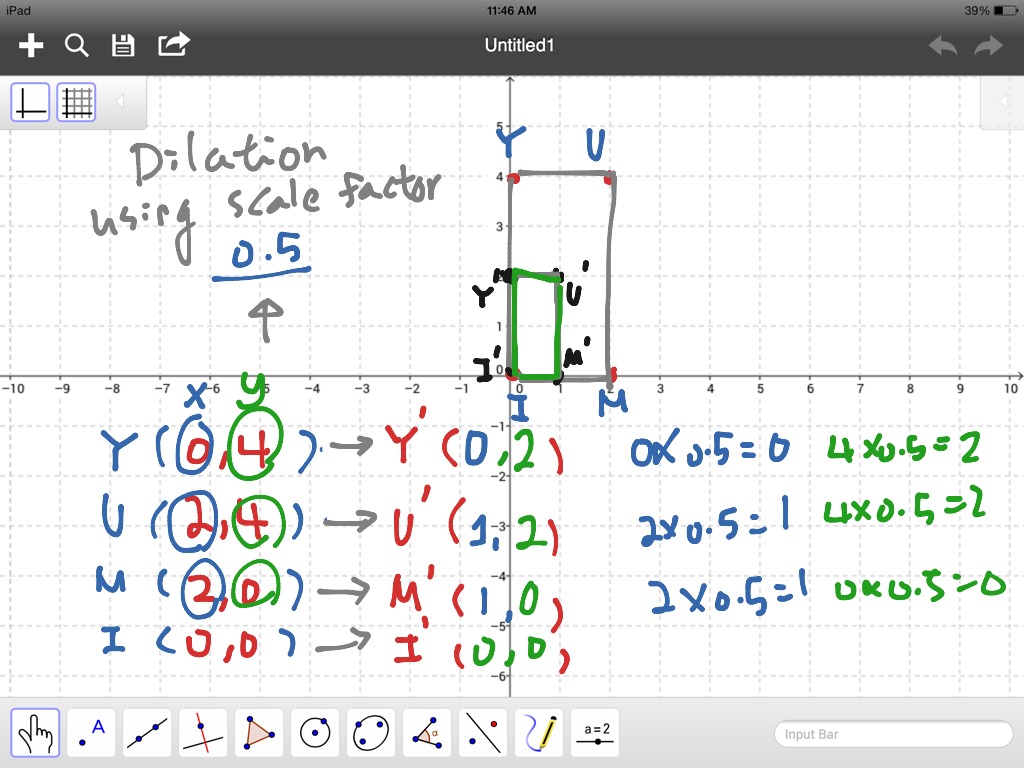
Formula for Dilations
- Multiply both coordiantes by scale factor ( 2 ⋅ 1 2, 4 ⋅ 1 2)
- Simplify (1, 2)
- Graph (if required)
How to "make" a dilation?
Walk to release oxytocin and stimulate labor. Being active may release oxytocin, which may help you dilate faster by starting contractions. Go for a slow walk around your neighborhood, or climb the stairs in your home. Ask someone to go with you so that you’re not alone in case you need help.
How do you calculate the scale factor of a dilation?
- The definition of scale factor is that it is a number that multiplies times a given quantity to produce a smaller or larger version of the original number. ...
- You calculate the scale factor of similar figures by taking the ratio of corresponding parts of the two figures. ...
- A scale factor gives the ratio of the representation to the actual object.
What is the formula for dilation?
Formula for Time Dilation. The time dilation formula is given by, T =T 0 /√1−(v 2 /c 2) where, T is the time observed. T 0 is the time observed at rest v is the velocity of the object. c is the velocity of light in a vacuum (3 × 10 8 m/s 2) Derivation of Time Dilation
How to find the scale factor of a dilation?
- Take the x-coordinate of P' = 3 and the x-coordinate of P = 1.
- Substitute the values in the formula: 3 ÷ 1 = 3.
- Now, take the y-coordinate of P' = 9 and the y-coordinate of P = 3.
- Apply the same formula: 9 ÷ 3 = 3. Thus, we get the scale factor of 3 from both the coordinates.

How do you calculate dilation?
The basic formula to find the scale factor of a dilated figure is: Scale factor = Dimension of the new shape ÷ Dimension of the original shape.
What is an example of dilation in math?
Dilation Examples If the scale factor is 2, then every coordinate point of the original triangle is multiplied by the scale factor 2. Therefore, the dilated triangle will be A'B'C' and the coordinate points obtained are A'(0, 4), B'(4, 2), C'(-4, -4). Dilation with scale factor 2, then multiply by 2.
