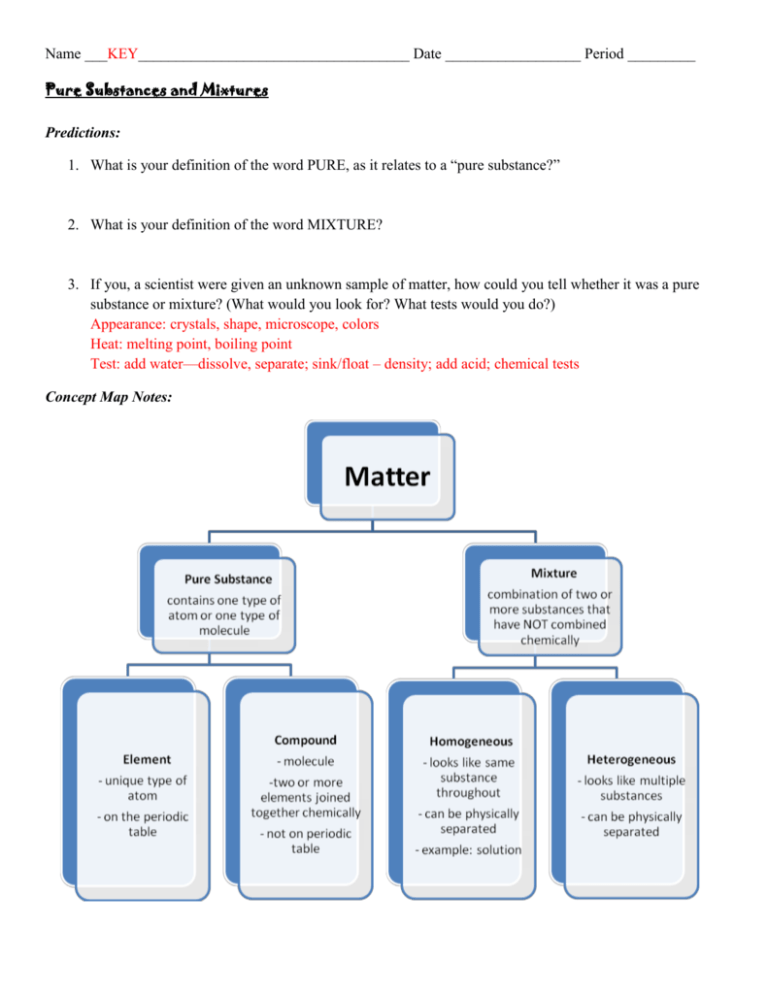
How would you determine the melting point of unknown organic compound mention the procedure and significance to determine the melting point?
- Powder the crystalline substance.
- Attach the capillary tube to a thermometer which is immersed in a bath of liquid paraffin.
- Heat the beaker slowly and go on stirring the liquid in the beaker so that the temperature remains uniform throughout.
- The temperature is noted when the substance starts melting.
How do you find the melting point of an unknown sample?
Identification. As a compound's melting point is a physical constant, it can be used to support the identity of an unknown solid. The melting point can be looked up in a reference book (this value would then be called the "literature melting point"), and compared to the experimental melting point.
How do you determine the melting point of a substance?
The most common and most basic method of determination is the capillary method. This method involves placing the sample in a capillary tube and running an experiment that will heat the sample until it reaches melting point. The melting point can then be recorded.
How would you determine the melting point of unknown organic compound mention the procedure and significance to determine the melting point?
ProcedurePowder the crystalline substance. ... Attach the capillary tube to a thermometer which is immersed in a bath of liquid paraffin. ... Heat the beaker slowly and go on stirring the liquid in the beaker so that the temperature remains uniform throughout. ... The temperature is noted when the substance starts melting.
Why is melting point determination important and how can it be used to identify unknown compound?
Melting point determination of different elements helps to understand the purity of a substance. A pure substance has a melting range of one or two degrees but the range of melting of impure substances is much higher than the pure substance. The melting point also depends on the structure of the molecule.
How do you determine boiling point and melting point?
Calculate the change in boiling or freezing temperature using one the following formulas: ΔTf = Kf * m or ΔTb = Kb* m. Add the value obtained for ΔTb to the standard boiling point of the solvent (ex. 100 C for water) or subtract the value obtained for ΔTf from the standard freezing point of the solvent (ex.
Why is it important to determine the melting point of a compound?
The melting point determination of organic compounds helps people understand the physical and chemical properties of the substance. Many different factors affect the melting point of any substance, such as the force of attraction, impurities present in the substance, and the molecules' size and structure.
Which chemical is used in determination of melting point of a sample?
Take Benzoic acid on a tile and crush it into a fine powder. Take a capillary tube and by heating one end close the end of the tube. Hold the closed end of the capillary tube between your finger and thumb as shown in figure (a) above. Dip the open end of the capillary tube in the finely powdered Benzoic acid.
Why is it important to identify unknown substances?
Unknown materials and substances found on-site, in products, or during processing can be a major cause for concern. Being able to effectively and precisely identify them enables public and private sector organisations such as corporations, police, hospitals and councils to take action to prevent risk.
How do you tell which substance will have a higher melting point?
The presence of polar and especially hydrogen-bonding groups on organic compounds generally leads to higher melting points. Molecular shape, and the ability of a molecule to pack tightly into a crystal lattice, has a very large effect on melting points.
How do you tell if a substance has a high melting point?
In general, the greater the charge, the greater the electrostatic attraction, the stronger the ionic bond, the higher the melting point.
What is the melting point of a substance?
