How do you do a ray amputation? The technique of central ray amputation involves the use of a circumferential incision at the midproximal phalanx in conjunction with a dorsal longitudinal incision. The dorsal incision is extended through the extensor.
How do you do a ray amputation foot?
Procedure OutlineIntroduction and Surgical Approach.Incision.Dissect Tissue off Metatarsal Head.Continue Dissection to Amputate Toe.Continue Dissection to Create Skin Flaps Along Periosteum.Remove Metatarsal Head.Closure.
When is Ray amputation done?
In situations where we are removing digits such as fingers, hand surgeons perform an operation called 'ray amputations'. In a finger example, ray amputations are the removal of an entire finger along with the corresponding metacarpal bones in the hand.
What is complete ray amputation?
Ray amputation, which involves the excision of the toe and part of the metatarsal, provides a more viable option of ensuring an adequate surgical debridement of the septic margins.
Why is Ray amputation done?
Ray resection of the finger is performed to reduce pain and improve function by removing the finger using metacarpal resection.
What is a first ray amputation?
Partial first-ray resections are used to help salvage the foot and maintain bipedal ambulation. Losing the first metatarsophalangeal joint has biomechanical consequences that lead to further foot deformities and result in more proximal amputations of the ipsilateral limb, such as a transmetatarsal amputation.
What are the 3 types of amputations?
Above-knee amputation, removing part of the thigh, knee, shin, foot and toes. Below-knee amputation, removing the lower leg, foot and toes. Arm amputation. Hand amputation.
What is a 2nd ray amputation?
Second ray amputation surgical technique With a skin marker, a dorsal longitudinal incision following the shaft of the second metatarsal and then curving around the base of the 2nd toe at the level of the metatarsophalangeal joint (racquet-type incision) was planned (Figure 3A).
What is a 5th ray amputation?
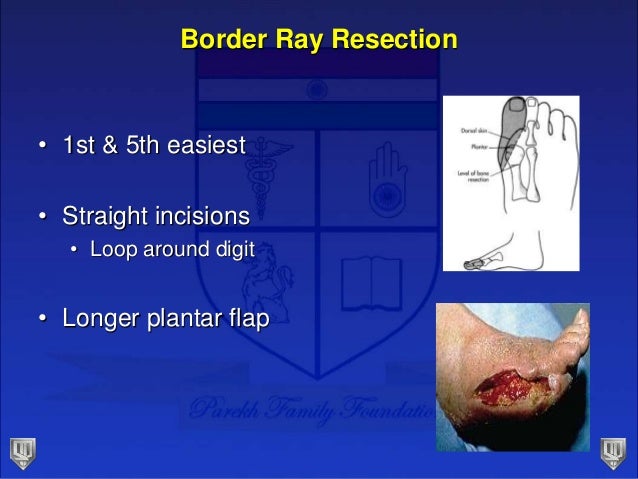
Bone resection for partial fifth toe amputation. ( a, b) Toe amputation was performed through the base of the proximal phalanx. Ray amputation is typically at the neck of the fifth metatarsal although partial or complete fifth toe amputation is an option under special circumstances including gangrene.
What is a ray in podiatry?
segment of a closely packed medi- al longitudinal arch whose proper. function is critical in allowing the. chief load-bearing segment of the. human foot to accept body weight.
Can bone grow back after amputation?
Complete bone regeneration occurred frequently by five weeks following amputation through the distal one-quarter of the distal phalanx. Amputation through the central region of the distal phalanx yielded substantial bone growth, but the form of the regrowth was imperfect even three months after amputation.
Why do amputees have a shorter lifespan?
How Does Traumatic Amputation Affect Life Expectancy? Post-traumatic lower limb amputees have an increased morbidity and mortality from cardiovascular disease. Psychological stress, insulin resistance, and behaviors such as smoking, alcohol use, and physical inactivity are prevalent in traumatic lower limb amputees.
What happens to the bone after amputation?
