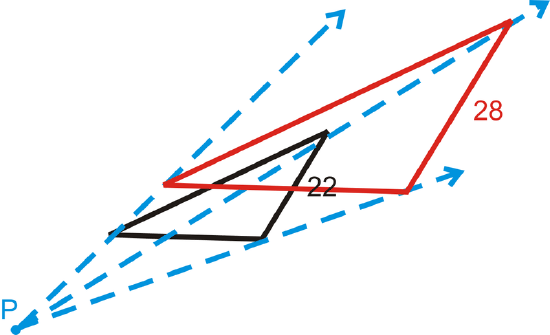
How to Perform Dilations
- Step 1. Identify the center of dilation. Imagine this as the fixed location of the projector. ...
- Step 2. Identify the original points of the polygon. ...
- Step 3. Identify the scale factor . ...
- Step 4. Multiply each original point of the polygon by the scale factor to get the new points. ...
- Step 5. Plot the new points and connect the dots to get your dilated shape.
How to fill a shape?
How to Fill a Shape With an Image in Photoshop
- Add a Shape To get started, we need a document with a shape we want to use. ...
- Add an Image To fill the shape with an image, we’re going to place the image on top of the layer stack. ...
- Resize the Image It’s likely you’ll need to resize and reposition the image where it makes the most sense. ...
- Add a Clipping Mask
How do you calculate dilation in geometry?
- Take the x-coordinate of P' = 3 and the x-coordinate of P = 1.
- Substitute the values in the formula: 3 ÷ 1 = 3.
- Now, take the y-coordinate of P' = 9 and the y-coordinate of P = 3.
- Apply the same formula: 9 ÷ 3 = 3. Thus, we get the scale factor of 3 from both the coordinates.
How to calculate dilations?
The simple formula of C1V1 = C2V2 is a lifesaver for those who are wanting to do dilutions.
- C1 is the concentration of the starting solution.
- V1 is the volume of the starting solution.
- C2 is the concentration of the final solution.
- V2 is the volume of the final solution.
What is the formula for dilation?
Formula for Time Dilation. The time dilation formula is given by, T =T 0 /√1−(v 2 /c 2) where, T is the time observed. T 0 is the time observed at rest v is the velocity of the object. c is the velocity of light in a vacuum (3 × 10 8 m/s 2) Derivation of Time Dilation
How to plot images of points de and F?
Is it easier to divide a square by two?
Can you add videos to your watch history?
About this website
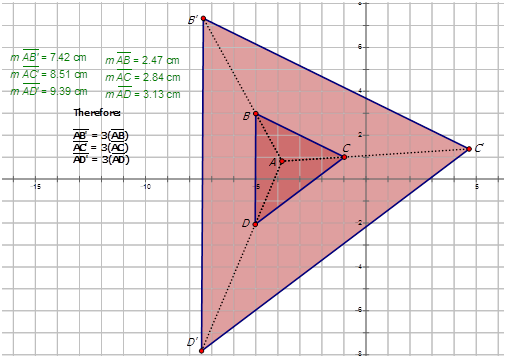
What does it mean to dilate a shape?
Dilation is a process of changing the size of an object or shape by decreasing or increasing its dimensions by some scaling factors.
How do you dilate a shape by 2?
To dilate the figure by a factor of 2, I will multiply the x-value of each point by 2. I plotted all the new points to find the new triangle. To dilate the figure by a factor of 2, I will multiply the x and y-value of each point by 2.
How do you dilate a shape by 1 2?
0:412:38Transformation: Dilation to a factor of 1/2 - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipNow we have to dilate to a factor of 1/2. So. We are basically multiplying each x and y by 1/2 orMoreNow we have to dilate to a factor of 1/2. So. We are basically multiplying each x and y by 1/2 or dividing by 2 so 1/2 times 2 or 1/2 of 2 is 1.
How do you dilate a shape from the origin?
Dilations centered at the origin If you are dilating a figure centered at the origin, you can multiply the coordinates of the points in the preimage by the scale factor to determine the points in the image.
What's the rule for dilation?
