynamic cycle to generate refrigerating effect with the use of an evaporator, compressor, condenser & expansion valve. This process is basically a thermodynamic process where working fluid absorbs heat from the surrounding at low temperature and reject the heat to the atmosphere at a higher temperature.
What are the four steps of refrigeration?
The refrigeration has the following four steps: CompressionExpansionCondensationEvaporation
What are the four stages of refrigeration?
Refrigeration has the following four stages: CompressionExpansionCondensationEvaporation
What is the refrigeration process?
The process of useless heat elimination from a specific area, point, or substance and transfer this heat to another area, point, substance, or atmo...
What are the types of refrigeration cycle?
The major common types of the refrigeration cycle are given below: Gas CycleVapour absorption cycleVapour compression cycle
Who invented refrigeration?
n 1755, Scottish professor William Cullen invented the first artificial refrigeration.
In a refrigeration cycle, the flow of refrigerant is controlled by?
An expansion or throttling valve uses to control the refrigerant flow.
What Are the Four Major Components of Refrigeration?
CompressorCondenserExpansion valveEvaporator
What is Refrigeration Cycle?
The refrigeration cycle is a thermodynamic cycle which uses to remove heat from a specific area you want to cool. The refrigeration cycle is also known as a heat pump cycle. This cycle is designed for refrigeration systems, air conditioning systems, and heat pumps.
What happens to the liquid refrigerant after condensation?
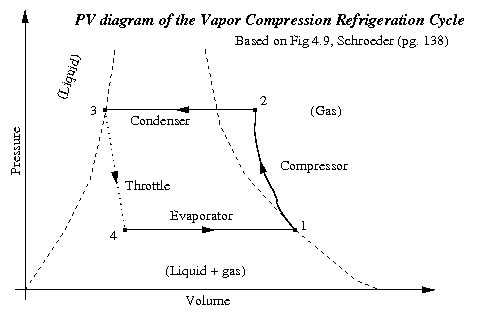
After the condensation process, the liquid refrigerant pushes into a throttling valve. As the refrigerant enters into this valve, it expands; due to that, the pressure and temperature of the liquid refrigerant reduce (As you can see in the above graph). However, the volume and enthalpy of the refrigerant increases.
How does an evaporator work?
The evaporator uses to transform the liquid refrigerant into vapor refrigerant. The evaporator connects with the cold reservoir. As the liquid refrigerant enters the evaporator, it absorbs heat by the cold reservoir and the refrigerant transfers from the liquid state to the vapour state.
What happens to the temperature of vapor refrigerant during compression?
Due to the compression process, the temperature of the vapor refrigerant increases from T1 to T2, and pressure increases from P1 to P2. Line 1 to 2 of the above-given graph represents this process.
Why does the gas cycle have lower efficiency than the vapor compression cycle?
This is because the vapour compression cycle works on the Rankine cycle while the gas cycle operates on the basis of the reverse Brayton cycle. Therefore, the working medium does not absorb or release heat at a constant temperature.
What is the most important part of the refrigeration cycle?
The compressor is the most important part of the refrigeration cycle. It uses to increase the temperature and pressure of the gas. Before the compression process, the refrigerant has low pressure and temperature.
How does a compressor work?
The compressor has a piston that moves up and down inside the compression chamber. As the refrigerant enters the compression chamber, the inlet and outlet valve close, and the piston compresses the refrigerant.
What is a condenser coil?
The condenser. The condenser, or condenser coil, is one of two types of heat exchangers used in a basic refrigeration loop. This component is supplied with high-temperature high-pressure, vaporized refrigerant coming off the compressor. The condenser removes heat from the hot refrigerant vapor gas vapor until it condenses into a saturated liquid ...
What happens to the refrigerant after condensing?
condensation. After condensing, the refrigerant is a high-pressure, low-temperature liquid, at which point it’s routed to the loop’s expansion device.
How does a fan cool a refrigerant?
This happens when refrigerant enters the evaporator as a low temperature liquid at low pressure, and a fan forces air across the evaporator’s fins, cooling the air by absorbing the heat from the space in question into the refrigerant .
What is the first step in the refrigeration cycle?
The compressor. Compression is the first step in the refrigeration cycle, and a compressor is the piece of equipment that increases the pressure of the working gas. Refrigerant enters the compressor as low-pressure, low-temperature gas, and leaves the compressor as a high-pressure, high-temperature gas.
