
How do you find the end behavior of a polynomial function?
The end behavior of a polynomial function is the behavior of the graph of f ( x) as x approaches positive infinity or negative infinity. The degree and the leading coefficient of a polynomial function determine the end behavior of the graph.
How do you find the end behavior of a graph?
In other words, the end behavior of a function describes the trend of the graph if we look to the right end of the -axis (as approaches ) and to the left end of the -axis (as approaches ). For example, consider this graph of the polynomial function . Notice that as you move to the right on the -axis, the graph of goes up.
How do you find the end behavior of a rational function?
Determine the end behavior of the rational function. Step 1: Look at the degrees of the numerator and denominator. If the degree of the denominator is larger than the degree of the numerator, there is a horizontal asymptote of y = 0 y = 0, which is the end behavior of the function.
When is the behavior of the function at both ends?
When is even, the behavior of the function at both "ends" is the same. The sign of the leading coefficient determines whether they both approach or whether they both approach . When is odd, the behavior of the function at both "ends" is opposite. The sign of the leading coefficient determines which one is and which one is .
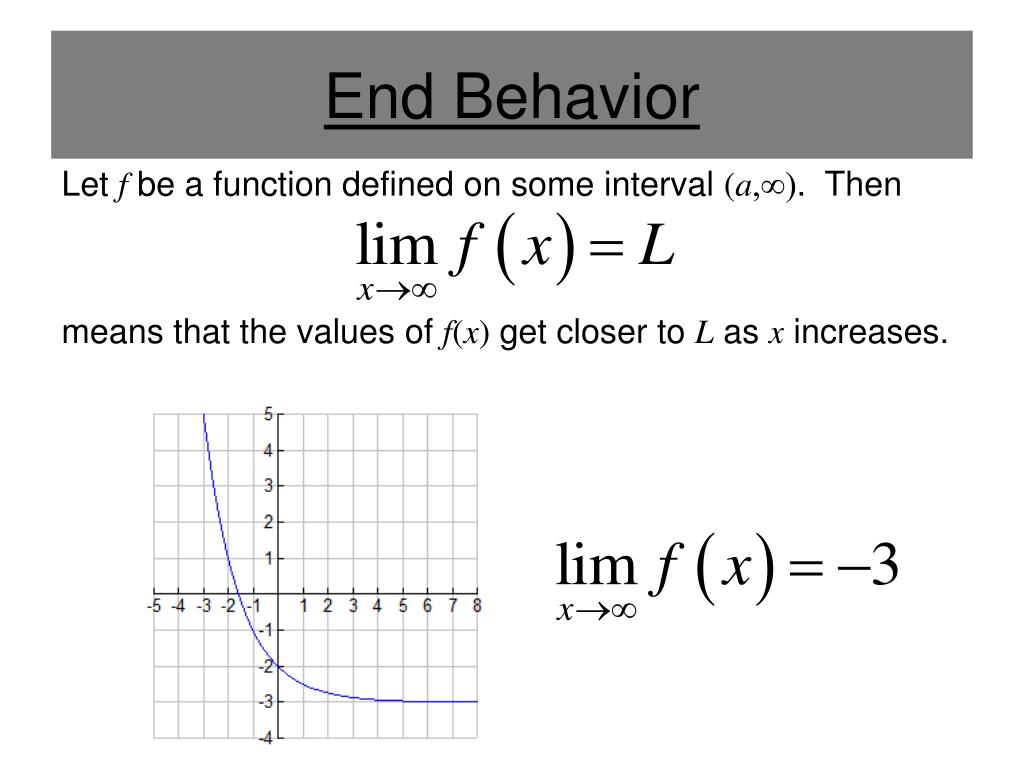
How do you find the left and right end behavior model?
0:452:20Left and Right End-behavior models - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo we would say that e to the negative x is a great left and behavior model because it models theMoreSo we would say that e to the negative x is a great left and behavior model because it models the end behavior as X approaches negative infinity. All right well what about the right end behavior it.
How do you determine the right and left hand behavior of a function?
If the degree, n, of the polynomial is even, the left hand side will do the same as the right hand side. If the degree, n, of the polynomial is odd, the left hand side will do the opposite of the right hand side.
How do you determine the endpoint of a behavior?
To determine its end behavior, look at the leading term of the polynomial function. Because the power of the leading term is the highest, that term will grow significantly faster than the other terms as x gets very large or very small, so its behavior will dominate the graph.
How do you know if the end behavior is up or down?
End behavior refers to the appearance of a graph as it is followed indefinitely in either horizontal direction. Leading coefficient POSITIVE: both "ends" are UP. Leading coefficient NEGATIVE: both "ends" are DOWN. Leading coefficient POSITIVE: left end is DOWN and right end is UP.
How do you determine left and right-hand limits?
0:563:06How to find the left and right hand limit by not using a calculator - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnother. Negative number so we have a negative divided by negative which gives us a positive soMoreAnother. Negative number so we have a negative divided by negative which gives us a positive so therefore that tells us this graph the left-hand limit is going to positive infinity.
How do you determine your right-hand side?