Conclusions: Rapid and substantial losses in bone content and strength occur early after amputation and are not regained by 12 months of becoming ambulatory. Early post-amputation may be the most critical window for preventing bone loss.
What is a 5th ray amputation?
Bone resection for partial fifth toe amputation. ( a, b) Toe amputation was performed through the base of the proximal phalanx. Ray amputation is typically at the neck of the fifth metatarsal although partial or complete fifth toe amputation is an option under special circumstances including gangrene.
What is a second ray amputation of the foot?
Second ray amputation surgical technique With a skin marker, a dorsal longitudinal incision following the shaft of the second metatarsal and then curving around the base of the 2nd toe at the level of the metatarsophalangeal joint (racquet-type incision) was planned (Figure 3A).
Do they amputate for arthritis?
Believe it or not, many patients prefer amputation to the intense pain and suffering they've had with the arthritis. With a prosthetic device, they can walk again pain free.
How long after your leg is amputation before prosthetic?
If the prosthesis is a traditional one that uses suction to attach to your remaining limb, you will likely receive it after your amputation site has healed, which usually takes about six weeks. If the site heals well and there are no complications, you can begin to use your prosthetic.
What is the difference between a Boyd amputation and a calcaneus amputation?
The Boyd amputation preserves the calcaneus, and the calcaneus is fused to the tibia. This relieves the problem of migration of the heel pad because the heel pad remains firmly attached to the calcaneus. Both malleoli are preserved.
What is the term for amputation of the foot at the ankle?
Pirogoff – Amputation of the foot at the ankle wherein the anterior two thirds of the calcaneus is removed, and the posterior process of the calcaneum is retained at the skin flap and opposed to the cut end of the tibia. Both malleoli are preserved.
Which type of amputation provides a broad weight-bearing surface of the heel?
Types of amputations are: Boyd – Similar to Syme amputation (below), but provides a broad weight-bearing surface of the heel by creating an arthrodesis between the distal tibia and the tuber of the calcaneus. This provides more length and better preserves the weight-bearing function of the heel pad than the Syme.
How is a wound closed?
The wound is closed by placing the skin flap over the stump and suturing the skin. Although the skin flap technique is similar to the one used in the Syme amputation of the ankle, do not confuse these two very distinct procedures. Transmetatarsal – Amputation of all toes at the metatarsals.
How to help an amputated limb?
Recover the amputated part if possible. Remove dirt or debris from the amputated part and residual limb, which is the part of the body that remains after an amputation. Provide pain management and psychological support, and transport to the appropriate trauma center.
How to treat a detached amputated part?
If the part is completely detached, control the bleeding after cleansing the site by covering the wound with a pressure dressing. Wrap the amputated part in sterile saline soaked gauze and place it in a watertight container or resealable plastic bag. Place the protected part in an iced saline container. Do not allow the damaged part to come in direct contact with ice. Transport the amputated part with the patient.
Why are military victims more likely to experience multiple amputations and junctional bleeding than civilians?
Military victims are more likely to experience multiple amputations and junctional bleeding than civilians due to the difference in trauma mechanisms. Junctional bleeding occurs between the trunk and the limbs (high-level amputations) and between the pelvic area and legs.
What percentage of traumatic amputations are of the wrist?
The loss of one arm is the second most common traumatic amputation. Only about 10 percent of traumatic amputations are of the wrist and hand. [2]
How to preserve amputated body parts?
If the finger or limb is still attached to the body, clean the wound surface with sterile saline. Gently place the damaged skin back to its normal position.
What is traumatic amputation?
Traumatic amputations are a common combat injury. Soldiers report traumatic amputations as among the most emotionally disturbing forms of injury. Fortunately, the survival rate associated with these severe injuries is unprecedented, due to improvements in immediate treatment and stabilization. Advances in the military arena are paving ...
Which is easier to reattach: a crush or a sharp amputation?
A sharp or guillotine amputation has well-defined edges which minimizes the damage to the associated anatomy. This type of amputated body part is easiest to reattach. A crush amputation has more soft tissue and arterial damage.