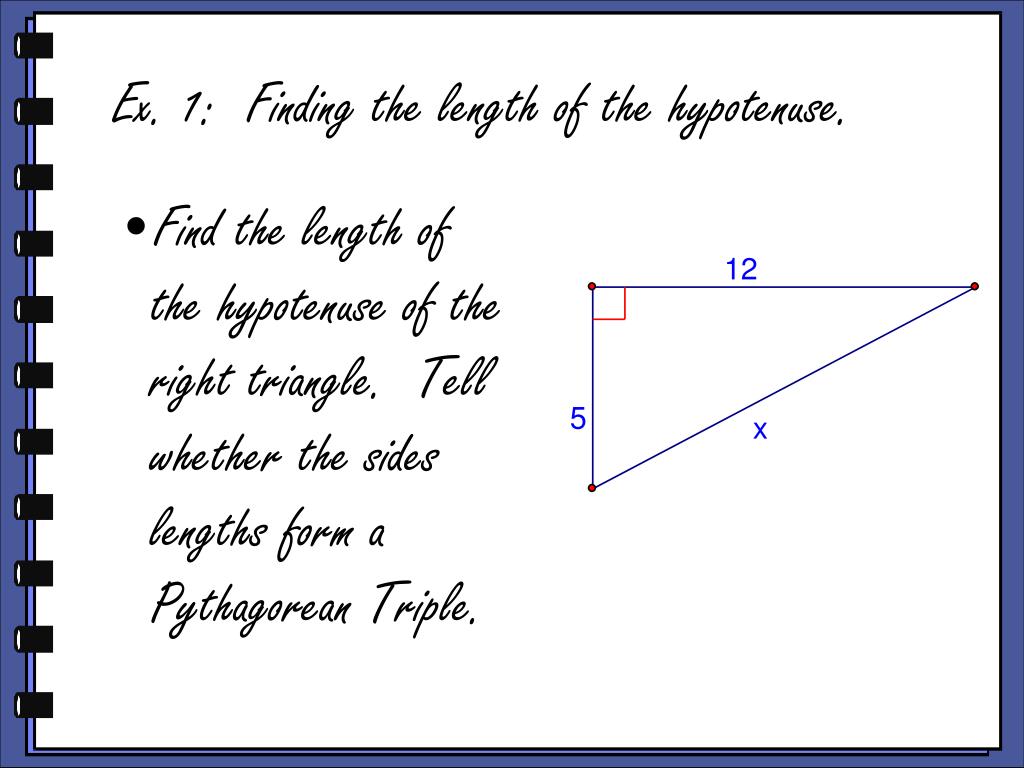
- The Pythagorean Theorem, a2+b2=c2, a 2 + b 2 = c 2 , is used to find the length of any side of a right triangle.
- In a right triangle, one of the angles has a value of 90 degrees.
- The longest side of a right triangle is called the hypotenuse, and it is the side that is opposite the 90 degree angle.
What are the formulas derived from the Pythagorean theorem?
Read below to see solution formulas derived from the Pythagorean Theorem formula: The length of the hypotenuse is the square root of the sum of the sides squared. The length of side a is the square root of the squared hypotenuse minus the square of side b. The length of side b is the square root of the squared hypotenuse minus the square of side a.
Which is the longest side of the Pythagoras theorem?
According to the definition, the Pythagoras Theorem formula is given as: c 2 = a 2 + b 2. The side opposite to the right angle (90°) is the longest side (known as Hypotenuse) because the side opposite to the greatest angle is the longest.
What is the Pythagorean theorem of right triangle?
Pythagoras theorem states that “ In a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse side is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides “. The sides of this triangle have been named as Perpendicular, Base and Hypotenuse. Here, the hypotenuse is the longest side, as it is opposite to the angle 90°. ...
What is the hypotenuse of the Pythagorean theorem?
This calculator solves the Pythagorean Theorem equation for sides a or b, or the hypotenuse c. The hypotenuse is the side of the triangle opposite the right angle. For right triangles only, enter any two values to find the third. See the solution with steps using the Pythagorean Theorem formula.
What is c2 in Pythagorean theorem?
The Pythagorean Theorem describes the relationship among the three sides of a right triangle. In any right triangle, the sum of the areas of the squares formed on the legs of the triangle equals the area of the square formed on the hypotenuse: a2 + b2 = c2.
