
How do you calculate colligative properties?
How are colligative properties determined? You determine colligative properties by making measurements. The vapor pressure lowering ΔP relative to that of pure solvent A is ΔP = P A − P.
What is an example of a colligative property?
A colligative property is a property that depends on the number of solute particles in a solution and not on the identity of a solute. Vapor pressure lowering, boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, and osmotic pressure are all examples of colligative properties.
What is colligative property of solute?
The relative lowering of pressure and lowering of pressure are colligative property. A relation between the pressure of the solution, the vapour pressure of the pure solvent and the mole fraction of the solute was discovered by a French chemist Raoult.
How to determine the molecular weight of a solution using colligative properties?
Molecular weight determination using solution colligative properties. The use of colligative properties of solution in the determination of molecular weight of various compounds has been one of the simplest methods. Since colligative properties of solutions depend only on the number of molecules of solute in them,...
How do you find colligative properties?
Colligative Properties Equations The equations for the four colligative properties are as follows. Tf=−iKfm T f = − i K f m where Tf is the change in freezing point of the solution, Kf is a constant, and m is the molality of the solution measured in kg/mol.
What determines the colligative properties of a solution?
Colligative properties of solutions are properties that depend upon the concentration of solute molecules or ions, but not upon the identity of the solute. Colligative properties include vapor pressure lowering, boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, and osmotic pressure.
What does colligative property depend on?
(R) Colligative property depends on the number of solute particles dissolved in the solution.
What are the 4 colligative properties?
These colligative properties include vapor pressure lowering, boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, and osmotic pressure. This small set of properties is of central importance to many natural phenomena and technological applications, as will be described in this module.
Why colligative properties depend only on the concentration?
By definition, one of the properties of a solution is a colligative property if it depends only on the ratio of the number of particles of solute and solvent in the solution, not the identity of the solute.
What are colligative properties explain?
A colligative property is a property of a solution that is dependent on the ratio between the total number of solute particles (in the solution) to the total number of solvent particles. Colligative properties are not dependent on the chemical nature of the solution's components.
Do colligative properties depend on nature of solvent?
The colligative property of a solution depends on the the total number of solute particles in the solution. These properties do not depend on the chemical nature of its components. Therefore, colligative properties do not depend on the nature of the solvent.
Do colligative properties depend on temperature?
colligative properties, which depend only on solute concentration and temperature and are independent of the nature of the solute particles.
How many colligative properties are there?
four colligative propertiesThere are four colligative properties: vapor pressure lowering, boiling point ele- vation, freezing point depression, and osmotic pressure. This means that a solution shows a decreased vapor pressure, an increased boiling point and a decreased freez- ing point in comparison to the pure solvent (water in our case).
Why colligative properties are called so?
These properties are called colligative properties; the word colligative comes from the Greek word meaning “related to the number,” implying that these properties are related to the number of solute particles, not their identities.
What is colligative property of water?
Colligative properties of water. The colligative properties of solutions consist of freezing point depression, boiling point elevation, vapor pressure lowering, and osmotic pressure.
What are colligative properties give two examples?
Colligative properties include freezing point depression, boiling point elevation, vapour pressure lowering, and osmotic pressure.
Does colligative properties depend on identity of solvent?
The colligative property of a solution depends on the the total number of solute particles in the solution. These properties do not depend on the chemical nature of its components. Therefore, colligative properties do not depend on the nature of the solvent.
What do colligative properties depend on Brainly?
Colligative properties depend on the number of solute particles in the solution.
Do colligative properties depend on temperature?
colligative properties, which depend only on solute concentration and temperature and are independent of the nature of the solute particles.
How does a solute affect the colligative properties of a solution quizlet?
Colligative Properties depend on the concentration (molality or molarity) of solute molecules or ions (the number of dissolved particles in solution). Solute is nonvolatile and solvent is water. For nonelectrolytes, values of colligative properties are the same for different solutes at the same concentration.
Are Colligative properties physical or chemical?
The physical modifications that occur from applying solute to a solution are colligative properties. Colligative properties rely on the quantities...
Why are Colligative properties important?
Colligative properties include lowering of vapour pressure, elevation of the boiling point, depression of the freezing point, and osmotic pressure....
Why is Molality used in Colligative properties?
Molality is not only used in freezing depression points for colligative properties, since the colligative properties only depend on the number of p...
What are the other Colligative properties of solution?
Solutions’ colligative properties are properties that depend on the concentration of molecules or ions of the solute, but not on the identity of th...
What does freezing point depression mean?
Depression from Freezing Point. The freezing point of a solution is smaller than the pure solvent’s freezing point. This suggests that for freezing...
What is colligative property?
A colligative property is a property of a solution that is dependent on the ratio between the total number of solute particles (in the solution) to the total number of solvent particles. Colligative properties are not dependent on the chemical nature of the solution’s components. Thus, colligative properties can be linked to several quantities ...
