What does the Order of amino acids determine?
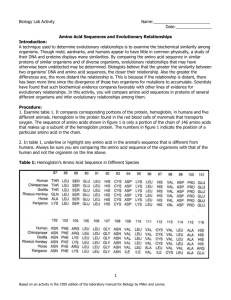
The genetic code is the sequence of nucleotide bases in nucleic acids ( DNA and RNA) that code for amino acids. These gene codes not only determine the order of amino acids in a protein, but they also determine a protein's structure and function.
How can amino acid sequence be determined from DNA?
The sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide is determined by the sequence of the corresponding codons in the mRNA molecule that was translated, where one mRNA codon “codes for” one amino acid. In all, less than 5% of the DNA bases in a gene end up in mRNA codons and are translated.
What does deduced amino acid sequence mean?
deduced amino acid sequence ( plural deduced amino acid sequences ) ( biochemistry) a sequence of amino acids predicted from a sequence of nucleotides using information about codons used in a particular organism quotations . 2009, Stanley, Pamela; Schachter, Harry; Taniguchi, Naoyuki, “N-Glycans”, in Essentials of Glycobiology [1 ...
Does sequence of three bases form an amino acid?
What is the amino acid sequence produced? Each group of three bases in mRNA constitutes a codon, and each codon specifies a particular amino acid (hence, it is a triplet code). The mRNA sequence is thus used as a template to assemble—in order—the chain of amino acids that form a protein.
How do you determine the sequence of a protein?
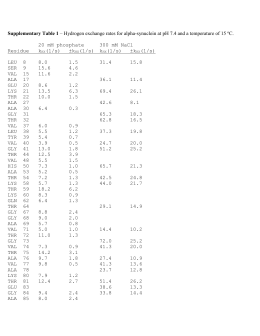
The two major direct methods of protein sequencing are mass spectrometry and Edman degradation using a protein sequenator (sequencer). Mass spectrometry methods are now the most widely used for protein sequencing and identification but Edman degradation remains a valuable tool for characterizing a protein's N-terminus.
How do you determine the number of amino acids in a sequence?
2:506:48How to find a number of Amino acids in protein chain? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo we would find number of codons. Minus 1 so we have SEC 336 codons so 336 divided by 3 minus 1 soMoreSo we would find number of codons. Minus 1 so we have SEC 336 codons so 336 divided by 3 minus 1 so 336 divided by 3 would be 112 this would be number of codons.
What does determine your amino acid sequencing?
Like words in a sentence, the DNA sequence of a gene determines the amino acid sequence for the protein it encodes. In the protein-coding region of a gene, the DNA sequence is interpreted in groups of three nucleotide bases, called codons. Each codon specifies a single amino acid in a protein.
What determines the amino acid sequence of a protein quizlet?
The amino acid sequence of a polypeptide is coded by a gene. the sequence of bases in the DNA of the gene determines the sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide. Proteins have either single polypeptides or more than one polypeptides linked together. Proteomes are all the proteins produced by a cell Or an organism.
How many amino acids are in a protein sequence?
twenty amino acidsProteins are built from a set of only twenty amino acids, each of which has a unique side chain. The side chains of amino acids have different chemistries. The largest group of amino acids have nonpolar side chains.
How do you find the sequence of amino acids and codons?
To use an amino acid codon wheel, start from the center and follow the RNA codons until you have the 3 nucleotide bases. Next, translate the three bases into an amino acid from the mRNA codons. The process is called RNA translation. Once established, follow the RNA sequence to find the amino acid that it translates to.
What is an amino acid sequence example?
A ribosome will read the mRNA three or letters at a time; each set is called a codon. So to a ribosome it will look like this: AAA-CGA-GGC-UAA. That first codon, AAA, tells the ribosome to start building the protein with the amino acid lysine.
How do you determine amino acid sequence from mRNA?
0:595:29The Genetic Code- how to translate mRNA - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe answer is in the codon. We interpret mRNA in a series of three nucleotides at a time called aMoreThe answer is in the codon. We interpret mRNA in a series of three nucleotides at a time called a codon a single codon will correspond to a specific amino acid.
How do you determine the number of amino acids in a nucleotide?
Each group of three nucleotides encodes one amino acid.
How do you determine the number of amino acids in a peptide chain?