What is c2 equal to?
How to tell if you're at an C2 level in EnglishTestScore equivalent to the C2 level¹EF SET71 - 100IELTS8.0 - 9.0TOEIC (R&L) Totaln/aCambridge English Scale200 - 2302 more rows
Is c2 the hypotenuse?
The Pythagorean theorem applies to right triangles. Recall that the Pythagorean Theorem states, for a right triangle with legs of length a and b and hypotenuse of length c, that a2+b2=c2. The hypotenuse is the side that is across from the right angle, and it is the longest side of the triangle.
How do you solve C Squared in Pythagorean theorem?
The hypotenuse formula is simply taking the Pythagorean theorem and solving for the hypotenuse, c . Solving for the hypotenuse, we simply take the square root of both sides of the equation a² + b² = c² and solve for c . When doing so, we get c = √(a² + b²) .
How do you solve Pythagorean Theorem?
The length of the hypotenuse is the square root of the sum of the sides squared.c=√a2+b2.a=√c2−b2.b=√c2−a2.
What do you need C2 for?
A C2 Proficiency qualification shows that you can: study demanding subjects at the highest level, including postgraduate and PhD programmes. negotiate and persuade effectively at senior management level in international business settings. understand the main ideas of complex pieces of writing.
Can you solve Pythagorean Theorem with only C?
3:334:56Solve Applications Using the Pythagorean Theorem (c only)YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe square root of C squared is equal to one factor of C 289 is a perfect square 289 equals 17 timesMoreThe square root of C squared is equal to one factor of C 289 is a perfect square 289 equals 17 times 17.
How do you work the Pythagorean Theorem backwards?
Pythagorean Theorem, In Reverse The converse of the Pythagorean Theorem states that if the square of the third side of a triangle is equivalent to the sum of its two shorter sides, then it must be a right triangle. In other words, the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem is the same Pythagorean Theorem but flipped.
What is c2 a2 b2 2abcosc?
Law of Cosines. Suppose we have a triangle with one of its angles, θ, identified. Suppose further that the length of the side of the triangle that is opposite the angle θ is c. The other two sides of the triangle have length a and b. Then the law of cosines is the formula c2 = a2 + b2 - 2abcos(θ) Problem.
How do you find the square root of 2?
Root 2 is an irrational number as it cannot be expressed as a fraction and has an infinite number of decimals. So, the exact value of the root of 2 cannot be determined.
How do you do 3 squared?
If n is an integer then n² is a perfect square. For example, 3 squared is written as 3² and 3² = 3 × 3 = 9.
What does 2 mean in math?
In mathematics, the number 2 represents a quantity or value of 2. The whole number between 1 and 3 is 2.
What does C2 mean in physics?
An equation derived by the twentieth-century physicist Albert Einstein, in which E represents units of energy, m represents units of mass, and c2 is the speed of light squared, or multiplied by itself. (See relativity.)
What is the difference between C1 and C2 English?
The main difference between the two tests is the level of English that they allow you to achieve. C1 Advanced is targeted at the C1 level of the Common European Framework of Reference for Languages (CEFR), while C2 is targeted at the C2 CEFR level. C2 Proficiency is therefore the more difficult of the two exams.
What is C1 level English?
If a person is at C1, this is advanced level. He/she can do the following: Understand a wide range of more demanding, longer texts, and recognise implicit meaning in them. Express him/herself fluently and spontaneously without much obvious searching for the right expression.
What is the formula for Pythagorean Theorem?
The formula for Pythagoras, for a right-angled triangle, is given by; P 2 + B 2 = H 2
What does Pythagoras theorem state?
Pythagoras theorem states that, in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the square of the other two sides.
What is the formula for hypotenuse?
The hypotenuse is the longest side of the right-angled triangle, opposite to right angle, which is adjacent to base and perpendicular. Let base, pe...
Can we apply the Pythagoras Theorem for any triangle?
No, this theorem is applicable only for the right-angled triangle.
What is the use of Pythagoras theorem?
The theorem can be used to find the steepness of the hills or mountains. To find the distance between the observer and a point on the ground from t...
Can the diagonals of a square be found using Pythagoras theorem?
Yes, the diagonals of a square can be found using the Pythagoras theorem, as the diagonal divides the square into right triangles.
