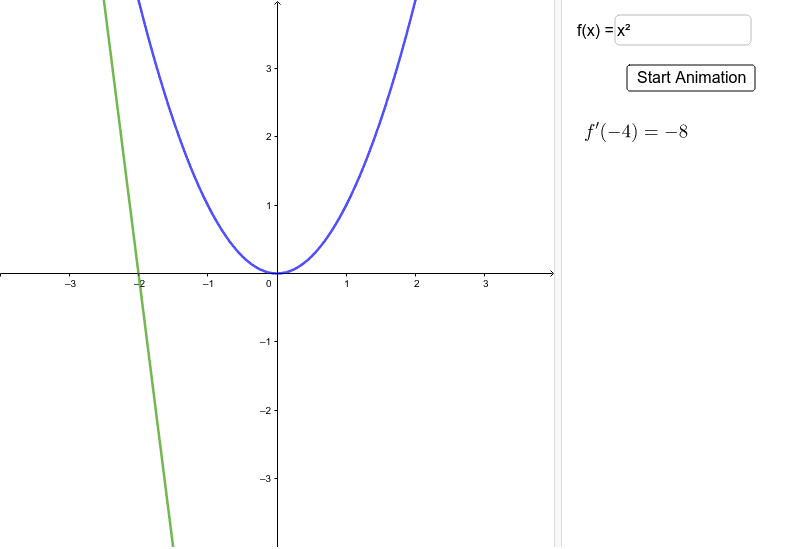
Derivative Graph Rules
- If the slope of f (x) is negative, then the graph of f’ (x) will be below the x-axis.
- If the slope of f (x) is positive, then the graph of f’ (x) will be above the x-axis.
- All relative extrema of f (x) will become x-intercepts of f’ (x).
- All points of intersection of f (x) will become relative extrema of f’ (x).
How to find the first derivative?
Steps to find the Derivative:
- Change x by the smallest possible value and let that be ‘ h’ and so the function becomes f (x+h).
- Get the change in value of function that is : f (x + h) – f (x)
- The rate of change in function f (x) on changing from ‘ x ’ to ‘ x+h ’ will be
How do you calculate derivative?
- Find f ( x + h ).
- Plug f ( x + h ), f ( x ), and h into the limit definition of a derivative.
- Simplify the difference quotient.
- Take the limit, as h approaches 0, of the simplified difference quotient.
How can sketch a graph of a derivative?
Draw graph of derivative Step 1: Table of values for -x 2 + 2. the y-values are in the right-hand column. Step 2: Sketch your graph by plotting a few points (from Step 1) and connecting them with curved lines (for a polynomial function) or straight lines (for a linear function or absolute value function ). We have a polynomial function here, so ...
How do you find the derivative of a derivative?
To derive the derivative of cosec x, we will use the following formulas:
- d (sin x)/dx = cos x.
- cos x /sin x = cot x.
- 1/sin x = cosec x.
What is the second derivative of a graph?
How to graph a slope?
What are the x-values of the original points of inflection?
What are critical points in graphs?
What is the original increasing slope?

How do you use a graph to match a derivative?
6:017:37Matching Function Graphs With Their Derivative Graphs - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe derivative is equal to zero since we have a horizontal tangent line there we have that rightMoreThe derivative is equal to zero since we have a horizontal tangent line there we have that right there and now since we have an increasing function we want this side over here to be above the x-axis.
What is the derivative of a linear graph?
The derivative of a linear function mx + b can be derived using the definition of the derivative. The linear function derivative is a constant, and is equal to the slope of the linear function.
How do you find the derivative of two functions on a graph?
0:126:37Ex: Find a Derivative Function Value Using the Quotient Rule ... - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipMinus the numerator times the derivative of the denominator divided by the denominator squared.MoreMinus the numerator times the derivative of the denominator divided by the denominator squared.
How do you find the derivative of a straight line graph?
0:106:38The derivative of a linear function - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipFunction f prime. Then the tangent slope of F at X is equal to the value of the derivative F PrimeMoreFunction f prime. Then the tangent slope of F at X is equal to the value of the derivative F Prime at X. So in other words if say F prime of X were equal to negative 3/4.
How do you find the derivative of a linear function?
0:032:18Derivatives of Linear Functions - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipFunction is a function of the form f of X equals MX plus B. Now the derivative is going to startMoreFunction is a function of the form f of X equals MX plus B. Now the derivative is going to start with the definition of the derivative f prime of x equals.
What is the easiest way to find derivatives?
0:095:32Basic Derivative Rules - The Shortcut Using the Power Rule - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo the derivative rule. Says that whenever you have a variable to a power we just pull that numberMoreSo the derivative rule. Says that whenever you have a variable to a power we just pull that number out front so the 10 is going to come right out front and then we simply subtract 1 from our exponent.
What is the formula to find the derivative?
0:0123:30Definition of the Derivative - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd it's equal to the limit. As h approaches zero of f of x plus h minus f of x divided by h. SoMoreAnd it's equal to the limit. As h approaches zero of f of x plus h minus f of x divided by h. So that's the formula that we need to use. So let's say if f of x is a linear function 5 x minus 4..
How do you find the equation of a graph?
To find the equation of a graphed line, find the y-intercept and the slope in order to write the equation in y-intercept (y=mx+b) form. Slope is the change in y over the change in x.
What's the derivative of a straight line?
The derivative is the constant function y=0 because the straight line y=1 has slope 0.
What is the derivative of linear transformation?
Show that the total derivative of a linear transformation T is simply T itself: A linear transformation is of the form T(u, v)=(au + bv, cu + dv) for some constants a, b, c, d ∈ R. We can write this as a matrix: T(u, v) = ( a b c d )( u v ) = ( au + bv cu + dv ) .
Why is derivative of linear a constant?
@coool, the slope of any non-vertical line is a real number (i.e., a constant). Therefore, the derivative of a linear function, which is nothing else but the slope of the graph of the function, is constant.
Derivative Calculator - Symbolab
Free derivative calculator - differentiate functions with all the steps. Type in any function derivative to get the solution, steps and graph
Derivative Calculator - Mathway
The Derivative Calculator supports solving first, second...., fourth derivatives, as well as implicit differentiation and finding the zeros/roots. You can also get a better visual and understanding of the function by using our graphing tool.
Derivative Calculator: Wolfram|Alpha
Free Online Derivative Calculator allows you to solve first order and higher order derivatives, providing information you need to understand derivative concepts.
Derivative Function - Desmos
Conic Sections: Parabola and Focus. example. Conic Sections: Ellipse with Foci
Functions Critical Points Calculator - Symbolab
Free functions critical points calculator - find functions critical and stationary points step-by-step
What is the second derivative of a graph?
The second derivative is a graph of the slope of the first derivative.
How to graph a slope?
How to Graph. Step 1: Critical points (maximums and minimums) of the original equation are where the zeros are now the zeros (y’ = 0). Plot those points. Step 2: Where the slope is positive in the original, y’ is positive. Draw the positive parts of the y’ graph with the maximums being where points of inflection were in y.
What are the x-values of the original points of inflection?
Original Points of Inflection: The x-values of the original points of inflection are the y’ critical points ( maximums and minimums ).
What are critical points in graphs?
Critical Points: These occur where the slope is 0. They are the minimums and maximums of your graph.
What is the original increasing slope?
Original Increasing Slope: Where the original equation has and increasing or positive slope, the y’ has y-values that are positive ( y’ > 0 ).
What happens to the graph of f' (x) if the slope is positive?
If the slope of f (x) is positive, then the graph of f’ (x) will be above the x-axis.
Is f odd or even?
Additionally, if f (x) is an odd function, then f’ (x) is an even function. And if f (x) is an even function, then f’ (x) is an odd function. This means that the derivative will more than likely have one less turn than the original function.
How to find derivative of graph?
How do I find the derivative of a graph without an equation? 1 At the point (i.e. at the value of the independent variable) at which you want to evaluate the derivative, draw a tangent. If you don’t want to mess up the paper, or the graph is not on paper, just position one edge of a ruler tangential to the graph at that point. 2 Extend the tangent to the x axis, or position the ruler so that the above-mentioned edge crosses the x axis. 3 With a protractor, measure the angle between the tangent and the x axis. Iff the tangent slopes downward toward the right, give the angle a negative sign. 4 Find the tangent of that angle, using your favorite calculator, spreadshe
How to tell if a derivative is above or below the axis?
You can begin by sketching tangent lines at a few random points, and determining whether the slope of the tangent line is positive, negative, or zero. This tells you whether the graph of the derivative is above or below the axis.
What is derivative in math?
Derivative is just finding the slope (that is the angle which tangent to the curve at a point makes with x-axis).
What is the derivative of a tangent that never hits the x axis?
Oh, and if the tangent never hits the x axis, no matter how far you extend it, then the derivative is 0.
How to tell if a graph is positive or negative?
You can also look at the degree to which the graph is positive or negative. Where the graph is more positive, the original graph is ascending more quickly, and where the graph is more negative, the original graph is descending more quickly.
Do you measure tangents on a graph?
If the graph is a straight line, you really only need to measure one tangent, but for other curves, the more the merrier, depending on how many curves you see, or what the largest exponent is that you think was in the original graph.
Is a tangent line a derivative?
We see that we found a tangent line to a circle, and we know that it is a derivative.
What is the second derivative of a graph?
The second derivative is a graph of the slope of the first derivative.
How to graph a slope?
How to Graph. Step 1: Critical points (maximums and minimums) of the original equation are where the zeros are now the zeros (y’ = 0). Plot those points. Step 2: Where the slope is positive in the original, y’ is positive. Draw the positive parts of the y’ graph with the maximums being where points of inflection were in y.
What are the x-values of the original points of inflection?
Original Points of Inflection: The x-values of the original points of inflection are the y’ critical points ( maximums and minimums ).
What are critical points in graphs?
Critical Points: These occur where the slope is 0. They are the minimums and maximums of your graph.
What is the original increasing slope?
Original Increasing Slope: Where the original equation has and increasing or positive slope, the y’ has y-values that are positive ( y’ > 0 ).
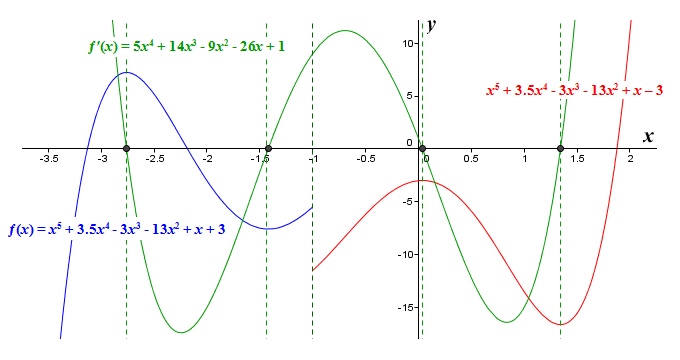
Original Equation
First Derivative
- The first derivative is the graph of the slopes of the original equation. How to Graph Step 1: Critical points (maximums and minimums) of the original equation are where the zeros are now the zeros (y’ = 0). Plot those points. Step 2:Where the slope is positive in the original, y’ is positive. Draw the positive parts of the y’ graph with the maximu...
Second Derivative
- The second derivative is a graph of the slope of the first derivative. How to Graph Follow the same steps as for graphing the first derivative, except use the first derivative graph like it was the original. The second deriviatve is just the derivative of the first derivative. Step 1: The critical points (maximums and minimums) of y’ are where y” = 0. Plot those points. Step 2:Where the sl…
Summary
- Points of inflection become critical points. Critical points become zeros. Asymptotesstay in the same spots.
Want More?
- For students of the Los Angeles South Bay, you can sign up for one of our at-your-home tutors. If you live outside the area, we are happy to work with you via video chat! Just click on the schedule a tutor button. You can also find more free math resources and our favorite study tools for other subjects by clicking on the corresponding buttons.