A pure substance generally has a melting point range of less than 2 °C. However, other compounds may also have melting points within 2 °C of your sample. One way to become more certain is to determine the mixed melting points of mixtures of your sample with other compounds.
What temperature does 2-furancarboxylic acid melt?
But 2-furancarboxylic acid and decanedioic acid also melt near 134 °C.
Does cinnamic acid change melting point?
If your unknow n is cinnamic acid, mixing it with pure cinnamic acid will not change the melting point. However, the other compounds will be "impurities" in your unknown, and the mixed melting points will be lower and have wider melting point ranges. Answer link.
Do impurities depress the melting range?
Impurities tend to depress and broaden the melting range, so your pure sample should have a higher and narrower melting range than the mixture.
What is the melting point of a compound?
A pure organic compound melts or freezes fairly sharply over a specific temperature range called its melting point. This physical constant can help identify a substance. Generally, any impurity added to a pure substance will lower its observed melting point and increase the range over which melting occurs. Therefore, when two pure organic substances possess a similar melting point, a mixture containing both substances will often melt at a lower temperature and over a broader range. Conversely, if a mixture of a known and unknown substance actually contains a single substance, the melting point of the mixture will not deviate from the melting point of the known.
What is the purpose of melting point?
determine the structure type and identify the four white powders. This includes conducting tests of melting point, flame color, solubility and the conductivity in water (H20). The melting point of a substance is the temperature at which the material changes from a solid to a liquid state. The determination of melting points is a form of identification and test method for organic substance. The melting point is an easy way measure and classify substances. Testing the flame color is an appropriate test
How to melt benzoic acid?
The first appearance of liquid occurred at 119° C, and the benzoic acid completely melted by 122° C giving a melting point range of 119° C to 122° C for benzoic acid. Repeating the procedure for 2-naphthol returned a melting point range of 118° C to 123° C. Next, a 1:1 mixture of benzoic acid and 2-naphthol received the same…show more content…
What is the melting point of benzoic acid?
The first appearance of liquid occurred at 119° C, and the benzoic acid completely melted by 122° C giving a melting point range of 119° C to 122° C for benzoic acid. Repeating the procedure for 2-naphthol returned a melting point range of 118° C to 123° C.
What happens when a mixture of a known and unknown substance actually contains a single substance?
Conversely, if a mixture of a known and unknown substance actually contains a single substance, the melting point of the mixture will not deviate from the melting point of the known. Davis (1913) demonstrated that pairs of substances with similar melting points melted at lower temperatures and over broader melting ranges when mixed.
How to distinguish a compound from another?
very different. These differences can be used to distinguish one from another by using the main properties for each compound. For example, if a substance could not conduct electricity and had low melting points, it would be labeled as a molecular compound since those properties correspond directly with the properties of a molecular compound. If a substance was able to conduct electricity and had high melting points, it would be labeled as a ionic compound because those properties correspond directly
How to explain density?
Explain what density is & how it relates to stratification. Density = mass/volume; how much mass fits into a space. Unit: kg/m3 3 Stratification = less-dense materials float on top of denser materials This is found in the
How to determine melting point of a mixture?
Mixed melting point determination 1 The melting point of the mixture is the same as the pure compound, which means that the unknown compound and the known compound are the same. 2 The melting point of the mixture is lower than either of the two pure components and the melting range is large. This is because the two compounds are different with the result that one is an impurity in the other.
What happens when you measure the melting point of a mixture?
If you prepare a mixture of your unknown chemical and the one you suspect it may be and measure the melting point of the mixture then there are two possible results: The melting point of the mixture is the same as the pure compound, which means that the unknown compound and the known compound are the same. The melting point of the mixture is lower ...
Why is the melting point of a mixture lower than the melting point of a pure compound?
This is because the two compounds are different with the result that one is an impurity in the other.
Is a mixed melting point useful?
The usefulness of mixed melting points is limited in that you must have some idea of the chemical nature of your unknown compound and a sample of the suspected compound must be available.
How do you know if a solvent is a solvent?
Smell: Most chemists can identify solvents by their distinctive smells (though this is a pretty bad idea).¹
How to get energy from a sample?
Step 1: Add energy to your sample. Step 2: This will cause something in the sample to go from a lower energy ground state into a higher energy excited state. Step 3: When the sample reverts to the lower energy ground state, the energy that it absorbed will be given off.
Why is chromatography used in chemistry?
Because it’s usually the case that you have some idea what these compounds are, you can figure out the identities of these compounds using this method. Which is vague, so I’ll just explain it:
How does mass spectrometry work?
Mass spectrometry involves ionizing a sample to give its molecules/atoms/molecular fragments positive charge. These particles are then accelerated toward a great big magnet, which bends the stream of particles toward a detector. Because big particles take longer to turn than small ones, this process separates each particle by mass.⁹
What do chemists do?
Chemists spend a lot of time with chemicals they’re trying to identify. Some chemists try to figure out what’s in that bottle that Uncle Merle had in the “lab” out in the back shed, while others try to figure out whether EvilCorp was dumping toxic waste directly into the mouths of endangered squirrels. Whichever is the case with you, it’s handy to have some method around to identify those pesky unidentified chemicals that are lying around.
Which isotopes are less abundant than hydrogen-1?
7. Other isotopes can also be used, provided that they have a spin of 1/2. The most common of these is carbon-13. Because these other isotopes are less abundant than hydrogen-1, it takes longer to obtain NMR spectra for them.
Can you identify an unknown substance?
It’s usually not used to identify an unknown substance , but to figure out the long-range structures of known materials. If you have a protein and want to know how it folds, or if you want to know what the structure of a crystal is, this will do the job. It requires that the sample be crystalline.