Explain the steps involved in finding the sides of a right triangle using Pythagoras theorem.
Step 1: To find the unknown sides of a right triangle, plug the known values in the Pythagoras theorem formula. Step 2: Simplify the equation to f...
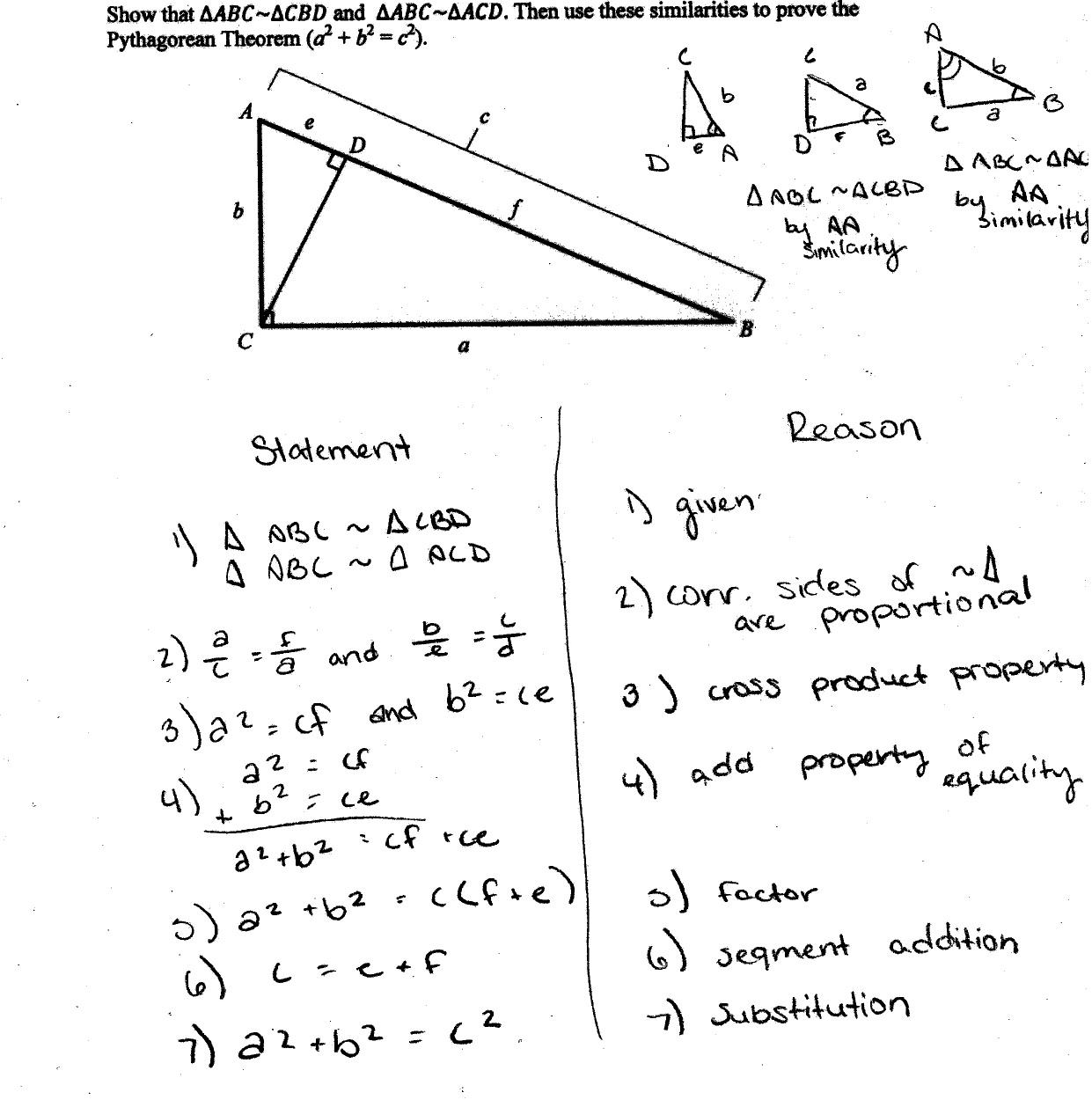
What are the different ways to prove Pythagoras theorem?
There are various approaches to prove the Pythagoras theorem. A few of them are listed below: Proof using similar triangles Proof using different...
