
From the above explanation, for finding the coterminal angles:
- add or subtract multiples of 360° from the given angle if the angle is in degrees.
- add or subtract multiples of 2π from the given angle if the angle is in radians.
Full Answer
What is the costal angle of rib?
Costal angle - Angulus costae. Anatomical Parts. Description. The external surface of the body of a rib is convex, smooth, and marked, a little in front of the tubercle, by a prominent line, directed downward and lateralward; this gives attachment to a tendon of the Iliocostalis, and is called the costal angle.
What is the costal angle of the sternum?
The costal angle is the angle beneath the the sternum. It is created by the costal cartilage that joins what are called the false ribs, the ones tha6t do not directly attach to the sternum via their own cartilage, but attach directly and indirectly to the cartilage of the 7th rib.
How do you find the sternal angle of Louis?
The angle of Louis (also called the sternal angle) is a useful place to start counting ribs, which helps localize a respiratory finding horizontally. If you find the sternal notch, walk your fingers down the manubrium a few centimeters until you feel a distinct bony ridge. This is the sternal angle.
How do you find the sternal angle of the rib cage?
If you find the sternal notch, walk your fingers down the manubrium a few centimeters until you feel a distinct bony ridge. This is the sternal angle. The 2nd rib is continuous with the sternal angle; slide your finger down to localize the 2nd intercostal space.
Where is the major fissure located?
Does inhalation cause chest angle to decrease?
About this website
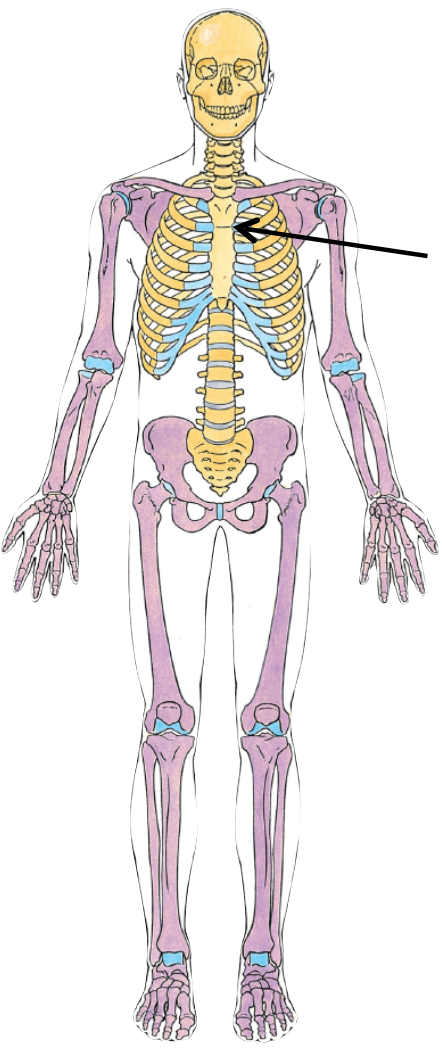
Where is the costal angle located?
the ribCostal angle - Angulus costae The angle of the rib (costal angle) is the region where the rib is the most strongly bent located on on the proximal part of the body of the rib.
What angle should the costal angle be?
Costal angle. The angle formed by the blending together of the costal margins at the sternum. It is usually no more than 90 degrees, with the ribs inserted at approximately 45-degree angles.
What is the costal angle from the sternum?
Anatomy. The sternal angle, which varies around 162 degrees in males, marks the approximate level of the 2nd pair of costal cartilages, which attach to the second ribs, and the level of the intervertebral disc between T4 and T5.
What is a normal costal margin angle?
Observe the costal angle which is the angle between the costal margins inferior to the xiphoid process. Normally, it is about 90 degrees. An abnormal finding is when the angle flattens out. This happens with chronic lung conditions associated with hyperinflation of the lungs (e.g., emphysema).
Why is the costal angle important?
Clinical Significance It marks the point at which the costal cartilages of the second rib articulate with the sternum. This is particularly useful when counting ribs to identify landmarks as rib one is often impalpable. The counting of ribs is essential when one is attempting to make a thoracic incision.
How do you calculate intercostal spaces from your back?
Counting ribs posteriorlySetup. Expose the chest of a patient. ... Rib. Start in the lower back in the middle between posterior midline and scapular line. ... Intercostal space. Moving your fingers upward, just above the twelfth rib lies eleventh (11th) intercostal space.Counting the rest.
How do you feel the angle of Louis?
To find it on yourself, place your fingers gently at the base of your throat in a central position and move your fingers downward until you can feel the top of the sternum, or rib cage. From this position, continue to move your fingers downward until you feel a boney lump. This is the "angle of Louis".
How is the sternal angle formed?
The sternal angle (of Lewis) is formed by the angle between the manubrium and the body of the sternum at the manubriosternal symphysis (see Fig. 6-2). This angle makes the sternum slightly convex anteriorly. The second costal cartilage articulates with the sternum at this angle.
How do you find the fifth intercostal space?
The ETC guideline aims to locate the fifth intercostal space by using a point that is one hand's width (distance across the second to fifth metacarpophalangeal joints) below the axilla. 4 The contralateral hand of the patient is placed on the side of the thorax with the palm in contact with the skin of the chest wall.
How do you calculate costal margin?
People can feel the costal margin by locating the base of the sternum and moving down and to the side to find the costal cartilage. The rib cage includes 12 pairs of ribs, the sternum and 12 vertebrae.
How do you find costal margin?
The costal margin is the medial margin formed by the cartilages of the seventh to tenth ribs. It attaches to the body and xiphoid process of the sternum. The thoracic diaphragm attaches to the costal margin. The costal angle is the angle between the left and right costal margins where they join the sternum.
What forms the costal margin?
Anatomical Parts The costal margin (costal arch) is an arch formed by the medial margin of the cartilages of false ribs and one true rib (seventh rib to the tenth rib).
What does the sternal angle feel like?
1:0012:36Sternal angle - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo it's not so much an angle you see as much as it is an angle that you feel or palpate. And so theMoreSo it's not so much an angle you see as much as it is an angle that you feel or palpate. And so the sternal angle is also called the sternal angle of Louis or Louie named.
What is the angle of Louis?
The angle of Louis is the eponymous name given to the sternal angle which is the palpable anatomical feature formed from the manubriosternal junction. The manubriosternal junction is the joint of the sternal body and the manubrium.
What is angle of Louis used for?
The angle of Louis (also called the sternal angle) is a useful place to start counting ribs, which helps localize a respiratory finding horizontally. If you find the sternal notch, walk your fingers down the manubrium a few centimeters until you feel a distinct bony ridge. This is the sternal angle.
What does the angle of Louis help find?
The sternal angle (of Louis) is the angle between the manubrium and body of the sternum it is located 5 cm inferior to jugular notch at the level of the 2nd costal cartilage; thus, it is a useful landmark for rib counting since the first rib is difficult to feel.
Pulmonary Examination Technique: Inspection, Palpation, Percussion
Introduction. During the pulmonary examination, inspection is a useful tool for the physician from which much information can be garnered. Visual inspection can be used to appreciate the level of distress, use of accessory muscles, respiratory position, chest structure, respiratory pattern, and other clues outside of the chest.
Chest Inspection, Palpation, and Percussion | Clinical Gate
Generalities. Chest inspection, palpation, and percussion are the foundations of physical exam. Percussion is 15 years older than the United States, the brainchild of an Austrian innkeeper’s son who figured out that patients’ chests could behave like barrels of wine.
Respiratory Assessment- Percussion - Physiopedia
Description [edit | edit source]. A thorough respiratory examination requires multiple elements of objective assessments to aid diagnosis and inform treatment. Percussion plays a key role in such an examination, when performed in conjunction with other techniques such as auscultation, palpation and imaging . Percussion produces audible sounds which can be interpreted by a skilled examiner to ...
Pulmonary examination - Knowledge @ AMBOSS
The examination of the pulmonary system is a fundamental part of the physical examination that consists of inspection, palpation, percussion, and auscultation (in that order). Recognition of surface landmarks and their relationship to underlying structures is essential.
Types of percussion note - Oxford Medical Education
What are the types of percussion notes? Percussion Note Common Causes Dull * Pleural effusion, presence of hepatic tissue, consolidation, pleural thickening Solid organ or fluid Resonant Normal lung Aerated lung tissue Hyperresonant Pneumothorax, COPD Hyperinflated lung tissue or air in the pleural space * Some authors refer to stony-dull as a separate percussion note. We […]
Chest Percussion: Uses, Procedure, Results - Verywell Health
A Word From Verywell . The ultimate goal of chest percussion is to loosen mucus secretions enough so that they may be coughed up. One of the benefits of this manual technique is that it can be performed in adults and children as young as 5.
Where is the major fissure located?
The major fissure can be located by drawing a line from the T2 spinous process to where the 6th rib meets the sternum. The minor fissure can be approximated by drawing a horizontal line from the 4th rib attachment of the sternum to the major fissure.
Does inhalation cause chest angle to decrease?
Normally, during inhalation the chest expands laterally, increasing this angle. When the diaphragms are flattened (as in COPD), inhalation paradoxically causes the angle to decrease. Harrison's sulcus: a horizontal grove where the diaphragm attaches to the ribs; associated with chronic asthma, COPD, & Rickets.
Where is the major fissure located?
The major fissure can be located by drawing a line from the T2 spinous process to where the 6th rib meets the sternum. The minor fissure can be approximated by drawing a horizontal line from the 4th rib attachment of the sternum to the major fissure.
Does inhalation cause chest angle to decrease?
Normally, during inhalation the chest expands laterally, increasing this angle. When the diaphragms are flattened (as in COPD), inhalation paradoxically causes the angle to decrease. Harrison's sulcus: a horizontal grove where the diaphragm attaches to the ribs; associated with chronic asthma, COPD, & Rickets.