What is the second heat exchanger in a refrigeration circuit?
The evaporator. The evaporator is the second heat exchanger in a standard refrigeration circuit, and like the condenser, it’s named for its basic function. It serves as the “business end” of a refrigeration cycle, given that it does what we expect air conditioning to do – absorb heat.
What is a refrigeration cycle?
In simple terms, a refrigeration cycle's mission is heat absorption and heat rejection. As any HVAC instructor will tell you (emphatically), you can't make cold, you can just remove heat. The refrigeration cycle, also called a heat pump cycle, is a means of routing heat away from the area you want to cool. This is accomplished by manipulating the ...
What are the components of a basic cycle?
There are certainly other components in most loops, but most would agree the four fundamental elements of a basic cycle are as follows: The compressor. The condenser. The expansion device. The evaporator.
How does the expansion valve work in refrigeration?
The expansion valve controls the flow of refrigerant and refrigerant vapour present in the liquid refrigerant changed into a liquid.
How does a refrigerant change phase?
In the evaporator, refrigerant changes its phase from liquid to vapour at normal pressure & temperature. To change this phase, refrigerant needs heat, i.e. latent heat of vaporization. This heat comes from adjacent medium i.e. air or liquid, based on the system. Medium loses heat so, medium is cooled.
How does liquid refrigerant work?
Liquid refrigerant absorbs heat from adjacent spaces or mediums and changes its phase from liquid to vapour. If the adjacent medium is air, liquid refrigerant takes heat from air and evaporation happens. By losing heat, air gets cooled. On the other hand, refrigerant takes heat and becomes heated.
Why is the compressor rotating?
When the power is on, compressor is started to rotate. Due to this rotation, there will be a slight low pressure at the inlet of compressor. Low pressure helps the refrigerant vapour to enter the compressor.
What is refrigeration cycle?
The refrigeration cycle is the main basic cycle for all air conditioning and refrigeration equipment. In this chapter, we will discuss, basic of a refrigeration cycle, mainly vapour compression cycle, main concept, parts, components, working principle along with a real example etc. Let’s get into Refrigeration cycle!
What does superheat mean?
Superheat, as the name suggest, means when heating is done in little different manner, basically heats after vapor or saturation temperature.
Where is refrigerant pumped?
Refrigerant is pumped in the refrigeration cycle or circuit.
What is the function of an evaporator?
Function of evaporator is, “to provide a heat transfer surface, through which, heat can pass from the refrigerated space to the liquid refrigerant flowing through evaporator coils and thereby vapourizing the liquid refrigerant”. Evaporator consists of wounded coils or pipes, in which, the flowing fluid (i.e. liquid refrigerant at low pressure low and low temperature) absorbs its latent heat of vapourization from the space to be coo ed and gets evaporated to vapour refrigerant. Due to removal of heat (i.e. absorption of heat) by refrigerant, the required space gets cooled producing refrigerating effect. In addition to the above four principal components, other devices such as receiver and strainer – drier assembly may be provided for safety considerations as well as for improving the COP of system.
What is the function of expansion valve?
Function of expansion device or valve is, “to reduce the pressure of liquid refngerant entering the evaporator, so that, liquid refrigerant wi// vapourize at very low temperature in the evaporator by absorbing latent heat from the substance or space to be cooled”. Thus, refrigerant can absorb heat from the substance or space to be cooled in the evaporator at the desired low temperature. Expansion valve also controls the amount of liquid refrigerant entering into the evaporator.
What is the purpose of the P-H chart?
P-h chart is essential to study a vapour compression refrigeration cycle. This chart acts as a tool in understanding the behaviour of a refrigerant. Pressure is plotted on Y-axis (i.e. ordinate axis) and enthalpy (i .e. abscissa axis) as shown in Fig. 3.
How many pressure regions are there in a vapour compression refrigeration system?
In any vapour compression refrigeration system running on vapour compression cycle (V.C.C.). there are two different pressure regions (Figure 5).
Why is the evaporator smaller in a VCC?
The amount of refrigerant circulated in vapour compression refrigeration system is less than air refrigeration system to achieve same refrigeration effect, because the heat removed away by the refrigerant in VCC is the latent heat. As a result of this, size of evaporator is smaller in vapour compression refrigeration system for the same refrigerating effect as compared to air refrigeration system.
What is the function of a strainer?