The expression on the right side of the "=" sign is the right side of the equation and the expression on the left of the "=" is the left side of the equation. x + 5 is the left-hand side (LHS) and y + 8 is the right-hand side (RHS).
What is the easiest way to find an endpoint?
0:372:04Finding Endpoint Given Midpoint - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo. We add them up and divide by 2 and that gives us the x coordinate of the midpoint. Same. ThingMoreSo. We add them up and divide by 2 and that gives us the x coordinate of the midpoint. Same. Thing with the Y's we add the Y's divided by 2 that gives us the y coordinate of midpoint.
How is the endpoint of a titration determined?
The point at which the indicator changes color is called the endpoint. So the addition of an indicator to the analyte solution helps us to visually spot the equivalence point in an acid-base titration. Endpoint: refers to the point at which the indicator changes color in an acid-base titration.
How would you describe the end of behavior of the graph?
The end behavior of a function f describes the behavior of the graph of the function at the "ends" of the x-axis. In other words, the end behavior of a function describes the trend of the graph if we look to the right end of the x-axis (as x approaches +∞ ) and to the left end of the x-axis (as x approaches −∞ ).
How do you describe end behavior examples?
0:454:04How to Describe End Behavior of Functions - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo we say the function approaches positive infinity as X approaches positive infinity so what we'veMoreSo we say the function approaches positive infinity as X approaches positive infinity so what we've done now is describe what happens to the function as.
How do you tell if it bounces or crosses?
If the graph touches the x-axis and bounces off of the axis, it is a zero with even multiplicity. If the graph crosses the x-axis at a zero, it is a zero with odd multiplicity. The sum of the multiplicities is the degree n.
How do you determine a behavior function?
A way that I am able to identify a behavior function is by observing what happened before the behavior. In this behavior function, the individual behaves in a certain way to get a preferred item, edible, or activity....There are 4 functions of behavior, which are:Access.Escape.Attention.Sensory.
What test is used to determine the left hand and right hand behavior of the graph of a polynomial function?
When graphing a function, the leading coefficient test is a quick way to see whether the graph rises or descends for either really large positive numbers (end behavior of the graph to the right) or really large negative numbers (end behavior of the graph to the left).
How do you describe the right end behavior of a function?
The end behavior of a function f describes the behavior of the graph of the function at the "ends" of the x-axis. In other words, the end behavior of a function describes the trend of the graph if we look to the right end of the x-axis (as x approaches +∞ ) and to the left end of the x-axis (as x approaches −∞ ).
What technique can you use to identify the function of behavior?
Functional analysis can provide practitioners and researchers a means to determine what is maintaining a problem behavior. While a FA may not be necessary in all scenarios, it can be utilized when other methods of behavior assessment do not lead to desired outcomes.
How to find the end behavior of a polynomial function?
End behavior: The end behavior of a polynomial function describes how the graph behaves as {eq}x {/eq} approaches {eq }pminfty. {/eq} We can determine the end behavior by looking at the leading term (the term with the highest {eq}n {/eq}-value for {eq}ax^n {/eq} , where {eq}n {/eq } is a positive integer and {eq}a {/eq} is any nonzero number) of the function. Depending on the sign of the coefficient ( {eq}a {/eq}) and the parity of the exponent ( {eq}n {/eq}), the end behavior differs;
What is the y intercept of a polynomial function?
Intercepts: The y-intercept of a polynomial function is the point {eq} (0,b) {/eq} that crosses through the y-axis. The x-intercept (s) of a polynomial function (if they exist) are the point (s) {eq} (a,0) {/eq} that cross through the x-axis. If we have an odd number of copies of a certain x-intercept, then the graph will pass through the intercept (think of how {eq}x^3 {/eq} behaves at its intercept). If we have an even number of copies of a certain x-intercept, then the graph will just touch the intercept (think of how {eq}x^2 {/eq} behaves at its intercept).
How to find the y intercept?
To identify the y-intercept, we need to plug in 0 into the function, i.e., {eq}f (0)= (0-2)^2 (0+1) (0+5)= (-2)^2 (1) (5)= (4) (1) (5)=20. {/eq} So, the y-intercept is {eq}mathit { (0,20)} {/eq}:
Where do we start the intercept?
We start at the top left corner of the coordinate plane and cross the x-axis through the point {eq} (-2,0) {/eq} since we only have one copy of this intercept.
Who is Jenna Feldman?
Jenna Feldman has been a High School Mathematics teacher for ten years. She has worked with students in courses including Algebra, Algebra 2, Precalculus, Geometry, Statistics, and Calculus. She has a bachelor’s degree in mathematics from the University of Delaware and a Master of Education degree from Wesley College.
What is the asymptote of a function when the degree of the numerator is greater than?
The degrees are not equal - move to the next step. Step 3: If the degree of the numerator is greater than the degree of the denominator, then there is a slant/oblique asymptote (if the degree of the numerator is exactly one larger than the degree of the denominator), or the function is asymptotic to a polynomial.
How to find the end behavior of a rational function?