A dilation is a type of transformation that enlarges or reduces a figure (called the preimage) to create a new figure (called the image)....Rules for Dilations.Scale Factor,Size change for preimage0 < k < 1Dilation image is smaller than preimagek = 1Dilation image is the same size as the preimage1 more row•Jul 26, 2022
How do you dilate a shape by 1 4?
0:042:26vid 1.4.3 dilate triangle by 1/4 - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd if you're multiplying by 1/4. You're really dividing by 4 that's what the fraction means thatMoreAnd if you're multiplying by 1/4. You're really dividing by 4 that's what the fraction means that means that's the device sign so you're dividing it by 4.
What does 2cm dilated mean?
What happens when I'm 2 cm dilated? As with 1 cm dilated, being 2 cm dilated doesn't mean that labor is imminent. Some women who are 2 cm dilated may go into labor within hours. Others will remain 2 cm dilated for a few days or weeks until labor progresses.
How do you dilate a shape by 2 3?
1:395:47Dilation By A Scale Factor Of 1/2 and 2/3 - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo we're going to take 2/3 of those dimensions. Instead of going 6 to the right we're going to doMoreSo we're going to take 2/3 of those dimensions. Instead of going 6 to the right we're going to do two-thirds of that which is 4 to the right. So 1 2 3 4. And instead of going up 9 2/3 of 9 is 6.
What are the two types of dilation?
A dilation that creates a larger image is called an enlargement. A dilation that creates a smaller image is called a reduction. A dilation stretches or shrinks the original figure.
How do you dilate if you are not at origin?
A dilation with any point other than the origin as the center of dilation can be accomplished by first translating the center of dilation and figure so the origin becomes the center, and then translating back: Example 7: Find a coordinate rule for the dilation with center (5, –3) and scale factor 2.
How do you dilate a circle by 2?
Dilation To dilate a circle, we start with our standard equation: x2+y2=r2 To dilate the circle we multiply our desired factor squared into the right side of the equation. For example, two multiply the diameter of the circle by two, our equation would now be x2+y2=22(r2).
What is a scale factor of 2?
The scale factor of 2 means the new shape obtained after scaling the original shape is twice of the shape of the original shape.
How do you draw a dilation with a scale factor of 2?
0:131:35Drawing Dilations - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo for example draw dilation ABC using a scale factor of two and the origin as the center dilation.MoreSo for example draw dilation ABC using a scale factor of two and the origin as the center dilation. So to do this start with your center dilation. In this case the origin. So that's right here.
How do you dilate a triangle by 2 with a compass?
0:123:07Constructing a Dilation 128-3.12 - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThen I'm going to take my compass. And set it so it's the same distance. As line segment PA. AndMoreThen I'm going to take my compass. And set it so it's the same distance. As line segment PA. And with a point of the compass over to point a and draw an arc along the line.
Dilation Calculator - Find the Center of Dilation
Get the coordinates of the center points of the final transformed image from the original one instantly with this free online dilation calculator.
Dilation Calculator - Conversion Calculator
Dilation Calculator - How to calculate a scale factor dilation? First, determine the change in X and Y of the original image.
Dilation calculator geometry - Emaths.net
Emaths.net offers both interesting and useful answers on dilation calculator geometry, radical expressions and synthetic division and other math topics. In the event that you need advice on variable as well as algebra ii, Emaths.net is certainly the right site to go to!
Dilation with Center not at Origin | Dilation Worksheets
Try our dilation with center not at origin worksheets with skills like writing the coordinate rule, finding coordinates, drawing dilated shapes and more.
How to plot images of points de and F?