Function of strainer is “to remove impurities from the refrigeration system”, The common form of strainer is a fine mesh screen made up of metal, which traps the impurities, contaminants and foreign particles from the system. The strainer can be washed off and refitted or it can be replaced by new one.
What is the major problem with V.C.R. systems?
Leakage of refrigerant in V.C.R. system is the major problem.
How does a compressor transfer heat from a refrigerant to a condenser?
Now this low-pressure, low-temperature vapor is drawn to the compressor where it is compressed into a high-temperature, high-pressure vapor. The compressor discharges it to the condenser, so that it can give up the heat that it picked up in the evaporator. The refrigerant vapor is at a higher temperature than the air passing across the condenser (air-cooled type); or water passing through the condenser (water-cooled type); therefore that is transferred from the warmer refrigerant vapor to the cooler air or water.
How does heat travel from the evaporator to the evaporator?
Heat will travel from the warmer substance to the evaporator cooled by the evaporation of the refrigerant within the system , causing the refrigerant to "boil" and evaporate, changing it to a vapor. This is similar to the change that occurs when a pail of water is boiled on the stove and the water changes to steam, except that the refrigerant boils at a much lower temperature.
What is the purpose of a closed cycle?
The job of the refrigeration cycle is to remove unwanted heat from one place and discharge it into another. To accomplish this, the refrigerant is pumped through a closed refrigeration system. If the system was not closed, it would be using up the refrigerant by dissipating it into the surrounding media; because it is closed, the same refrigerant is used over and over again, as it passes through the cycle removing some heat and discharging it. The closed cycle serves other purposes as well; it keeps the refrigerant from becoming contaminated and controls its flow, for it is a liquid in some parts of the cycle and a gas or vapor in other phases.
What is the chemical compound that is compressed and condensed into a liquid and then permitted to expand into a?
E). Refrigerants, are chemical compounds that are alternately compressed and condensed into a liquid and then permitted to expand into a vapor or gas as they are pumped through the mechanical refrigeration system to cycle.
How does the refrigeration cycle work?
The refrigeration cycle is based on the long known physical principle that a liquid expanding into a gas extracts heat from the surrounding substance or area. (You can test this principle by simply wetting your finger and holding it up. It immediately begins to feel cooler than the others, particularly if exposed to some air movement. That's because the liquid in which you dipped it is evaporating, and as it does, it extracts heat from the skin of the finger and air around it).
What is the temperature of a cold?
Another definition describes it as the absence of heat, no process yet has been devised of achieving "absolute zero," the state in which all heat has been removed from any object, substance, or area. Theoretically this zero point would be 459.69 degrees below zero on the Fahrenheit thermometer scale, or 273.16 degrees below zero on the Celsius thermometer scale.
How to find change in heat in BTU?
Where Change in heat (in Btu) = Weight (in pounds) x Temperature Difference.
What is superheat in evaporator?
Simply put, superheat is anything above the saturation point. Superheat ensures the substance is 100% vapour. If we take R410a again as our example and we look at its saturation temperature at 118 PSI, it corresponds to 40⁰F. Now, this is a common pressure/temperature relationship as it pertains to an evaporator for comfort cooling. We sometimes refer to this as the saturated suction temperature or SST. If we were take an actual temperature of the suction line and it was measured at 50⁰F our superheat would be calculated at 10⁰F.
Why is superheat needed in a suction line?
As we will touch on later, superheat in the suction line is needed to ensure only vapour enters the compressor during a running cycle.
What is the role of a compressor in a refrigeration system?
The compressor acts as a vapour pump to move refrigerant around the system. A compressor is not designed to pump liquid. The condenser rejects heat picked up from the system (evaporator and compressor) and is responsible for ensuring that the refrigerant leaving is a sub-cooled liquid.
Why is my high pressure switch setting adjustable?
The setting of the switch is dependent upon the refrigerant being used.
How does an evaporator work?
Ah, for me this is where the magic happens. The evaporator's job is to absorb heat and remove moisture from the air passing over it , if we are speaking in terms of a standard evaporator coil. A standard coil removes latent heat and sensible heat from the air passing by. Latent heat removal is responsible for removing moisture or humidity from the air, as the humid air comes into contact with the cold coil, water vapour clings to it, the vapour changes state from a vapour to a liquid, known as condensation. The condensation is collected in the evaporator drain pan and exits via a drain line. Once the latent heat is removed (moisture from the air), sensible heat removal is able to take place at a greater pace.
What is a receiver in refrigeration?