What does "colligative" mean in science?
The word “colligative” has been adapted or taken from the Latin word “colligatus” which translates to “bound together ”. In the context of defining a solution, colligative properties help us understand how the properties of the solution are linked to the concentration of solute in the solution.
What are the physical modifications that occur when a solute is applied to a solution?
The physical modifications that occur from applying solute to a solution are colligative properties . Colligative properties rely on the quantities of solvent particles and the quantity of solvent, but they do NOT depend on the form of solvent particles, but they do depend on the type of solvent.
What happens when a semipermeable membrane is placed between a solution and a solvent?
When a semipermeable membrane is placed between a solution and solvent, it is observed that solvent molecules enter the solution through the semipermeable membrane and the volume of the solution increases. The semi-permeable membrane allows only solvent molecules to pass through it but prevents the passage of bigger molecules like solute.
What is the relationship between relative lowering in vapour pressure and mole fraction?
It states that the relative lowering in vapour pressure of a dilute solution is equal to the mole fraction of the solute present in the solution.
What happens to the surface of a solvent when a non volatile solute is added to it?
If a non- volatile solute is added to the solvent, the surface now has both solute and solvent molecules; thereby fraction of surface covered by solvent molecules gets reduced. Since the vapour pressure of the solution is solely due to solvent alone, at the same temperature the vapour pressure of the solution is found to be lower than that of the pure solvent.
What is the effect of adding a non volatile solute to a solvent?
1. Lowering of Vapour Pressure. In a pure solvent, the entire surface is occupied by the molecules of the solvent. If a non- volatile solute is added to the solvent, the surface now has both solute and solvent molecules; thereby fraction of surface covered by solvent molecules gets reduced.
Colligative properties
A binary solution is a mixture of two liquids that are completely miscible one with another, and there are two types of binary solutions,
Sample Problems
Question 1: Find the relative lowering of vapour pressure, if 18 g of glucose is dissolved in 90 g of water.
How to demonstrate the importance of colligative properties?
The best way to demonstrate the importance of colligative properties is to examine the consequences of Raoult's law. Raoult found that the vapor pressure of the solvent escaping from a solution is proportional to the mole fraction of the solvent. But the vapor pressure of a solvent is not a colligative property.
What are the two types of physical properties?
Physical properties can be divided into two categories. Extensive properties (such as mass and volume ) depend on the size of the sample. Intensive properties (such as density and concentration) are characteristic properties of the substance; they do not depend on the size of the sample being studied. This section introduces a third category that is a subset of the intensive properties of a system. This third category, known as colligative properties, can only be applied to solutions. By definition, one of the properties of a solution is a colligative property if it depends only on the ratio of the number of particles of solute and solvent in the solution, not the identity of the solute.
What happens when a solute is added to a solvent?
When a solute is dissolved in a solvent, the number of solvent molecules near the surface decreases, and the vapor pressure of the solvent decreases.
How to demonstrate osmotic pressure?
Osmotic pressure can be demonstrated with the apparatus shown in the figure below. A semipermeable membrane is tied across the open end of a thistle tube. The tube is then partially filled with a solution of sugar or alcohol in water and immersed in a beaker of water. Water will flow into the tube until the pressure on the column of water due to the force of gravity balances the osmotic pressure driving water through the membrane.
Why is the line in the phase diagram vertical?
This line is almost vertical because the melting point of a substance is not very sensitive to pressure. Adding a solute to a solvent doesn't change the way the melting point depends on pressure.
Is a solution a colligative property?
By definition, one of the properties of a solution is a colligative property if it depends only on the ratio of the number of particles of solute and solve nt in the solution, not the identity of the solute. Very few of the physical properties of a solution are colligative properties. As an example of this limited set of physical properties, ...
Does the rate of a solvent condense to form a liquid?
This has no effect on the rate at which solvent molecules in the gas phase condense to form a liquid. But it decreases the rate at which the solvent molecules in the liquid can escape into the gas phase. As a result, the vapor pressure of the solvent escaping from a solution should be smaller than the vapor pressure of the pure solvent.
What are colligative properties?
A colligative property is a property that depends on the number of solute particles in a solution and not on the identity of a solute. Vapor pressure lowering, boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, and osmotic pressure are all examples of colligative properties.