plot the images of points de and F after dilation centered the origin with a scale factor of 1/2 so we're going to center around the origin we want to scale this thing down by 1/2 so one way to think about it is the points that will correspond to points de and F are going to be 1/2 as far away from the origin because of our scale factor is 1/2 in either direction so for example let's let's think about Point D first Point D is at negative 8 so if we scale if we have a scale factor of 1/2 what point D will map to is going to be at negative 4 on the x-direction and on the y-direction D is at negative 9 so this is going to be at negative 4 point 5 half of that so that is going to be right over there that's where point D is going to be or the image of point D after the scaling now let's think about point E e is 2 more than the origin in the X direction so it's only going to be one more once we scale it by 1/2 and it's 7 more in the Y direction so it's going to be at 3 and 1/2 7 times one half is three and 1/2 so we're going to stick it right over there and then finally F it's 6 its x-coordinate is 6 more than the origin and its y-coordinate is 6 less so it's image after scaling is going to be three more in the x-direction and 3 less in the y-direction so it's going to be right over there so we've plotted the images of the point so if you were to connect these points you would essentially have dilated down d EF with the center at with width and your center of dilation would be the origin so let's just write these coordinates point D and point D remember what's the point negative 8 negative 9 that's going to map to well we're going to take half of each of those so negative 4 and negative 4 point 5 point e maps to well II was it's at 2 7 so it maps to 1 3.5 3.5 and then finally Point F was it 6 negative 6 so it maps to 3 it maps to 3 negative 3 so the important thing to recognize is the center of our dilation was the origin so in each dimension in the X direction or in the Y direction we just halved the distance from the origin because the scale factor was 1/2 we got it right
Is it easier to divide a square by two?
It's easier to divide points by two than it is to do a length just like that. When we divide the points, then we also divide the length. For example, let's say we have a square with side length 2 and vertices at (2, 2), (0, 2), (2, 0), and (0, 0). If we shrink this square by 2, we divide each point by 2.
Can you add videos to your watch history?
Videos you watch may be added to the TV's watch history and influence TV recommendations. To avoid this, cancel and sign in to YouTube on your computer.
What is the scale factor of a dilation?
Scale factor: The scale factor is the ratio of the distance from a center of dilation to a point on the dilated image and the distance from a center of dilation to the corresponding point on the original image. The scale factor is also the ratio of the lengths of the corresponding sides of the dilated image and the original image. If scale factor > 1, the dilation is an enlargement where the dilated image is larger than the original image. If scale factor < 1, the dilation is a reduction where the dilated image is smaller than the original image.
What is dilation transformation?
Dilation: A dilation is a transformation that maps point {eq}P {/eq} to point {eq} {P}' {/eq} with scale factor {eq}k {/eq} and center of dilation {eq}O {/eq}. A point {eq} {P}' {/eq} is mapped so that {eq}O, P, {/eq} and {eq} {P}' {/eq} are on the same line, and {eq}frac {overline {O {P}'}} {overline {OP}} = k {/eq}.
What is the horizontal distance from (0, 0) to (4, 4)?
The horizontal distance from (0, 0) to (4, 4) is 4. The vertical distance from (0, 0) to (4, 4) is also 4. Multiplying these distances by the scale factor {eq}frac {1} {4} {/eq} gives us the horizontal distance of 1 and the vertical distance of 1.
What is vertical distance?
Vertical distance: A difference in the {eq}y {/eq}-coordinates of two points.
What degree does Jiwon have?
Jiwon has a B.S. degree in the mathematics/ science field and over 4 years of tutoring experience. She fell in love with math when she discovered geometry proofs and that calculus can help her describe the world around her like never before.
How to Calculate the Scale Factor in Dilation?
The scale factor can be calculated when the original dimension and the changed dimension is given. Let us find the scale factor of a triangle with the original dimensions and scaled up dimensions. As seen above, after dilation, the coordinates of Δ PQR changed as follows:
How to find scale factor?
The basic formula to find the scale factor of a dilated figure is: Scale factor = Dimension of the new shape ÷ Dimension of the original shape.
How to find dimension of new shape?
This formula can be written in another way which helps to find the dimension of the new shape: Dimensions of the original shape × Scale factor = Dimension of the new shape
What is scale factor?
Scale factor is a number by which the size of any geometrical figure or shape can be changed with respect to its original size. It is the ratio of the sizes of the original figure with the dilated figure.
What is dilation in geometry?
Dilation Geometry. Dilation means changing the size of an object without changing its shape. The size of the object may be increased or decreased based on the scale factor. For example, a square of side 5 units can be dilated to a square of side 15 units, but the shape of the square remains the same. 1. Dilation Definition. 2.
What is the process of resizing or transforming an object called?
The process of resizing or transforming an object is called dilation. It is a transformation that makes the objects smaller or larger with the help of the given scale factor. The new figure obtained after dilation is called the image and the original image is called the pre-image. Dilation can be of two types:
How many units are in a dilated square?
Dimensions of the new shape = Dimensions of the original shape × Scale factor. Substituting the values in the formula: The length of the dilated square = 5 × 4 = 20 units. Therefore, the length of each side of the new dilated square will be 20 units.
How to get coordinates of an image?
Multiply the coordinates of the original point (2, 1), called the image, by 3. Image's coordinates = (2 * 3, 1 * 3) to get the coordinates of the image (6, 3). Perform a Dilation of 4 on point A (2, 3) which you can see in the picture below. Multiply the coordinates of the original point (2, 3), called the image, by 4.
Why do we use prime notation?
Like other transformations, prime notation is used to distinguish the image fromthe pre-image. The image always has a prime after the letter such as A'. Example 2. Dilations can also reduce the size of shape. The picture below demonstrations a dilation of 1 2 Any time that the scale factor is a fraction, the image will get smaller.
What is dilation in photography?
What is a Dilation? A dilation is a type of transformation that changes the size of the image. The scale factor, sometimes called the scalar factor, measures how much larger or smaller the image is. Below is a picture of each type of dilation (one that gets larger and one that gest smaller). Example 1.
How to simplify a dilation?
1) Multiply both coordiantes by scale factor. (2 * ½, 4 * ½) 2) Simplify. (1, 2) 3) Graph (if required) see picture below. Problem 4. Perform a Dilation of 1/3 on point A (3, 6) which you can see in the picture below.
Steps for Dilating Points
Step 1: Measure the vertical and horizontal distances from the point to the center of dilation.
Example Problem 1 - Dilating Points
Which graph plots the point A under a dilation about the point B with a scale factor of 2?
Example Problem 2 - Dilating Points
Which graph plots the point A under a dilation about the point B with a scale factor of {eq}\frac {1} {3} {/eq}?
How to plot images of points de and F?
plot the images of points de and F after dilation centered the origin with a scale factor of 1/2 so we're going to center around the origin we want to scale this thing down by 1/2 so one way to think about it is the points that will correspond to points de and F are going to be 1/2 as far away from the origin because of our scale factor is 1/2 in either direction so for example let's let's think about Point D first Point D is at negative 8 so if we scale if we have a scale factor of 1/2 what point D will map to is going to be at negative 4 on the x-direction and on the y-direction D is at negative 9 so this is going to be at negative 4 point 5 half of that so that is going to be right over there that's where point D is going to be or the image of point D after the scaling now let's think about point E e is 2 more than the origin in the X direction so it's only going to be one more once we scale it by 1/2 and it's 7 more in the Y direction so it's going to be at 3 and 1/2 7 times one half is three and 1/2 so we're going to stick it right over there and then finally F it's 6 its x-coordinate is 6 more than the origin and its y-coordinate is 6 less so it's image after scaling is going to be three more in the x-direction and 3 less in the y-direction so it's going to be right over there so we've plotted the images of the point so if you were to connect these points you would essentially have dilated down d EF with the center at with width and your center of dilation would be the origin so let's just write these coordinates point D and point D remember what's the point negative 8 negative 9 that's going to map to well we're going to take half of each of those so negative 4 and negative 4 point 5 point e maps to well II was it's at 2 7 so it maps to 1 3.5 3.5 and then finally Point F was it 6 negative 6 so it maps to 3 it maps to 3 negative 3 so the important thing to recognize is the center of our dilation was the origin so in each dimension in the X direction or in the Y direction we just halved the distance from the origin because the scale factor was 1/2 we got it right
Is it easier to divide a square by two?
It's easier to divide points by two than it is to do a length just like that. When we divide the points, then we also divide the length. For example, let's say we have a square with side length 2 and vertices at (2, 2), (0, 2), (2, 0), and (0, 0). If we shrink this square by 2, we divide each point by 2.
Can you add videos to your watch history?
Videos you watch may be added to the TV's watch history and influence TV recommendations. To avoid this, cancel and sign in to YouTube on your computer.
