When solving a Hess’s law problem, remember your objective is to manipulate the reference equations such that when you add them up, the target equation is obtained. Follow these two rules when changing the reference equations: If the equation is multiplied by any factor, the ΔH must be multiplied by the same factor.
What does Hess's law make it possible for you to do?
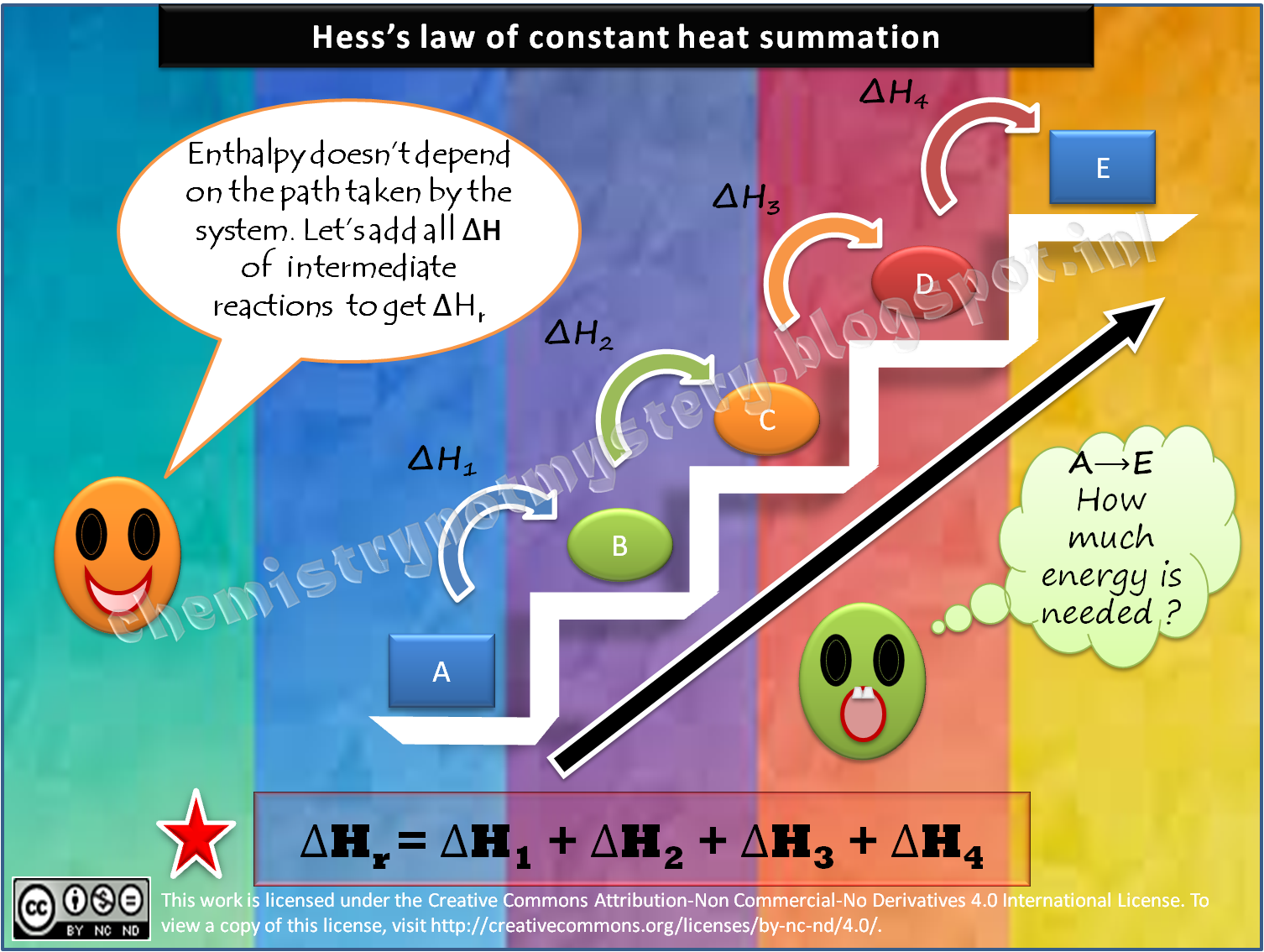
Hess's law is due to enthalpy being a state function, which allows us to calculate the overall change in enthalpy by simply summing up the changes for each step of the way, until product is formed. All steps have to proceed at the same temperature and the equations for the individual steps must balance out.
How is Hess's law used in real life?
Applications of Hess's Law:
- Thermochemical equations can be added subtracted or multiplied like ordinary algebraic equations.
- Hess's law is useful to calculate heats of many reactions which do not take place directly.
- It is useful to find out heats of extremely slow reaction.
- It is useful to find out the heat of formation, neutralization, etc.
How do you explain Hess's law?
Facts About Hess's Law
- Hess's Law takes its name from Russian chemist and physician Germain Hess. ...
- To apply Hess's Law, all of the component steps of a chemical reaction need to occur at the same temperature.
- Hess's Law may be used to calculate entropy and Gibb's energy in addition to enthalpy.
What are some real life Hess law applications?
Why It Matters
- What will we do when the oil runs out? ...
- How do we get the energy in a given molecule from its original source to the final product ready for the gas tank? ...
- Oil from algae is looking very feasible. ...
- Many plants can be made into ethanol. ...
How do you solve a Hess law problem?
0:0711:22Hess's Law - Chemistry Tutorial - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipLaw Hess's law states that the enthalpy change associated with a reaction carried out in multipleMoreLaw Hess's law states that the enthalpy change associated with a reaction carried out in multiple steps is equal to the sum of the enthalpy.
How do you calculate Hess's law?
Hess's Law, also known as "Hess's Law of Constant Heat Summation," states that the total enthalpy of a chemical reaction is the sum of the enthalpy changes for the steps of the reaction. Therefore, you can find enthalpy change by breaking a reaction into component steps that have known enthalpy values.
What is an example of Hess's law?
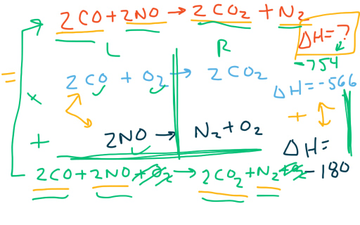
Example #8: The standard enthalpy change of formation of propane is impossible to measure directly. That is because carbon and hydrogen will not directly react to make propane....Hess' Law of Constant Heat Summation. Using three equations and their enthalpies.C3H8(g)ΔH1 = −2219.9 kJH2(g)ΔH3 = −285.8 kJ1 more row
What is Hess's Law for Dummies?
Hess's law states that the energy change in an overall chemical reaction is equal to the sum of the energy changes in the individual reactions comprising it.
How do you calculate heat of formation using Hess's law?
3:134:26Hess' Law: Enthalpies of Formation - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIt's one mole for each of them if we had formation equations in which we had two moles or if we hadMoreIt's one mole for each of them if we had formation equations in which we had two moles or if we had to manipulate it to form two or three moles for our target equation. Then we would have to multiply.
How is Hess law applied in calculating enthalpy?
Hess's law is due to enthalpy being a state function, which allows us to calculate the overall change in enthalpy by simply summing up the changes for each step of the way, until product is formed. All steps have to proceed at the same temperature and the equations for the individual steps must balance out.
How do you calculate the enthalpy of a reaction?
Use the formula ∆H = m x s x ∆T to solve. Once you have m, the mass of your reactants, s, the specific heat of your product, and ∆T, the temperature change from your reaction, you are prepared to find the enthalpy of reaction. Simply plug your values into the formula ∆H = m x s x ∆T and multiply to solve.
How do you draw a Hess law diagram?
4:5511:04How to Draw Energy Cycle for Enthalpy Change of FormationYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWe have formation of tin oxide. So therefore that is bottom here I can have one box to represent theMoreWe have formation of tin oxide. So therefore that is bottom here I can have one box to represent the elements element two tin oxide there will be the formation of tin oxide.
How do you make a Hess law diagram?
0:202:042. Hess Cycles and Enthalpy Level Diagrams (2) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo if Delta H for the red is minus 50 going to change that to plus 50. Keep the minus 90 the sameMoreSo if Delta H for the red is minus 50 going to change that to plus 50. Keep the minus 90 the same which gives an overall change of minus 40 kilojoules per mole.
How do you calculate the enthalpy change of two reactions?
Putting in enthalpy (endothermic) is the reverse, the opposite of exothermic (giving off enthalpy). Hence, we change the sign EVERY time we reverse an equation....Hess' Law of Constant Heat Summation. Using two equations and their enthalpies.2CO(g) + C(s) ---> C3O2(g)ΔH° = +127.3 kJCO(g)ΔH f o = −110.5 kJ
How do I calculate enthalpy?
Use the formula ∆H = m x s x ∆T to solve. Once you have m, the mass of your reactants, s, the specific heat of your product, and ∆T, the temperature change from your reaction, you are prepared to find the enthalpy of reaction. Simply plug your values into the formula ∆H = m x s x ∆T and multiply to solve.
How do you calculate bond enthalpy?
Enthalpy values use the mean bond energy which is an average over different molecules. We can use the mean bond energy to calculate the ΔH of a reaction by using the formula: ΔH = Σ bond energies broken - Σ bond energies made. You can only use bond enthalpies to calculate ∆H when all substances are in the gas phase.
How do I calculate delta H?
Thus, the ΔH of a reaction is calculated by subtracting the sum of the enthalpies of the reactants from the sum of the enthalpies of the products. If ΔH is positive, the reaction is endothermic and absorbs heat from the surroundings.
How do you calculate change in H?
If you want to calculate the enthalpy change from the enthalpy formula:Begin with determining your substance's change in volume. ... Find the change in the internal energy of the substance. ... Measure the pressure of the surroundings. ... Input all of these values to the equation ΔH = ΔQ + p * ΔV to obtain the change in enthalpy:More items...•
What are the rules followed in Hess law?
Hess’s Law of Constant Heat Summation (or just Hess’s Law) states that regardless of the multiple stages or steps of a reaction, the total enthalpy change for the reaction is the sum of all changes. This law is a manifestation that enthalpy is a state function.
Why is Hess's law useful?
Hess’s law is useful to calculate heats of many reactions which do not take place directly. It is useful to find out heats of extremely slow reaction. It is useful to find out the heat of formation, neutralization, etc.
What is Hess’s law explain?
The Hess’ law states that the change of enthalpy in a chemical reaction (i.e. the heat of reaction at constant pressure) is independent of the pathway between the initial and final states. … If enthalpy change is known for each equation, the result will be the enthalpy change for the net equation.
Why is Hess’s law important?
It allows us to combine equations to generate new chemical reactions whose enthalpy changes can be calculated, rather than directly measured.
What is Hess law explain with example?
The Hess’s law states that when reactants are converted to products, the change in enthalpy is the same whether the reaction takes place in one step or in a series of steps. Consider the reaction for the formation of carbon monoxide (CO) from graphite .
Is Hess’s law valid?
If a process written as the sum of several stepwise processes, the enthalpy change of the total process equals the sum of the enthalpy changes of the various steps. Hess’s law is valid because enthalpy is a state function.
How can Hess’s law be used in real life?
The industry, generally, can measure how much energy each process releases when it is performed, so that they can make effective energy choices.
What is Hess law explain with example?
The Hess’s law states that when reactants are converted to products, the change in enthalpy is the same whether the reaction takes place in one step or in a series of steps. Consider the reaction for the formation of carbon monoxide (CO) from graphite .
Why is Hess’s law important?
It allows us to combine equations to generate new chemical reactions whose enthalpy changes can be calculated, rather than directly measured.
What is the most important consequences of Hess’s law?
A consequence of our observation of Hess’s Law is therefore that the net heat evolved or absorbed during a reaction is independent of the path connecting the reactant to product (this statement is again subject to our restriction that all reactions in the alternative path must occur under constant pressure conditions).
What is Hess’s Law?
He introduced the concept known as Hess’s Law of Constant Heat of Summation or Hess’s Law for short.
What are the requirements for Hess's law?
For example, if there are multiple steps to the reactions, each equation must be correctly balanced. Also , all the steps of the reaction must start and end at constant temperatures and pressures in order to keep reaction conditions constant.
What is the law of enthalpy?
Overall, it states that the total enthalpy change of a reaction is the sum of all the changes, no matter the number of steps or stages in the reaction (i.e. net enthalpy and the number of steps in a reaction are independent of each other). The ideas of this law are seen throughout science, such as in the principle of conservation of energy, or the first law of thermodynamics, and the statement that enthalpy is a state function.
How to make sure all the steps given are necessary for the overall reaction?
To make sure all the steps given are necessary for the overall reaction, add the equations and cross off repeated compounds to make a overall equation.
Can we use Hess's law to solve?
Now that we have the official enthalpy values, we can use Hess’s Law equation to solve.
Is the direction of reaction correct?
As for reaction (ii), the direction is correct because O 2 (g) as a reactant and SO 2 (g) as a product are both seen in the desired reaction; however, when adding the equations together, one O 2 (g) and one SO 2 (g) are missing (there is also an extra S (s) that needs to be canceled out). This can be fixed by multiplying reaction (ii) by a factor of 2. If you multiply (or divide) this, you also have to multiply (or divide) the ∆H value by the same coefficient.