What is the Pythagorean Theorem?
The Pythagorean Theorem states that the sum of the squared sides of a right triangle equals the length of the hypotenuse squared.
What is the side of the triangle opposite the right angle?
This calculator solves the Pythagorean Theorem equation for sides a or b, or the hypotenuse c. The hypotenuse is the side of the triangle opposite the right angle.
What is the length of side A?
The length of side a is the square root of the squared hypotenuse minus the square of side b.
What is the smallest Pythagorean triple?
The smallest known Pythagorean triple is 3, 4, and 5. Showing the work:
What is the area of a right triangle?
The area of a right triangle is side a multiplied by side b divided by 2.
How to solve for hypotenuse?
This problems is like example 1 because we are solving for the hypotenuse . Step 1. Identify the legs and the hypotenuse of the right triangle . The legs have length 14 and 48. The hypotenuse is X. Next step . Step 2. Substitute values into the formula (remember 'C' is the hypotenuse). A 2 + B 2 = C 2 14 2 + 48 2 = x 2.
What is the hypotenuse of the Pythagorean theorem?
The picture below shows the formula for the Pythagorean theorem. For the purposes of the formula, side c ¯ is always the hypotenuse. Remember that this formula only applies to right triangles .
How long are the legs of a spherical sphere?
The legs have length 24 and X are the legs. The hypotenuse is 26.
Why are the legs 6 and 8?
The legs have length 6 and 8. X is the hypotenuse because it is opposite the right angle.
Can you add videos to your watch history?
Videos you watch may be added to the TV's watch history and influence TV recommendations. To avoid this, cancel and sign in to YouTube on your computer.
What is the Pythagorean theorem?
The Pythagorean theorem describes how the three sides of a right triangle are related in Euclidean geometry. It states that the sum of the squares of the sides of a right triangle equals the square of the hypotenuse. You can also think of this theorem as the hypotenuse formula. If the sides of a right triangle are a and b and the hypotenuse is c, the formula is
What is the sum of the measures of the angles of a right triangle?
Recall that a right triangle is a triangle with an angle measuring 90 degrees. The other two angles must also total 90 degrees, as the sum of the measures of the angles of any triangle is 180. Read on to answer "what is the Pythagorean theorem and how is it used?".
What is the hypotenuse of a right triangle?
The hypotenuse of the right triangle is the side opposite the right angle, and is the longest side. This side can be found using the hypotenuse formula, another term for the Pythagorean theorem when it's solving for the hypotenuse. Recall that a right triangle is a triangle with an angle measuring 90 degrees.
Can you use the Pythagorean theorem to solve missing pieces?
Sometimes you may encounter a problem where two or all three side lengths missing. In such cases, the Pythagorean theorem calculator won't help - you will use trigonometric functions to solve for these missing pieces. This can be accomplished by hand or by using our triangle calculator.
Who discovered the hypotenuse theorem?
a² + b² = c². The theorem was credited to the ancient Greek philosopher and mathematician Pythagoras, who lived in the sixth century BC.
Is a triangle a right triangle?
If the slope of the other segment forming the angle is -1 then the lines would be perpendicular since 1 * -1 = -1. Therefore, the triangle is a right triangle.
Can you calculate anything in any order?
You can calculate anything, in any order.
How Do You Know When To Use Pythagoras or Trigonometry?
If you need to find a missing side, Pythagoras or trigonometry can be used. If you have two known sides in a triangle, use Pythagoras to find the third side. If you know a side and an angle, use trigonometry.
How to derive Pythagoras theorem in 3D?
We can derive Pythagoras’ theorem in 3D by considering 2 separate right-angled triangles within a cuboid.
How many Pythagorean triples are there?
There are an infinite number of Pythagorean triples.
What are the three integers in a Pythagorean triple?
Pythagorean triples are three integers a, b and c , such that a2 + b2 = c2. For example 3, 4 and 5 form the a Pythagorean triple because 32 + 42 = 52. Pythagorean triples can be found using the formulae of a = m2 – n2, b = 2mn, c = m2 + n2.
What is the longest side of a right angled triangle?
The hypotenuse is the longest side of a right-angled triangle. To find it:
What is the length of the diagonal of a cuboid?