8:1810:4810. How to calculate number of amino acid residue in protein ... - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo now the final and correct formula is the number of amino acid in simple protein. It is equal toMoreSo now the final and correct formula is the number of amino acid in simple protein. It is equal to molecular weight of protein. Divided by adjusted average molecular weight of amino acid residues.
Do you use mRNA to find amino acids?
Each group of three bases in mRNA constitutes a codon, and each codon specifies a particular amino acid (hence, it is a triplet code). The mRNA sequence is thus used as a template to assemble—in order—the chain of amino acids that form a protein.
How do you determine the number of codons?
The number of codons produced is dependent on the number of base pairs in each codon. The number of codons that is made, can be easily calculated by 4n. This is because there are four possible base pairs, so for each base pair you add to a codon. You could add an A, T, C, or G.
How is the amino acid sequence determined?
The amino acid sequence of a protein is determined by the information found in the cellular genetic code. The genetic code is the sequence of nucleotide bases in nucleic acids ( DNA and RNA) that code for amino acids.
How many amino acids are in proteins?
Although there are hundreds of amino acids found in nature, proteins are constructed from a set of 20 amino acids.
How many amino acids are there in the human body?
While amino acids are necessary for life, not all of them can be produced naturally in the body. Of the 20 amino acids, 11 can be produced naturally. These nonessential amino acids are alanine, arginine, asparagine, aspartate, cysteine, glutamate, glutamine, glycine, proline, serine, and tyrosine. With the exception of tyrosine, nonessential amino ...
What are nonessential amino acids?
With the exception of tyrosine, nonessential amino acids are synthesized from products or intermediates of crucial metabolic pathways. For example, alanine and aspartate are derived from substances produced during cellular respiration. Alanine is synthesized from pyruvate, a product of glycolysis.
What are the structural properties of amino acids?
Generally, amino acids have the following structural properties: All amino acids have the alpha carbon bonded to a hydrogen atom, carboxyl group, and amino group. The "R" group varies among amino acids and determines the differences between these protein monomers.
What are amino acids made of?
From a structural perspective, amino acids are typically composed of a carbon atom, a hydrogen atom, a carboxyl group along with an amino group and a variable group.
How are amino acids joined together?
The resulting amino acids are joined together through dehydration synthesis, a process in which a peptide bond is formed between the amino acids. A polypeptide chain is formed when a number of amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds.
Most recent answer
You can go search for your protein of interest at NCBI or UNIPROT, in case if you have nucleotide sequence you can try ORF Finder or ORF Prediction tools available online. Especially, if you are working with mammalian proteins, try checking GENECARDS.
Similar questions and discussions
We have dataset containing large numbers of proteins belonging to PDB, SwissProt, TargetDB and unknown sources. We have no idea about their nucleotide sequences, but we are interested in understanding codon preference in these proteins.
What is the relationship between amino acids and codons called?
The full set of relationships between codons and amino acids (or stop signals) is called the genetic code . The genetic code is often summarized in a codon chart (or codon table), where codons are translated to amino acids.
What is the order of the protein translation?
mRNA codons are read from 5′ end to 3′ end, and its order specifies the order of amino acids in a protein from N-terminus to C-terminus.
What is the start codon in mRNA?
Our cells use a very smart strategy to solve this problem – the “start codon”. Because the translation only begins at the start codon (AUG) and continues in successive groups of three, the position of the start codon ensures that the mRNA is read in the correct frame (in the example above, in Frame 3).
How many stop codons are there in a protein?
Three “ Stop ” codons mark the end of a protein and terminate the translation.
What is a short chain of amino acids called?
Note: A short chain of amino acids is often referred to as a “polypeptide”. When the number of amino acids adds up (usually > 30 units) and the polypeptide chain folds into a 3D structure, we call it a “protein”.
What happens when nucleotides are inserted?
Mutations could also happen when nucleotides are inserted or deleted from the original DNA sequence. The insertion or deletion of “one or two” nucleotides can change the reading frame ( frameshift mutation ). A frameshift can totally mess up the amino acid orders “downstream” the mutation site.
What is the process that makes copies of a gene called?
First, inside the nucleus, a process that makes copies of a certain gene in the form of massager RNAs ( mRNAs ), called transcription.