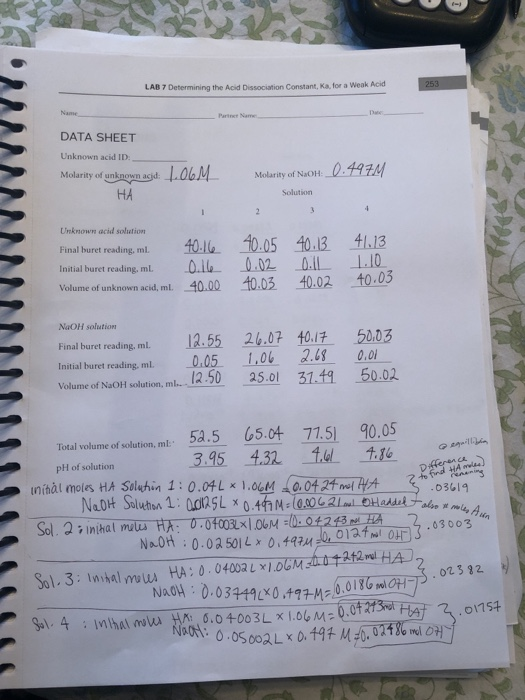
This experiment opts to use two methods to determine the Ka of the weak acid. The first method is the use of the pH of a solution that contains a known concentration of a weak acid. In this method, a plot of pH against volume of the base added produces an S-shaped graph that is used to establish the Ka of the acid.
How do you calculate Ka rating?
- Category C: Service entrance, more severe environment: 10kV, 10kA surge.
- Category B: Downstream, greater than or equal to 30 ft from category C, less severe environment: 6kV, 3kA surge.
- Category A: Further downstream, greater than or equal to 60 ft from category C, least severe environment: 6kV, 0.5kA surge.
How do you calculate Ka from concentration and pH?
How do you calculate Ka from pH? As noted above, [H3O+] = 10–pH. Since x = [H3O+] and you know the pH of the solution, you can write x = 10–2.4. It is now possible to find a numerical value for Ka. Ka = (10–2.4)2 / (0.9 – 10–2.4) = 1.8 x 10–5.
How do you determine Ka from a titration curve?
[H 3 O +] = Ka From the graph we can determine the pH at this point and since pH=-log10[H 3 O +], we can determine [H 3 O +] at this point and thus obtain the Ka for this equilibrium. Neat! Since this is a polyprotic acid, this corresponds to Ka1. Guess what you can determine from the pH at the midpoint of the second titration.
How do you solve Ka?
How to Calculate the Ka of a Weak Acid from pH
- Steps in Determining the Ka of a Weak Acid from pH. Step 1: Write the balanced dissociation equation for the weak acid. ...
- Formula and Vocabulary Used in Calculating the Ka of a Weak Acid from pH. ...
- Example Problem 1 - Calculate the Ka of a Weak Acid from pH. ...
- Example Problem 2 - Calculate the Ka of a Weak Acid from pH. ...

How do you find experimental Ka value?
Ka from Titration Curve At the equivalence point, the pH of the solution is equivalent to the pKa of the solution. Thus using Ka = – log pKa equation, we can quickly determine the value of Ka using a titration curve.
How is Ka measured?
The Ka value is found by looking at the equilibrium constant for the dissociation of the acid. The higher the Ka, the more the acid dissociates. Thus, strong acids must dissociate more in water. In contrast, a weak acid is less likely to ionize and release a hydrogen ion, thus resulting in a less acidic solution.
How do you find the KA of something?
Set up an ICE table for the chemical reaction. Solve for the concentration of H3O+ using the equation for pH: [H3O+]=10−pH. Use the concentration of H3O+ to solve for the concentrations of the other products and reactants. Plug all concentrations into the equation for Ka and solve.
How do you find Ka in a titration?
3:113:56Find the Ka Using a Titration Curve - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd I get two point four times ten to the minus four. And that's how you find the KA of an acid fromMoreAnd I get two point four times ten to the minus four. And that's how you find the KA of an acid from the titration curve the pKa of the acid is the same as the pH halfway to equivalence.
How do you determine Ka from pKa?
How do you calculate Ka from pKa? To create a more manageable number, chemists define the pKa value as the negative logarithm of the Ka value: pKa = -log Ka. If you already know the pKa value for an acid and you need the Ka value, you find it by taking the antilog.
How do you find KA of a weak acid?