Pythagoras equation in 3D tells us that the length of the diagonal of a cuboid is d = √ ( 𝑥2 + y2 + z2) , where 𝑥, y and z are the side lengths of the cuboid.
What is the Pythagoras theorem?
Pythagoras’ theorem is a2 + b2 = c2, where a and b are the two shorter sides of a right-angled triangle and c is the longest side, opposite the right angle. The theorem is used to find a missing side of a right-angled triangle when the other two sides are known.
What is a Pythagorean triple?
A Pythagorean triple is any group of three integer values that satisfies the equation a2 + B2 = C2 is called a Pythagorean triple. therefore any triangle that has sides that form a Pythagorean triple must be a right triangle. When all three sides are whole numbers you have a Pythagorean triple. For example A = 3 B = 4 C = 5 this can also be called a 3,4,5 triangle. Here is how you do the equation for example 3 squared plus 4 squared = 5 squared, in other words 9 + 16 = 25 therefor because these are all whole numbers the triangle must be a Pythagorean triple.#N#There are four main Pythagorean triples families there is the 3,4,5, the 6,8,10, the 5,12,13, and the 8,15,17 triangles. If you multiply any of the three integers by the same amount you will still have a Pythagorean triple. For example 3,4,5, multiplied by two will give you 6,8,10, witch is a Pythagorean triple.#N#Review- The integers represent the lengths of the sides of the triangles in a,b,c, order. If you do the equation and you don't come out with a whole number the integers are not a Pythagorean triple. Remember when multiplying Pythagorean triples families multiply all three numbers by the same amount.#N#Key words...#N#Pythagorean triple- A right triangle where the sides are in the ratio of integers. (Integers are whole numbers like 3, 12 etc)#N#integer-Includes the counting numbers {1, 2, 3, ...}, zero {0}, and the negative of the counting numbers {-1, -2, -3, ...}#N#Whole numbers- There is no fractional or decimal part. And no negatives.#N#Example: 5, 49 and 980 are all whole numbers.#N#Pythagorean triples families- every triple is a whole number multiple of the base triple.
What happens if you multiply 3 integers by the same amount?
If you multiply any of the three integers by the same amount you will still have a Pythagorean triple. For example 3,4,5, multiplied by two will give you 6,8,10, witch is a Pythagorean triple. Review- The integers represent the lengths of the sides of the triangles in a,b,c, order.
What is the longest side of a right angled triangle?
Hypotenuse- In geometry, a hypotenuse is the longest side of a right-angled triangle, the side opposite the right angle. Leg - Either sides of a right triangle that are opposite to the hypotenuse. Right triangle - A triangle that has one corner of a ninety degree angle. Ask Question.
Where did the Pythagorean theorem come from?
The name Pythagorean theorem came from a Greek mathematician by the named Pythagoras. Pythagoras developed a formula to find the lengths of the sides of any right triangle. Pythagoras Discovered that if he treated each side of a right triangle as a square (see figure 1) the two smallest squares areas when added together equal the area ...
What is the formula in Pythagorean Theorem?
The Pythagoras theorem equation is expressed as, c2 = a2 + b2, where ‘c’ = hypotenuse of the right triangle and ‘a’ and ‘b’ are the other two legs. Hence, any triangle with one angle equal to 90 degrees produces a Pythagoras triangle and the Pythagoras equation can be applied in the triangle.
What is the formula in Pythagorean Theorem?
The Pythagoras theorem equation is expressed as, c2 = a2 + b2, where ‘c’ = hypotenuse of the right triangle and ‘a’ and ‘b’ are the other two legs. Hence, any triangle with one angle equal to 90 degrees produces a Pythagoras triangle and the Pythagoras equation can be applied in the triangle.
What is Pythagoras most famous formula?
The Pythagorean Theorem is one of the world’s most famous equations. If you’re not familiar with it, it can be described as a² + b² = c². This formula is used to calculate the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle.
What is the Pythagorean theorem question?
Pythagoras’ theorem states that in a right triangle (or right-angled triangle) the sum of the squares of the two smaller sides of the triangle is equal to the square of the hypotenuse. In other words, a2 + b2 = c2.
Who made the formula a2 b2 c2?
Pythagoras developed a formula to find the lengths of the sides of any right triangle. Pythagoras Discovered that if he treated each side of a right triangle as a square (see figure 1) the two smallest squares areas when added together equal the area of the larger square.