The greater the pressure gradient, the stronger the windspeed. Thus, on surface weather maps, the strongest winds are happening where the isobars are closest together and the weakest winds are happening where the isobars are spaced furthest apart.
What direction do the winds travel in the northern hemisphere?
away from higher pressures. T/F- In both the Northern and the Southern Hemispheres, the circulation around highs is clockwise and the circulation around lows is counterclockwise. On a surface weather map, why do surface winds tend to cross the isobars?
What is the direction of wind flow in the upper levels?
In the upper levels, this creates relatively high heights to the south of the jet and relatively low heights to the north. The Pressure Gradient Force flows from a southerly to northerly direction. However, the Coriolis force shifts the wind flow to the right of the path of motion.
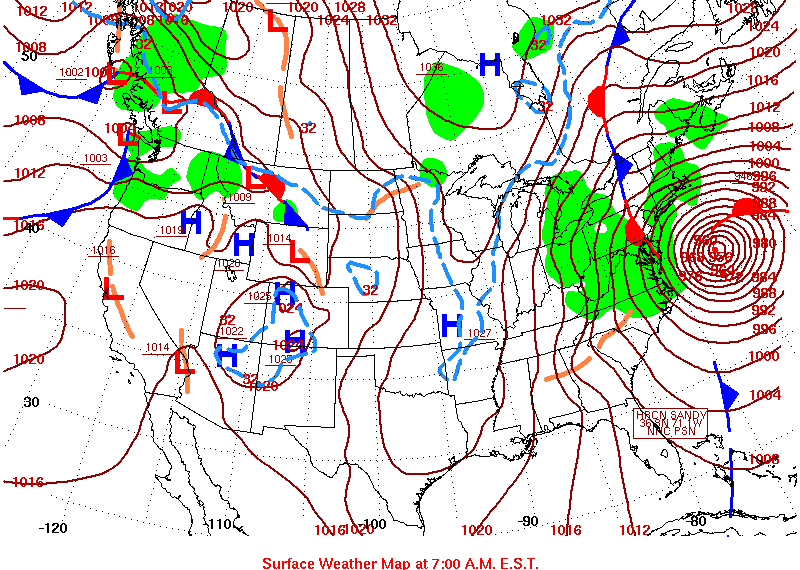
What data is shown on the surface weather map?
Pressure, wind, temperature, cloud cover, and weather data are shown. Plotting the surface weather data on a map is just the beginning. You really can't tell, for example, what is causing the cloudy weather with rain (the dot symbols) and drizzle (the comma symbols) in the NE portion of the map above or the rain shower along the Gulf Coast.
How does a meteorologist map out a weather forecast?
A meteorologist would usually begin by drawing some contour lines of pressure to map out the large scale pressure pattern. We will look first at contour lines of temperature, they are a little easier to understand (the plotted data is easier to decode and temperature varies across the country in a fairly predictable way).
What are the lines of equal wind speed?
What is vertical motion in jet streaks?
What are arrows in flow patterns?
What determines the amount of divergence/convergence due to jet streak dynamics?
How does the wind move in a baroclinic system?
What side of a trough does a jet streak go on?
Where does divergence occur in a jet?
See 4 more
About this website

Where are the strongest winds found?
The Guinness Book of World Records and National Geographic Atlas have both listed this bay in Antarctica as the windiest place on the planet. Katabatic winds in Commonwealth Bay are recorded at over 150 mph on a regular basis, and the average annual wind speed is 50 mph.
How do you read a windy map?
The wind on the map is colored a certain color from blue to purple. Yes, these are the colors of the rainbow just in a slightly different order: blue — little wind, green to red — more wind, purple — too much wind. Just look at the map to determine how much wind is now in some particular part of the world.
How do you read a weather map?
4:175:15How to Read Weather Maps - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipFirst in the southern hemisphere wind flows clockwise around low pressure systems. And anti-MoreFirst in the southern hemisphere wind flows clockwise around low pressure systems. And anti-clockwise. And high pressure. Systems in the northern hemisphere wind flows anti-clockwise.
How do you find the wind direction on a map?
5:187:29Maps direction and wind direction. - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipComes from the east. So if it blows from east to west it's going towards the west.MoreComes from the east. So if it blows from east to west it's going towards the west.
How is wind represented on a weather map?
Wind direction is indicated by the line that extends out from the station plot sky cover circle. The direction the line points is the direction from which the wind is blowing. Wind speed is indicated by the shorter lines, called "barbs," which extend from the longer line.
How is wind shown on weather maps?
Wind direction is indicated by the direction from which it originates. For example, a southerly wind blows from the south to the north. What do the lines making a circle around the low pressure area indicate? This means that every location on that line is at the same pressure (isobar).
What does a large L on a weather map indicate?
Atmospheric pressure is measured with an instrument on the ground called a barometer, and these measurements are collected at many locations across the U.S. by the National Weather Service. On weather maps, these readings are represented as a blue “H” for high pressure or a red “L” for low pressure.
What are the main symbols on a weather map?
Answer Key One of the main symbols on a weather map include a wind barb to display the wind speed and direction. Other symbols include colored lines to designate warm or cold air fronts, isobars for air pressure, and symbols for cloud types.
How do you read the wind direction on a synoptic chart?
In terms of the wind direction, air moves around high pressure in a clockwise direction and low pressure in an anticlockwise direction, so isobars also tell us the direction and speed of the wind.
What does it mean when it says wind is NW?
Definitions of northwest wind. a wind from the northwest. synonyms: northwester. type of: air current, current, current of air, wind. air moving (sometimes with considerable force) from an area of high pressure to an area of low pressure.
What is the most common wind direction?
east-westGenerally, prevailing winds blow east-west rather than north-south. This happens because Earth's rotation generates what is known as the Coriolis effect. The Coriolis effect makes wind systems twist counter-clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere.
When wind direction is described what direction?
Wind direction is measured relative to true north (not magnetic north) and is reported from where the wind is blowing. An easterly wind blows from the east or 90 degrees, a southerly from the south or 180 degrees and a westerly from the west or 270 degrees.
What do the Colours mean on windy?
Red is used for tropical storm/gale force winds, as the winds are dangerous enough to produce certain damages. Light white/purple indicates hurricane force winds (Category 1), and grey is used for major hurricane (Category 3). Dark blue indicates winds for jet stream and other extremely rare winds.
How do you understand windy?
1:357:30Windy.com introduction (Quick User Guide) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo the highlighting here in color makes it quite easy to spot the peaks. And troughs in wind terms.MoreSo the highlighting here in color makes it quite easy to spot the peaks. And troughs in wind terms. And below that there are wind direction arrows. On the very bottom line of the screen.
What does it mean when it says wind is NW?
Definitions of northwest wind. a wind from the northwest. synonyms: northwester. type of: air current, current, current of air, wind. air moving (sometimes with considerable force) from an area of high pressure to an area of low pressure.
What does SSW wind mean?
south-southwest wind180° — south wind (S) 202.5° — south-southwest wind (SSW)
Jet Stream Winds at 300 mb (~30,000 ft) (GFS 10-day Forecast)
Jet Stream Winds at ~30,000 ft (GFS 10‑day Forecast) Local Weather. Local weather by ZIP or City Local area snow depth CURRENT WEATHER MAPS Fronts & Pressure Centers Current U.S. Temperatures Northwest U.S. Northeast U.S. Mid-Atlantic U.S. Midwest U.S. Central Plains U.S. Southeast U.S. Southern Plains U.S. Southwest U.S. Alaska
Jet Stream | Wind Maps | Weather Underground
The Jet Stream map shows today's high wind speed levels and jetstream directions. Jet streams are fast flowing, relatively narrow air currents found in the atmosphere around 10 kilometers above ...
Entrance of Jet Streaks - National Weather Service
Fig. 3: Example vertical cross-section of a jet streak (solid lines are equal wind speed lines/isotachs in kts) and the divergence (bold dashed circle; DIV) and low-level jet (LLJ) isentropic ascent (large bold arrow) response to the upper divergence in the right entrance region of the jet. The outer solid line with arrowheads represents a simplified direct thermal circulation within the ...
What are the lines of equal wind speed?
Fig. 2:Example of the entrance and exit regions of a straight jet streak. Dashed lines are lines of equal wind speed (isotachs); solid lines are height lines along which the total wind blows. The small arrows denote a component of the ageostrophic wind due to jet streaks that results in divergence and convergence in exit and entrance regions.
What is vertical motion in jet streaks?
Thus, the atmosphere attempts to restore (thermal wind) balance through vertical motion. The vertical motion is attained through ageostrophic winds. Thus, vertical motion is required within entrance and exit regions of jets.
What are arrows in flow patterns?
Solid lines are constant height lines. Arrows are a component of the ageostrophic wind due to troughs and ridges that results in convergence (con) and divergence (div) aloft.
What determines the amount of divergence/convergence due to jet streak dynamics?