How do you dilate 2?
To dilate the figure by a factor of 2, I will multiply the x and y-value of each point by 2. I plotted all the new points to find the new triangle. To dilate the figure by a factor of 2, I will multiply the x and y-value of each point by 2.
How do you dilate a figure by 2 3?
1:395:47Dilation By A Scale Factor Of 1/2 and 2/3 - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipInstead of going 6 to the right we're going to do two-thirds of that which is 4 to the right. So 1 2MoreInstead of going 6 to the right we're going to do two-thirds of that which is 4 to the right. So 1 2 3 4. And instead of going up 9 2/3 of 9 is 6.
How do you dilate a figure by 1 2?
0:412:38Transformation: Dilation to a factor of 1/2 - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWe are basically multiplying each x and y by 1/2 or dividing by 2 so 1/2 times 2 or 1/2 of 2 is 1.MoreWe are basically multiplying each x and y by 1/2 or dividing by 2 so 1/2 times 2 or 1/2 of 2 is 1. So the x-coordinate for a prime is 1 and 1/2 of 10 is 5.
How do you dilate a figure by 1 3?
You must observe the distances from the center of the dilation at point A to the other points B, C and D. The dilation image will be 1/3 of each of these distances. AB = 6, so A'B' = 2. AD = 9, so A'D' = 3....PhotographyArts and CraftsGraphing CalculatorFood ServiceLogosGrow Toys2 more rows
How do you tell if a transformation is a dilation?
A dilation (similarity transformation) is a transformation that changes the size of a figure. It requires a center point and a scale factor , k . The value of k determines whether the dilation is an enlargement or a reduction. If |k|>1 , the dilation is an enlargement.
What is a dilation simple definition?
A dilation is a proportional change in the size of a shape. The length of each side in the shape is multiplied by the same number, but the shape...
What are dilation in math examples?
A dilation in math occurs when the size of a geometric shape in changed in a proportional manner. If the size of the shape is increased, the dila...
How do you dilate by a scale factor of 2?
To dilate by a scale factor of 2, multiply the length of each side of the shape by 2. If the shape is on a coordinate plane, multiply the coordinat...
How do you find a dilation in math?
A dilation is a proportional increase or decrease in the size of a geometric shape. To find the dilation, divide the length of the sides in the pos...
What is dilation in geometry?
Dilation is a process of changing the size of an object or shape by decreasing or increasing its dimensions by some scaling factors. For example, a circle with radius 10 unit is reduced to a circle of radius 5 unit. The application of this method is used in photography, arts and crafts, to create logos, etc. In Geometry, there are four basic types of transformations. They are:
What is the only change in the dilation process?
The only change in the dilation process is that the distance between the points changes. It means that the length of the sides of the original image and the dilated image may vary. There are two types of dilation processes.
What is dilation in photography?
Dilation is used to make the objects larger or smaller. This transformation produces an image that is the same as the original shape. But there is a difference in the size of the shape. A dilation should either stretch or shrink the original shape. This transformation is expressed by the term “ scale factor .”.
What is the scale factor of a dilation?
Scale Factor is defined as the ratio of the size of the new image to the size of the old image. The center of dilation is a fixed point in the plane. Based on the scale factor and the center of dilation, the dilation transformation is defined.
What are the coordinate points of a dilated triangle?
Therefore, the dilated triangle will be A’B’C’D’ and the coordinate points obtained are A’ (-1, 2), B’ (2, 2), C’ (1, -1), D’ (-2, -1)
What are the features of shapes that remain unchanged during the dilation transformations?
Some features of shapes that remain unchanged during the dilation transformations are: Parallel and perpendicular lines in the figure remain the same as the parallel and perpendicular lines of the dilated figure. The only change in the dilation process is that the distance between the points changes.
What is it called when a dilation creates a larger image?
If a dilation creates a larger image, then it is known as enlargement.
What is dilation in math?
In mathematics, dilation is a type of transformation in which the size of a shape or geometric figure is changed, but the relative proportions and shape remain the same. Below are several examples.
Why are the quadrilaterals and cubes dilated?
The quadrilateral and cube above are dilated to produce smaller versions of the respective shapes. The model airplane to the right is dilated to one-thousandth the size of the real plane.
What is the dilated factor of ABC?
Triangle ABC is dilated by a factor of 2 to produce triangle DEF. The coordinates of the vertices of triangle ABC are A (-2, -3), B (-3, 2), and C (3, -1). Dilating triangle ABC by a factor of 2 results in triangle DEF with vertices D (-4, -6), E (-6, 4) and F (6, -2).