STEP 2 Write the Ka expression for the weak acid. STEP 3 Describe each equilibrium concentration in terms of x. STEP 4 Assume that the initial concentration of weak acid is approximately equal to the equilibrium concentration....Weak AcidEquationKapropionic acidCH3CH2CO2H H+ + CH3CH2CO2-1.3 × 10-512 more rows
How do you find Ka given volume and pH?
As noted above, [H3O+] = 10-pH. Since x = [H3O+] and you know the pH of the solution, you can write x = 10-2.4. It is now possible to find a numerical value for Ka. Ka = (10-2.4)2 /(0.9 - 10-2.4) = 1.8 x 10-5.
How is KA related to pH?
More the Ka, more would be dissociation and hence stronger would be the acid. The lesser the pH, the stronger would be the acid. It depends on the concentration of acid, conjugate base hydrogen ions. It depends on the concentration of hydrogen ions.
How do you find KA from KB given pH?
21:1725:577.3 Using Ka and Kb to Calculate pH - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo we found KB to be 1.8 times 10 to the negative fifth.MoreSo we found KB to be 1.8 times 10 to the negative fifth.
What is the unit of Ka?
Kiloampere (kA), a unit of electric current. kiloannus or kiloannum (ka), a unit of time equal to one thousand (103) years.
What does Ka measure?
What is the Ka value? The acid dissociation constant (Ka) is used to distinguish strong acids from weak acids. Strong acids have exceptionally high Ka values. The Ka value is found by looking at the equilibrium constant for the dissociation of the acid. The higher the Ka, the more the acid dissociates.
What is KA and pKa?
Ka is the acid dissociation constant. pKa is simply the -log of this constant. Similarly, Kb is the base dissociation constant, while pKb is the -log of the constant. The acid and base dissociation constants are usually expressed in terms of moles per liter (mol/L).
Introduction
A common analysis of a weak acid or a weak base is to conduct a titration with a base or acid of known molar concentration to help determine the equilibrium constant, Ka, for the weak acid or weak base. If this titration is conducted very carefully and very precisely, the results can lead to a valid approximation of an equilibrium constant.
Objectives
Conduct a reaction between solutions of a weak acid and sodium hydroxide.
Sensors and Equipment
This experiment features the following sensors and equipment. Additional equipment may be required.
What acid gives vinegar its sour taste?
Acetic acid, the acid that gives vinegar its sour taste, is a weak acid that dissociates into acetate and hydronium ions in solution. CH3CO2H + H2O <--> CH3CO2−+ H3O+. Typical household vinegar is a 0.9 M solution with a pH of 2.4. Using the data, it's possible to calculate the dissociation constant:
What is the ka of an acid?
By Chris Deziel. Every acid has a characteristic dissociation constant (Ka), which is a measure of its ability to donate hydrogen ions in solution. In other words, Kaprovides a way to gauge the strength of an acid. Larger values signify stronger acids. The pH (power of hydrogen) of a solution is a measure of the concentration ...
What is the equation for a compound that is acidic?
The general equation describing what happens to an acid (HA) in solution is: HA + H20 <--> H30++ A- , where A-is the conjugate base.
What is the pH of an aqueous solution?
The pH of an aqueous acid solution is a measure of the concentration of free hydrogen (or hydronium) ions it contains: pH = -log [H+] orpH = -log [H30+] . The last equation can be rewritten: [ H30+] = 10-pH.
Formula and Vocabulary Used in Calculating the Ka of a Weak Acid from pH
pH: a measure of hydronium ion concentration in a solution. A pH less than 7 indicates an acid, and a pH greater than 7 indicates a base. It is represented as {eq}pH = -Log [H_ {3}O]^+ {/eq}
Example Problem 1 - Calculate the Ka of a Weak Acid from pH
Calculate the Ka value of a 0.50 M aqueous solution of acetic acid ( CH3COOH ) with a pH of 2.52.
Example Problem 2 - Calculate the Ka of a Weak Acid from pH
Calculate the Ka value of a 0.021 M aqueous solution of nitrous acid ( HNO2) with a pH of 3.28.
What is the indicator used to titrate an unknown acid?
In this part of the lab, you will titrate the unknown acid using the indicator phenolphthalein. This will allow you to determine the molarity of the acid again and compare your results to those obtained with the pH sensor in Part C.
How is the strength of an acid measured?
The strength of an acid is measured by its ability to donate a proton (H+); the strongest acids dissociate 100% in water, donating all of their protons to water. For example, when HCl donates its proton in water, the proton bonds to a water molecule to form a hydronium ion (H3O+),