Within jet entrance and exit regions , the cross-stream component of the inertial advective part of the ageostrophic wind (i.e., the small arrows in Fig. 2) dictates the amount of divergence/convergence (and subsequent vertical motion) due to jet streak dynamics. Upper-level divergence (convergence) often is associated with upward (downward) vertical motion in the atmosphere.
How does the wind move in a baroclinic system?
In a baroclinic system (systems that tilt with height), the lower-level pressure/height falls under the right entrance region/ divergence aloft cause a wind to be directed toward the pressure falls area (i.e., wind moves toward lower pressure). The wind moves toward the falls from all directions, including from the south where it is warmer and from the north where it is colder. This wind is the isallobaric component of the ageostrophic wind(small arrows in Fig. 2). South and/or east of the right entrance region/upper-level divergence/low-level pressure falls area, the southerly ageostrophic flow moving toward the falls area complements the environmental southerly flow already in place (southerly bold arrow labeled t1 inFig. 2). Thus, an increase/ acceleration in the actual wind occurs near and south and/or east of the jet right entrance region (i.e., right rear quadrant of the jet streak).
What side of a trough does a jet streak go on?
If a strong jet streak is on the left side of a trough, the trough will amplify (dig)as shown below.
Where does divergence occur in a jet?
Fig. 6Same as Fig. 5 except for an anticyclonically- curved jet streak. Divergence aloft and upward motion occur in the jet right entrance region (left half of image) with convergence and descent in the jet right exit region (right half of image).
What is a geostrophic wind?
A geostrophic wind is a wind that results from a balance between what two forces?
What is a T/F wind?
T/F- An onshore wind blows from the water onto the land.
Which way is the circulation around highs and lows?
T/F- In both the Northern and the Southern Hemispheres, the circulation around highs is clockwise and the circulation around lows is counterclockwise.
Does T/F cause air to rush off vertically?
T/F- Pressure decreases with height causing an upward directed pressure gradient force. The air does not rush off vertically into space from this force because of the downward force of gravity.
Does wind speed increase Coriolis force?
Increasing wind speed decreases the Coriolis force and increasing latitude increases the. Coriolis force. increasing wind speed increases the Coriolis force and increasing latitude increases the. Coriolis force. Upper level winds in the middle latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere generally blow from west to.
What are the lines of equal wind speed?
Fig. 2:Example of the entrance and exit regions of a straight jet streak. Dashed lines are lines of equal wind speed (isotachs); solid lines are height lines along which the total wind blows. The small arrows denote a component of the ageostrophic wind due to jet streaks that results in divergence and convergence in exit and entrance regions.
What is vertical motion in jet streaks?
Thus, the atmosphere attempts to restore (thermal wind) balance through vertical motion. The vertical motion is attained through ageostrophic winds. Thus, vertical motion is required within entrance and exit regions of jets.
What are arrows in flow patterns?
Solid lines are constant height lines. Arrows are a component of the ageostrophic wind due to troughs and ridges that results in convergence (con) and divergence (div) aloft.
What determines the amount of divergence/convergence due to jet streak dynamics?
Within jet entrance and exit regions , the cross-stream component of the inertial advective part of the ageostrophic wind (i.e., the small arrows in Fig. 2) dictates the amount of divergence/convergence (and subsequent vertical motion) due to jet streak dynamics. Upper-level divergence (convergence) often is associated with upward (downward) vertical motion in the atmosphere.
How does the wind move in a baroclinic system?
In a baroclinic system (systems that tilt with height), the lower-level pressure/height falls under the right entrance region/ divergence aloft cause a wind to be directed toward the pressure falls area (i.e., wind moves toward lower pressure). The wind moves toward the falls from all directions, including from the south where it is warmer and from the north where it is colder. This wind is the isallobaric component of the ageostrophic wind(small arrows in Fig. 2). South and/or east of the right entrance region/upper-level divergence/low-level pressure falls area, the southerly ageostrophic flow moving toward the falls area complements the environmental southerly flow already in place (southerly bold arrow labeled t1 inFig. 2). Thus, an increase/ acceleration in the actual wind occurs near and south and/or east of the jet right entrance region (i.e., right rear quadrant of the jet streak).
What side of a trough does a jet streak go on?
If a strong jet streak is on the left side of a trough, the trough will amplify (dig)as shown below.
Where does divergence occur in a jet?
Fig. 6Same as Fig. 5 except for an anticyclonically- curved jet streak. Divergence aloft and upward motion occur in the jet right entrance region (left half of image) with convergence and descent in the jet right exit region (right half of image).