How to find scale factor?
The scale factor can be determined by taking the ratio of the distance between a point on the image and the center of dilation to the distance between a corresponding point on the preimage and the center of dilation.
What happens to the preimage when the scale factor is between 0 and 1?
If the scale factor is between 0 and 1, the preimage decreases in size.
What happens when the scale factor is greater than 1?
Scale factor greater than 1. If the scale factor is greater than 1, the preimage increases in size. Triangle ABC is dilated with respect to point O by a scale factor of to produce triangle GHI. The length of each side of the preimage is multiplied by to produce each corresponding side of the image.
What is the center of dilation?
Center of Dilation. All dilations begin with a center. This can be a single point on a coordinate grid, the middle of a polygon, or any fixed point in space. From that center of dilation, the preimage – the mathematical element before scaling – is enlarged, inverted, or shrunk to form the image.
How to check if a dilation is a preimage?
You can check this by drawing a line from the center of dilation through the preimage point. The dilation (image) must lie on that line, which it does.
How to calculate scale factor?
The scale factor of a dilation is the amount by which all original terms are enlarged or shrunk, usually on a coordinate plane. If you multiply the original coordinates: 1 By whole numbers other than 1 1, you enlarge the preimage in producing the image. 2 By 1 1, you produce an image congruent to the preimage. 3 By fractions or decimals, you shrink the preimage to produce the image. 4 By negative numbers, you will produce an image that is the inverse (upside down) of the preimage, equidistant from the center of dilation but on the opposite side.
How far is the plotted point from the center of dilation?
The plotted point of our preimage is 3 3 horizontal units away from the center of dilation. It is 2 2 vertical units away. Multiplying these distances times the scale factor, 4 4, means our new point must be 12 12 horizontal (x-axis) units from the center of dilation, and 8 8 vertical (y-axis) units from the same center of dilation, at (13, 11) ( 13, 11).
When you do not have coordinates for the points of a figure on a coordinate grid, do you calculate?
When you do not have coordinates for the points of a figure on a coordinate grid, you must calculate each line segment of the figure and multiply it times the absolute value of the scale factor:
Does the center of a dilation need to be inside the shape?
The center of the dilation does not need to be inside the shape. It could be one vertex of the polygon. Here we still have a square as the preimage, but the center of thedilation is the top-left vertex, so the dilated images (one smaller, one larger) all share that same vertex.
Is a preimage the same as a new dilation?
The image or enlargement has sides twice the length of the original preimage trapezoid. The new dilation is also the same shape as the preimage. The two polygons are similar:
What is dilation in geometry?
Dilation Geometry Definition: A dilation is a proportional stretch or shrink of an image on the coordinate plane based on a scale factor. Stretch = Image Grows Larger. Shrink = Image Grows Smaller. Note that a geometry dilation does not result in a change or orientation or shape!
What scale factor is used to dilate a triangle?
In this example, you have to dilate ▵OMG by a scale factor of 2 to create a new triangle: ▵O’M’G’.
What happens if the image is K=1/2?
If K=1/2, the image shrinks to half of its original size.
What happens when the scale factor is less than 1?
And when K<1 (the dilation scale factor K is a number less than 1), the image will shrink. Note that the scale factor cannot be less than or equal to zero (this would completing eliminate the figure).
How to find scale factor of dilation?
To find the scale factor for a dilation, we find the center point of dilation and measure the distance from this center point to a point on the preimage and also the distance from the center point to a point on the image. The ratio of these distances gives us the scale factor, as Math Bits Notebook accurately states.
What is dilation scale factor?
Using dilation scale factors, we can shrink or expand a figure to the size we desire, knowing that each angle is congruent, each segment is proportional, the slope of each segment is maintained, and the perimeter of the preimage and image have the same scale factor.
What does it mean when your eye is dilate?
At eye exams, the pupil dilates (widens), allowing in more light and giving your doctor a better view of the back of your eye. When you build model airplanes, cars, or buildings that are true in scale and measurement, you are performing a dilation. And even your shadow is a dilation as well.
What is the difference between a reduction and an enlargement?
A reduction (think shrinking) is a dilation that creates a smaller image, and an enlargement (think stretch) is a dilation that creates a larger image. If the scale factor is between 0 and 1 the image is a reduction. If the scale factor is greater than 1, the image is an enlargement.
Is shadow a dilation?
And even your shadow is a dilation as well.