
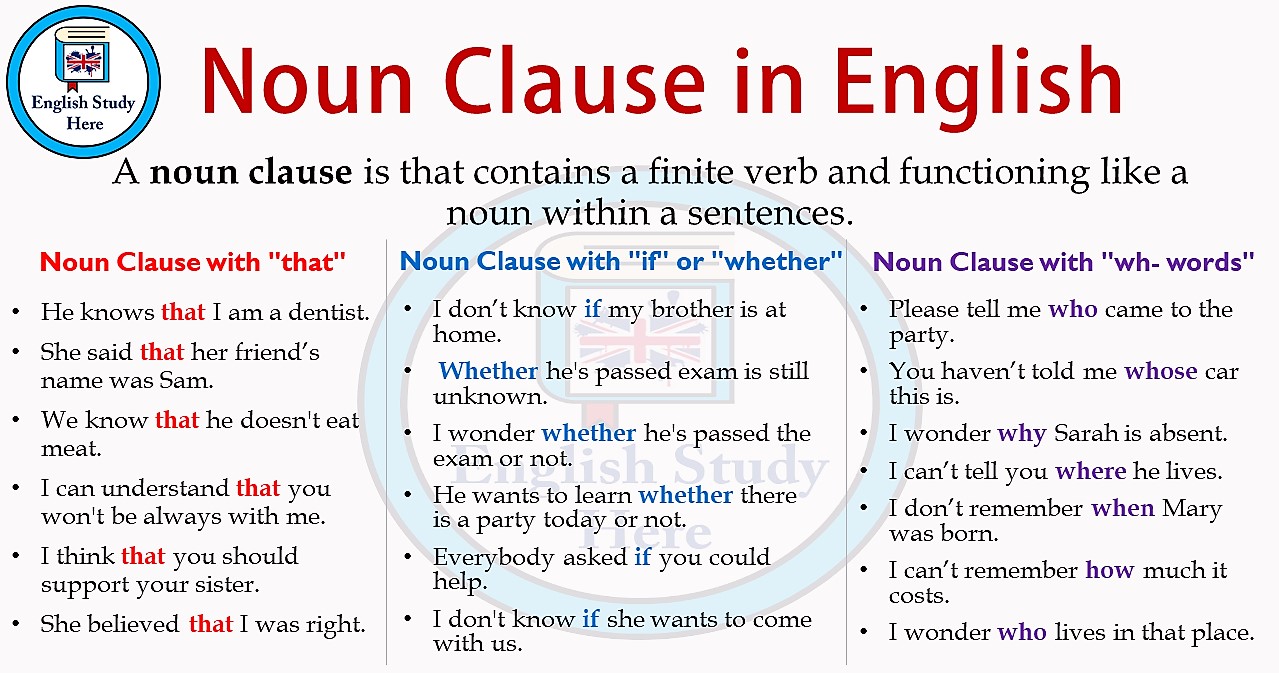
Noun clauses are dependent clauses that must be paired with an independent (main) clause. To see if a clause is a noun clause, identify its role in the sentence. If it is acting as a noun, it is a noun clause (as opposed to an adjective clause, for example).
What is an example of nominal clause?
In the following sentences, for example, the direct object slot contains a clause rather than a noun phrase. These are examples of nominal clauses (sometimes called 'noun clauses'): I know that the students studied their assignment . I wonder what is making Tracy so unhappy.
How do you identify a noun clause?
Noun clauses often begin with one of (but not only) these words: Noun clauses contain a subject and a verb but they cannot stand alone. Noun clauses are dependent clauses that must be paired with an independent (main) clause. To see if a clause is a noun clause, identify its role in the sentence.
What is a numnoun clause?
Noun clauses can operate just the same as an ordinary noun would. This means they can be the subject of a sentence, the direct object of a verb, or the object of a preposition.
What is a nominal definition?
Specifically, the nominal definition is a noun, noun phrase, or any word or word group that functions as a noun. Nominals are used to give more specifics than a simple noun.
What is a nominal clause in grammar?
A nominal clause, another kind of dependent clause, can fill noun positions in a sentence. Nominal clauses enable us to embed a clause within a larger sentence and use the sentence to make some observation or judgment about the nominal clause.
What are the types of nominal clause?
In English grammar, a noun clause is a dependent clause that functions as a noun (that is, as a subject, object, or complement) within a sentence. Also known as a nominal clause. Two common types of noun clause in English are that-clauses and wh-clauses: that-clause: I believe that everything happens for a reason.
How do you identify clauses in a sentence?
To identify the clauses in one long sentence, look for "connecting words." (These are also called "conjunctions.") These words, like and, but, or, and yet, go between two independent clauses.
How do you identify types of clauses?
Clauses come in four types: main (or independent), subordinate (or dependent), adjective (or relative), and noun. Every clause has at least one subject and one verb. Other characteristics will help you distinguish one type of clause from another.
Why do we use nominal clauses?
Nominal clauses are formed when an interrogative or nominal-that introduces a clause by serving as the subject of the clause or preceding the clause in order to serve a noun role in another structure.
Where do you live Please tell me nominal clause?
Answer. Answer: where do you live can you tell me .
What is the easiest way to identify phrases and clauses?
The quickest way to identify whether a group of words is a phrase or a clause is to look for both a subject and a verb. If you can find both, then it's a clause. If you can only find one or the other, then it's a phrase.
How can I learn clauses easily?
4:139:53Easy trick for identification of clauses - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipContinue to remain as main clauses are independent clauses because this end that is coordinatingMoreContinue to remain as main clauses are independent clauses because this end that is coordinating conjunction will not be part of these two either of these two clauses. And will not disturb.
How do you analyze a clause?
There are two types of clause: main and subordinate. A main clause normally makes sense on its own, and often functions as a complete sentence in its own right. A subordinate clause always depends on another clause (frequently the main clause) for its real meaning.
What are 5 examples of clauses?
Examples of clauses:Subject + verb (predicate). = complete thought (IC)I eat bananas. = complete thought (IC)Sharon speaks loudly. = complete thought (IC)
How do you separate clauses in a sentence?
Commas are used to separate two independent clauses. An independent clause can stand on its own as a sentence. They usually occur with coordinating conjunctions and, but, for, or, nor, so, yet.
What is an identifying clause?
Some adjective clauses identify or classify nouns: they tell us which person or thing is being identified in the sentence. In grammar, these are called identifying or restrictive clauses.
in What Way Can A Noun Clause Operate?
Noun clauses can operate just the same as an ordinary noun would. This means they can be the subject of a sentence, the direct object of a verb, or...
How to Identify A Noun Clause
A few identifiers will help you locate a noun clause in a sentence.Noun clauses often begin with one of (but not only) these words: 1. how 2. that...
Using Subjunctive in Noun Clauses
The subjunctive case appears in noun clauses. It is acceptable in formal writing and speaking but is not common in everyday language.The common use...
Summary: What Are Noun Clauses?
Define noun clause: The definition of a noun clause is a clause that functions as a noun in a sentence. Noun clauses, 1. contain a subject and a ve...
Grammar & Spelling
Check your text and writing for style, spelling and grammar problems everywhere on the web!
A Member Of The STANDS4 Network
Check your text and writing for style, spelling and grammar problems everywhere on the web!
What is a Noun Clause?
What does noun clause mean? A noun clause is a dependent clause that contains a subject and a verb. A noun clause functions as noun in a sentence.
In What Way Can a Noun Clause Operate?
Noun clauses can operate just the same as an ordinary noun would. This means they can be the subject of a sentence, the direct object of a verb, or the object of a preposition.
Noun Clause as an Object
A noun clause can function as a direct object, an indirect object, or the object of a preposition.
Noun Clause as a Subject
Since a noun clause is a noun, it can function as a subject of a sentence. Here are a few noun clause sentences where the noun clause is the subject of the sentence.
Using Subjunctive in Noun Clauses
The subjunctive case appears in noun clauses. It is acceptable in formal writing and speaking but is not common in everyday language.
Summary: What are Noun Clauses?
Define noun clause: The definition of a noun clause is a clause that functions as a noun in a sentence. Noun clauses,
What Are Relative Clauses Used for?
Nominal relative clauses are used as objects, subjects, or complements for the main clause and they act as a noun or a noun phrase, the reason why they are regarded as noun clauses or nominal.
Where Are Relative Clauses Placed?
Nominal relative clauses always come after a nominal relative pronoun that always follows the independent clause.
Nominal Relative Clauses vs. Adjectival Relative Clauses
Nominal relative clauses are objects or subjects, but adjectival relative clauses are adjectives. They add information to the preceding noun or noun phrase. There are some examples below:
