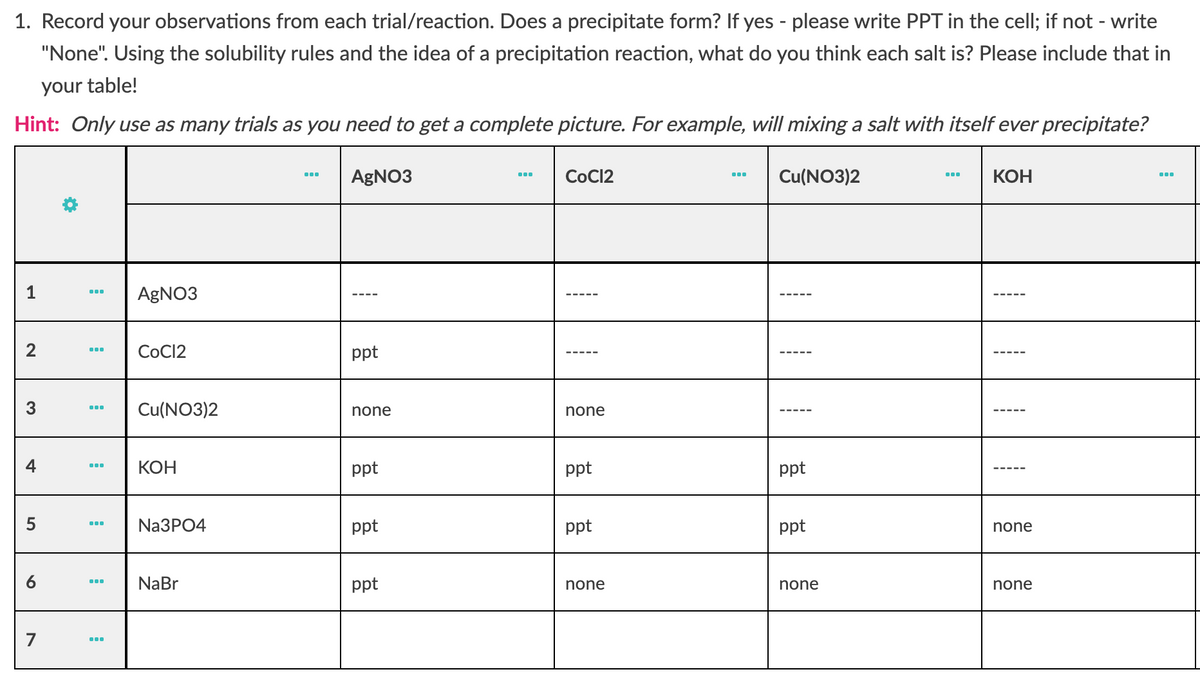
How do you figure out if a precipitate will form?
- Solution:
- Determine the possible products using the general double displacement equation.
- Predict whether either of the possible products is water insoluble.
- Write the complete equation.
How can you tell that a precipitate has formed?
Apr 15, 2020 · If there is a precipitation reaction, write the complete and net ionic equation that describes the reaction. Solution: Step 1: Determine the possible products using the general double displacement equation. Step 2: Predict whether either of the possible products is water insoluble. Step 3: Write the complete equation.
What does the formation of a precipitate indicate?
If the value of the ion product is greater than the value of the K sp, then a precipitate will form. The formation of the precipitate lowers the concentration of each of the ions until the ion product is exactly equal to the K sp , at which point precipitation ceases.
How do you find the composition of a precipitate?
How do you know what a precipitate is?
How is calcium hydroxide related to its counterions?
The of calcium hydroxide is related to the dissolved concentrations of its counterions: and are produced in a molar ratio of 1:2; for each molecule of calcium hydroxide that dissolves: Given a value of , the molar solubilities of each counterion may be determined by setting . It follows that: Now, we can use basic algebra to solve for :
What is the atomic mass of sodium chloride?
Once the solvent (water) evaporates, the solute will remain. Atomic mass of sodium is ~23. Atomic mass of chlorine is ~35.5.
Is double replacement a precipitation reaction?
Explanation: Double replacement reactions can be further categorized as precipitation reactions since it is possible to make a precipitate (solid) from mixing two liquids. Combustion reactions involve using oxygen to burn another species, and the products are carbon dioxide and water.
How to predict precipitate?
The key to predicting a precipitate is to learn the solubility rules. Pay particular attention to compounds listed as "slightly soluble" and remember that temperature affects solubility. For example, a solution of calcium chloride is typically considered soluble in water, yet if the water is cold enough, the salt doesn't readily dissolve. Transition metal compounds may form a precipitate under cold conditions, yet dissolve when it's warmer. Also, consider the presence of other ions in a solution. This can affect solubility in unexpected ways, sometimes causing a precipitate to form when you didn't expect it.
What is the finished reaction?
The finished reaction is: The solubility rules are a useful guideline to predict whether a compound will dissolve or form a precipitate. There are many other factors that can affect solubility, but these rules are a good first step to determine the outcome of aqueous solution reactions.
What is a precipitate in chemistry?
A precipitate will form if the resulting compound is insoluble in water. For example, a silver nitrate solution (AgNO 3) is mixed with a solution of magnesium bromide (MgBr 2 ). The balanced reaction would be:
Is AgBR soluble in water?
According to the solubility rules, all silver salts are insoluble in water with the exception of silver nitrate, silver acetate and silver sulfate. Therefore, AgBr will precipitate out. The other compound Mg (NO 3) 2 will remain in solution because all nitrates, (NO 3) -, are soluble in water. The resulting balanced reaction would be:
When two aqueous solutions of ionic compounds are mixed together, the resulting reaction may produce answer
When two aqueous solutions of ionic compounds are mixed together, the resulting reaction may produce a solid precipitate. This guide will show how to use the solubility rules for inorganic compounds to predict whether or not the product will remain in solution or form a precipitate . Aqueous solutions of ionic compounds are comprised ...
Can transition metals form precipitate?
Transition metal compounds may form a precipitate under cold conditions, yet dissolve when it's warmer. Also, consider the presence of other ions in a solution. This can affect solubility in unexpected ways, sometimes causing a precipitate to form when you didn't expect it.