Determining the End Behavior of a Rational Function. Step 1: Look at the degrees of the numerator and denominator. If the degree of the denominator is larger than the degree of the numerator, there is a horizontal asymptote of {eq}y = 0 {/eq}, which is the end behavior of the function. Step 2: If the degrees of the numerator ...
What is the horizontal asymptote of a function?
If the degree of the denominator is larger than the degree of the numerator, there is a horizontal asymptote of {eq}y = 0 {/eq}, which is the end behavior of the function. The degree of the numerator is 4, and the degree of the denominator is 3. Move to the next step.
What is the degree of the numerator?
The degree of the numerator is 3 and the degree of the denominator is also 3. Since the degree of the denominator is not larger than the degree of the numerator, we need to move to the next step.
What is the end behavior of a function?
End Behavior: The end behavior of a graph of a function is how the graph behaves as {eq}x {/eq} approaches infinity or negative infinity. The end behavior of a function is equal to its horizontal asymptotes, slant/oblique asymptotes, or the quotient found when long dividing the polynomials.
What is rational function?
Rational Function: A rational function is a function made up of a ratio of polynomials. Rational functions are of the form {eq}f (x) = dfrac {p (x)} {q (x)} {/eq}, where {eq}p (x) {/eq} and {eq}q (x) {/eq} are polynomials, and {eq}q (x) neq 0 {/eq}.
What is the degree of a polynomial?
Degree: The degree of a polynomial is the highest exponent on the variable.
What determines the end behavior of a graph?
The degree and the leading coefficient of a polynomial function determine the end behavior of the graph.
What is the leading coefficient in a function?
The leading coefficient is significant compared to the other coefficients in the function for the very large or very small numbers. So, the sign of the leading coefficient is sufficient to predict the end behavior of the function. To predict the end-behavior of a polynomial function, first check whether the function is odd-degree ...
What does it mean when you're graphing polynomials?
When you're graphing (or looking at a graph of) polynomials, it can help to already have an idea of what basic polynomial shapes look like. One of the aspects of this is "end behavior", and it's pretty easy. We'll look at some graphs, to find similarities and differences.
What does graph A and C represent?
Clearly Graphs A and C represent odd-degree polynomials, since their two ends head off in opposite directions. Graph D shows both ends passing through the top of the graphing box, just like a positive quadratic would. The only graph with both ends down is:
What happens when the ends of a graph are positive?
When the graphs were of functions with positive leading coefficients, the ends came in and left out the top of the picture , just like every positive quadratic you've ever graphed. When the graphs were of functions with negative leading coefficients, the ends came in and left out the bottom of the picture, just like every negative quadratic you've ever graphed.
What do odd degree polynomials behave like?
All even-degree polynomials behave, on their ends, like quadratics; all odd-degree polynomials behave, on their ends, like cubics.
Where does a positive cubic enter the graph?
A positive cubic enters the graph at the bottom, down on the left, and exits the graph at the top, up on the right. Since the leading coefficient of this odd-degree polynomial is positive, then its end-behavior is going to mimic that of a positive cubic. Therefore, the end-behavior for this polynomial will be: ...
Do odd degree polynomials go down?
But If they start "up" and go "down", they're negative polynomials. This behavior is true for all odd-degree polynomials. If you can remember the behavior for cubics (or, technically, for straight lines with positive or negative slopes), then you will know what the ends of any odd-degree polynomial will do. All even-degree polynomials behave, on ...
Do you know the end behavior of every even degree polynomial?
These traits will be true for every even-degree polynomial. If you can remember the behavior for quadratics (that is, for parabolas), then you'll know the end-behavior for every even-degree polynomial.

Determining The End Behavior of A Rational Function
Determining The End Behavior of A Rational Function - Vocabulary and Equations
- Rational Function:A rational function is a function made up of a ratio of polynomials. Rational functions are of the form {eq}f(x) = \dfrac{p(x)}{q(x)}{/eq}, where {eq}p(x){/eq} and {eq}q(x){/eq} are polynomials, and {eq}q(x) \neq 0{/eq}. End Behavior:The end behavior of a graph of a function is how the graph behaves as {eq}x{/eq} approaches infinity or negative infinity. The end behavio…
Example Problem 1: Determining The End Behavior of A Rational Function
- Determine the end behavior of the rational function. {eq}f(x) = \dfrac{4x^3 + 3x^2 - 2x - 1}{2x^3 + 3x - 4}{/eq} Step 1:Look at the degrees of the numerator and denominator. If the degree of the denominator is larger than the degree of the numerator, there is a horizontal asymptote of {eq}y = 0{/eq}, which is the end behavior of the function. The degree of the numerator is 3 and the degre…
Example Problem 2: Determining The End Behavior of A Rational Function
- Determine the end behavior of the rational function. {eq}f(x) = \dfrac{x^4 + 3x^2 - 1}{2x^3 + 5x}{/eq} Step 1:Look at the degrees of the numerator and denominator. If the degree of the denominator is larger than the degree of the numerator, there is a horizontal asymptote of {eq}y = 0{/eq}, which is the end behavior of the function. The degree of the numerator is 4, and the degre…