Receiver. A receiver is a storage device that stores refrigerant in the off-cycle after a pump down or stores refrigerant until it's needed. An example of this is winter operation, in cold ambient temperatures more refrigerant is needed to pressurize the system.
What temperature does water boil at?
Let's compare this to a boiling point of water. Water at sea level will boil at 212⁰F, (100⁰C) once the water reaches its boiling point, it is a liquid (within the pot) and vapour (hovering above the liquid inside the pot) at the same time. The water is at its saturated or boiling temperature.
How does a compressor discharge a high pressure liquid?
The compressor discharges high pressure, high temperature vapor through the discharge line (the smaller line).The fan on the condenser blows the heat out over the condenser coil , then the high pressure vapor will lose some energy and turn into a high pressure liquid.
How does a refrigeration cycle work?
Now that you have some basic hvac training on components that make up the refrigeration cycle, let’s learn how it actually works. The compressor discharges high pressure, high temperature vapor through the discharge line (the smaller line).The fan on the condenser blows the heat out over the condenser coil, then the high pressure vapor will lose some energy and turn into a high pressure liquid. The high pressure liquid will then go to the metering device , where it is turned into a low pressure liquid, and low temperature. It now passes over the evaporator coils that are inside, the heat that is being removed from the room is absorbed in the refrigerant and then turned into a vapor, at low pressure and low temperature. It is now going through the suction line (the bigger line) into the compressor where it turns the low pressure, low temperature into high pressure, high temperature liquid. Then the cycle starts all over again. Remember that compressors pump vapor only, at no point should it be sucking in liquid as this can damage the compressor.
What is the life force of a refrigeration system?
2. The Compressor – This is the life force of the refrigeration cycle, what it does is it will circulate refrigerant throughout the whole system. It will compress cold vapor into hot vapor, it also increases the low vapor pressure into high vapor pressure. 3. The Condenser – This is the coil that is located outside on a central air conditioning ...
What are the components of a refrigeration cycle?
1. The Evaporator – This is the coil that is inside of the house. Warm air will pass over the coil which contains the refrigerant, then the refrigerant absorbs the heat, ...
What is the purpose of metering devices?
4. The Metering Device – Controls the flow of the refrigerant to the evaporator. There are different kinds of metering devices, some of them will have pressure limiting devices to protect the compressor from overloading, while some will control the evaporators pressure or superheat.
What is the process of heat transferring through metal?
This is the process of heat transferring through metal. For example, if you heat up one end of a metal pipe the other end of the pipe will start to get hotter and heat up. The third way that heat can be transferred is the most important when it comes to hvac training, and this is called convection. Convection would be a transfer ...
What is convection heating?
Convection would be a transfer of heat through a medium such as water, air, or refrigerant. That is what is used to transfer heat in a central air conditioning system, car air conditioning system, refrigerator, freezer, anything that has to do with HVAC.
How Does an Air Conditioner Work?
There are two laws of physics that we should review before explaining the inner workings of your air conditioning system.
How does refrigerant change state?
After the refrigerant absorbs the heat, its state changes from a liquid to a vapor. This warmer refrigerant gas then gets transferred to the compressor (step 2 in the refrigeration cycle). Even though the refrigerant has absorbed heat from the indoor air, it is still fairly cool.
Why does refrigerant need to be colder than air?
The refrigerant needs to be colder than the indoor air in order to absorb heat. Once the refrigerant gets cooled down, it flows back into the evaporator coils where it begins the refrigeration cycle again. Hopefully, this helps you understand the basic workings of an air conditioner.
What happens to the refrigerant after it absorbs heat?
After the refrigerant absorbs the heat, its state changes from a liquid to a vapor. This warmer refrigerant gas then gets transferred to the compressor (step 2 in the refrigeration cycle).
How does heat flow from a colder body to a warmer body?
You can only transfer heat from a colder body to a warmer body through some kind of external work. Air conditioners transfer heat from the indoors to the outdoors.
What is the process of refrigerant?
Here are the basic parts of the refrigeration cycle (the same process that your refrigerator used to keep food cold): Air flows over the indoor coils, which contain extremely cold refrigerant. When air flows over the cold coils, heat from the air gets transferred to the refrigerant inside the coils.
Why do we increase the temperature of the refrigerant?
We increase the temperature of the refrigerant because it needs to be warmer than the outdoor air. Remember the 2 nd law of thermodynamics again—heat flows from warmer to cooler bodies.