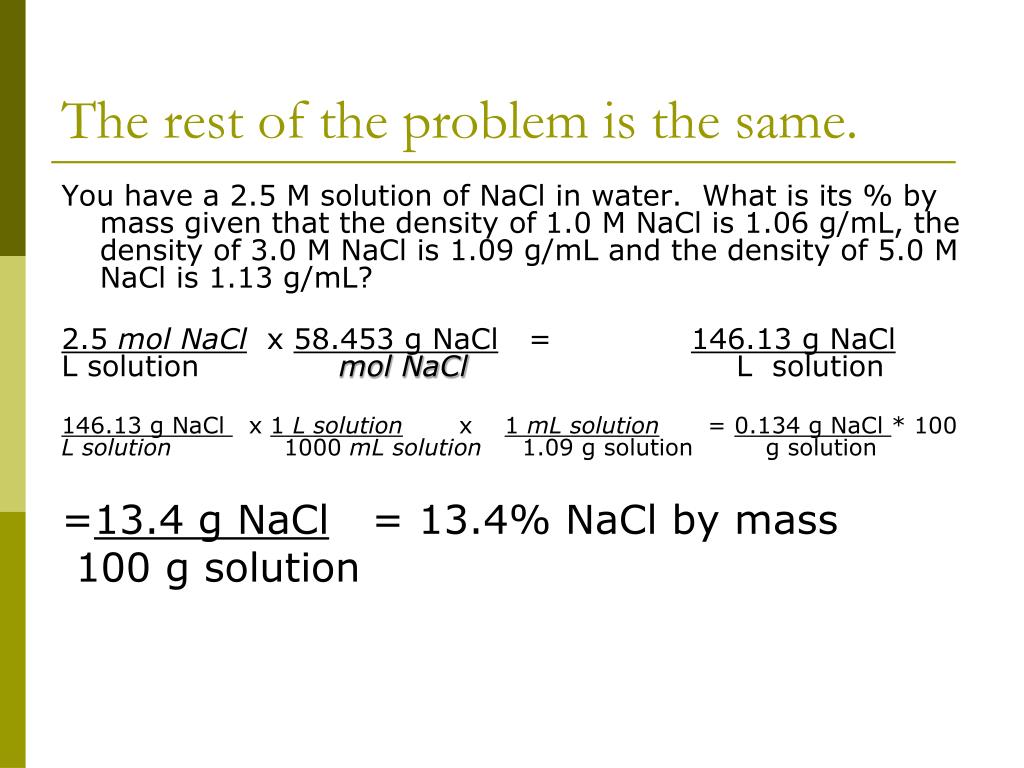
How to find molality of NaCl?
To calculate molality, we firstly need to figure out the number of moles of NaCl using the mass and molar mass. The molar mass of a substance is usually given as the grams of a substance per mole. NaCl has a molar mass of 58.5 g per mole.
What are the properties of a solution?
Colligative Properties. Colligative properties of solutions are properties that depend upon the concentration of solute molecules or ions , but not upon the identity of the solute. Colligative properties include vapor pressure lowering, boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, and osmotic pressure.
How to find how many molecules are in a solvent versus a solute?
A good approximation of how many molecules there are of solvent versus solute is the mole fraction, X solvent. If we simply multiply the new mole fraction of solvent by the standard vapor pressure (P osolvent) of the pure solvent, this will give us a good approximation of the new vapor pressure of the solvent.
How does adding solutes to a solvent lower its vapor pressure?
Now that we have seen how addition of solutes to a solvent can lower its vapor pressure, let's see if we can figure out how this relates to the boiling point of the same solvent. The normal boiling point of a liquid is defined as the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid is equal to standard pressure (1 atm). If we change the external pressure from 1 atm lower or higher, the boiling point changes as well. The boiling point is then simply the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the solvent equals the pressure of the surroundings. If you think about it, up until the vapor pressure reaches this point, the gas molecules cannot escape, right? The pressure on the surface is holding them in. Once you reach the boiling point temperature, the vapor pressure is then equal to the external pressure and the molecules can escape. Note that you really have to exceed the boiling point temperature to fully evaporate the liquid. I.e. steam is hotter than 100 o C.
How does solute affect the number of molecules at the surface?
Well, in the simplest terms, since some of the solute molecules will take up spaces at the surface of the liquid, this will limit the number of solvent molecules at the surface. Since only solvent molecules located at the surface can escape (evaporate), the sheer presence of the solute lowers the number of solvent molecules coming and going ...
What happens when a solute hits a solvent?
Another consideration is the type of solute. If the solute is an ionic species (a salt) then it is most likely going to split up into its component ions when it hits the solvent (normally water). If this is the case, we need to consider each particle that forms.
Does adding a solute to a solvent lower the freezing point?
This additional amount of entropy must now be overcome to allow the liquid to change phases into a solid (become ordered). This means that the temperature will have to be even lower than before. Thus addition of any type of solute to a solvent will lower its freezing point.
What is the purpose of colligative properties?
Since colligative properties of solutions depend only on the number of molecules of solute in them, this method is especially used for determining the molar masses of complex molecules, proteins, macromolecules, polymers.
Does boiling point rise when a nonvolatile solute is added to it?
We know that the boiling point of a pure solvent rises when a non-volatile solute is added to it. This elevation in boiling point is proportional to the molal concentration of the solute in the solution. Mathematically it is given as:
