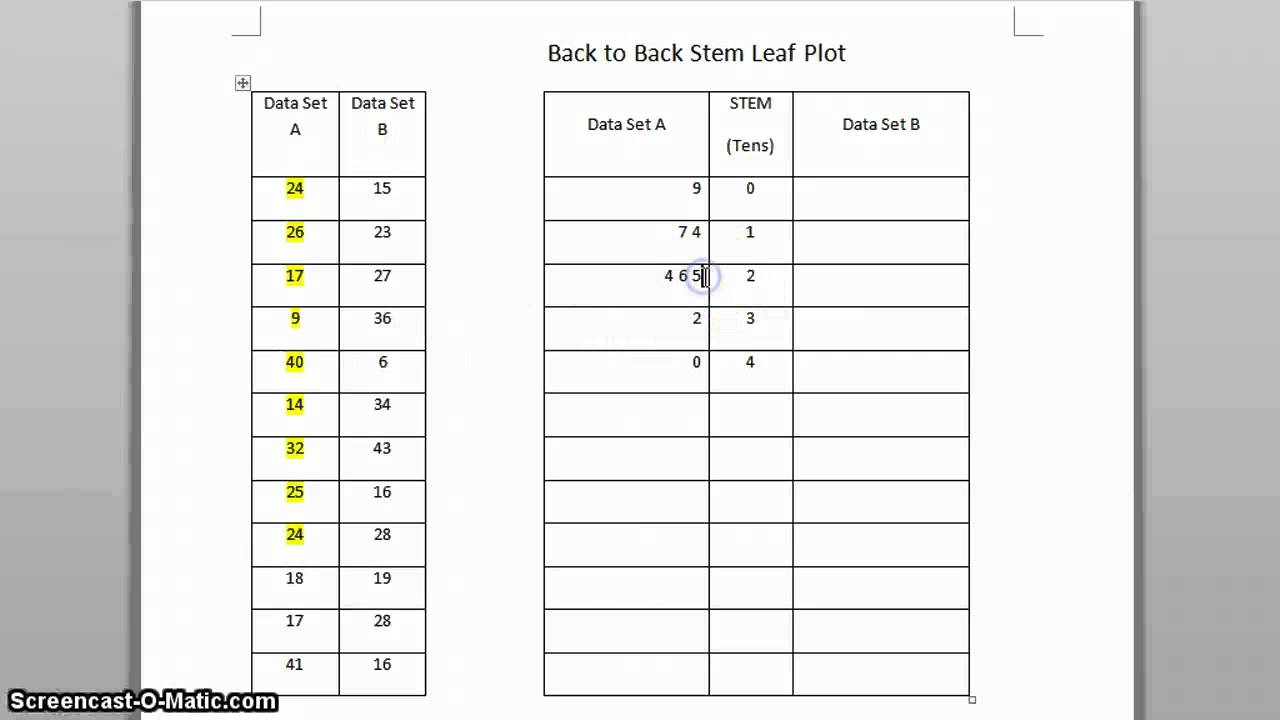
To create a stem and leaf plot:
- Click on QI Macros > Chart Templates > Stem and Leaf Plot to open the template:
- The template will open and contains some pre-populated sample data.
- Input or cut and paste your data into the yellow input areas:
- Double click on the Update Plot button and QI Macros will perform the analysis and create the two-sided plot:
How do you write a back to back stem-and-leaf plot?
In a back-to-back stem-and-leaf plot, one set of data is displayed on the left and one set of data is written on the right. The "leaf" values are still written in ascending order from the stem outwards. Remember!
How do you make a double sided stem-and-leaf plot?
2:395:02Two Sided Stem and Leaf Plots: Lesson (Basic Probability and ...YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipFirst we can do the scores in the 80s. There was 84 88 82 and 86. So if we put those in order theMoreFirst we can do the scores in the 80s. There was 84 88 82 and 86. So if we put those in order the smallest was 82. And then 84 6 and 8 next we can do the scores that were in the 90s.
How do you read a back to back Stemplot?
3:405:32Maths Tutorial: Back to Back Stem Plots (statistics) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipOne from the bottom one from the top one from the bottom one from the top this is the next highestMoreOne from the bottom one from the top one from the bottom one from the top this is the next highest number on from the bottom one from the top.
How do you make a double stem-and-leaf plot in Statcrunch?
0:001:322. Create a Stem and Leaf Plot/Stemplot in StatCrunchYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo you type in all the numbers into statcrunch and you go to graph stem-and-leaf it's also called aMoreSo you type in all the numbers into statcrunch and you go to graph stem-and-leaf it's also called a stem plot. Then you left-click.
What is a split stem-and-leaf plot?
A Split Stem and Leaf Plot takes an ordinary stem and leaf plot and “splits” the stem section into two entries. This way, instead of having many numbers in one leaf section, it is split into two separate categories.
How do you find the median in back to back stem-and-leaf?
0:191:30Find Median From Back-To-Back Stem and Leaf Diagram (Grade 3 ...YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo cross one out from both sides. Then cross another and then if you're left with two in the middle.MoreSo cross one out from both sides. Then cross another and then if you're left with two in the middle. You add them together. And divide by two or just find the halfway value.
Why do we use back to back stem-and-leaf plots?
A back to back stem-and-leaf plot is useful because it allows us to easily visualize the distribution of values in two datasets at the same time and quickly compare two distributions.
What is the most important thing to remember when making a Stemplot?
From the stem plot it should be easy to describe the distribution of the data. You should be able to identify the range, the median, the quartiles, as well as any potential outliers. Finally, the stem plot should also give you an idea of the shape of the distribution of the data.
How do you make a stem and leaf chart?
To make a stem and leaf plot, each observed value must first be separated into its two parts:The stem is the first digit or digits;The leaf is the final digit of a value;Each stem can consist of any number of digits; but.Each leaf can have only a single digit.
How do you create a stem-and-leaf plot in Word?
Click into the first cell in the table and type “Stem” or your preferred header for that column. Press the “Tab” key to move you into the next cell, the second header. Type “Leaf” or “Leaves” or your preferred header. If you created a table with additional columns, type those headers.
How do you make a stem-and-leaf plot with triple digits?
We call this the leaf. On the left side are the rest of the digits. This part is called the stem. When creating a three-digit stem-and-leaf plot, there will be one digit, or number, on the right (the leaf) and two on the left (the stem) for each number.
How do you make a stem-and-leaf plot on the computer?
Use the following steps to create a stem-and-leaf plot in Excel.Step 1: Enter the data. ... Step 2: Identify the minimum and maximum values.Step 3: Manually enter the “stems” based on the minimum and maximum values.Step 4: Calculate the “leaves” for the first row. ... Step 5: Repeat the calculation for each row.
How does a back to back stem and leaf plot work?
Back to back stem-and-leaf plots allow for easy comparison of two sets of like data. By breaking your data into 'stems' and 'leaves,' you can easily find the mode (i.e. the most frequently occurring number in a data set) and median (i.e. the middle number of a data set), as well as other information regarding the distribution of numbers.
Why are stem and leaf plots useful?
Stem-and-leaf plots are an effective way to present data , allowing us to see at a glance the distribution of numbers. They allow us to quickly tell if there are a lot of high or low numbers, and make it easier to find measures like the mode, which is the most common number in a data set, and the median, which is the middle number in a data set.
What are the digits in a stem and leaf plot?
As you recall, in a 2-digit stem-and-leaf plot, the digits in the tens place are the stems and the digits in the ones place are the leaves. If a number is only 1 digit, a 0 is the stem. Now, let's construct a back to back stem-and-leaf plot from this set of data:
How to find the mode of a plot?
Finding the mode is a two-step process. First , for each set of points, find the number that occurs the most in the leaf part of the plot. For Seattle, we can immediately see that the number that occurs the most is 4. The second step is to look at the stem that goes with that leaf. For Seattle, the stem is 0, so 4 is the mode.
What is different about a Back to Back Stem and Leaf Plot?
You do not have to have the same number of data points on each side of the plot.
How does a back to back plot work?
How Does a Back to Back Stem and Leaf Plot Work? On a normal plot, the stem is on the left and all the leaves are on the right. There is a vertical line separating the two. On a back to back plot, the stem remains the same. But to add another set of data points, we begin adding leaves to the LEFT side.
What is a stem and leaf plot?
So you know that Stem and Leaf Plots are great at taking a big list of numbers and organizing them in an easy to read fashion. You might even know about how if there are lots of data points you can use a Split Stem and Leaf Plot to separate the data even further, giving you a more readable plot.
Why does one side of a plot look odd?
If one side of the plot has many more data points than the other, it will look odd. The purpose of the plot is to organize the data. The second point is that the key must work for both sides of the plot. DO NOT mix units or try to save space by combining plots when they do not measure different things.
What is the purpose of the stem?
The stem now serves a double purpose. It anchors both sets of data points, keeping them separate but it still organizes both.
Why do you avoid back to back plots?
Some times a back to back plot is avoided because the stems are not identical. Don’t abandon a back to back plot because of this. You can add stems to accommodate more data. But, as in the first point, do not go overboard with this.
Can you split stems?
You can still split the stems if you need to!
When Should I Use a Back-to-Back Stem and Leaf Plot?
Use a back-to-back or double sided stem and leaf plot when you want to compare the spread and distribution of two data sets. You can also use side by side histograms for the same purpose or lay the plots on their sides for a different view:
What is a stem and leaf plot?
A stem and leaf plot shows the spread and distribution of a data set.
What is a back to back plot?
A back-to-back stem and leaf plot shows two data sets. The data sets share the same stem and have their own set of leaves.
Why do you include a stem with no leaves on the plot?
If you have a stem with no leaves, include it on the plot anyway to preserve the horizontal axis scaling and highlight the lack of values. That can be important when looking for outliers.
Why are stem and leaf plots better than histograms?
Stem and leaf plots have one advantage over histograms because they display the original data, while histograms only summarize them.
What is a stemplot?
Stem and leaf plots display the shape and spread of a continuous data distribution. These graphs are similar to histograms, but instead of using bars, they show digits. It’s a particularly valuable tool during exploratory data analysis. They can help you identify the central tendency, variability, skewness of your distribution, and outliers. Stem and leaf plots are also known as stemplots.
How many observations are there in a stem?
For example, the stem = 2 row with the leaf values of 4 and 5 has a count of 39. This number indicates there are 39 observations in this row and lower (towards the left tail). On the higher side of the median, the stem = 2 row with values of 8 and 9 has a count of 43. This count indicates there are 43 observations in that row and higher (towards the right tail).
What is the stem value of a leaf?
Because the leaf unit is 1, we know the stem values must start in the 10s place. Therefore, the stem values of 1, 2, 3, and 4 correspond to 10, 20, 30, and 40. Using this information, you can determine the value of every data point on this graph!
What is leaf unit?
The leaf unit or key allows us to interpret the value of each leaf. This stem and leaf plot uses a leaf unit, but others have a key, which provides similar information.
What is the first column of a distribution?
The first column contains cumulative counts. The format of these counts might not be intuitive at first. For each row, the counts sum that row and all rows further away from the median out to the distribution’s tail.
