Finding the Epicenter
- Check the scale on your map. ...
- Figure out how long the distance to the epicenter (in centimeters) is on your map. ...
- Using your compass, draw a circle with a radius equal to the number you came up with in Step #2 (the radius is the distance from the center of a ...
How do you find the epicenter of 3 points?
Finding the Epicenter Determine the epicenter distance from three different seismographs. The longer the time between the arrival of the P-wave and S-wave, the farther away is the epicenter. So the difference in the P- and S-wave arrival times determines the distance between the epicenter and a seismometer.
What are the 3 seismographs to find the epicenter of an earthquake?
The three circles intersect at a single point. This is the earthquake's epicenter (Figure below). Seismographs in Portland, San Francisco, and Salt Lake City are used to find an earthquake epicenter.
Why do you need 3 seismographs to locate an epicenter?
Scientists use triangulation to find the epicenter of an earthquake. When seismic data is collected from at least three different locations, it can be used to determine the epicenter by where it intersects. Every earthquake is recorded on numerous seismographs located in different directions.
How many seismographs do you need to find the epicenter?
threeIntroduction: The epicenter is the point on Earth's surface directly above an earthquake. Seismic stations detect earthquakes by the tracings made on seismographs. Tracings made at three separate seismic stations are needed to locate an earthquake epicenter.
How do you identify P and S waves on a seismograph?
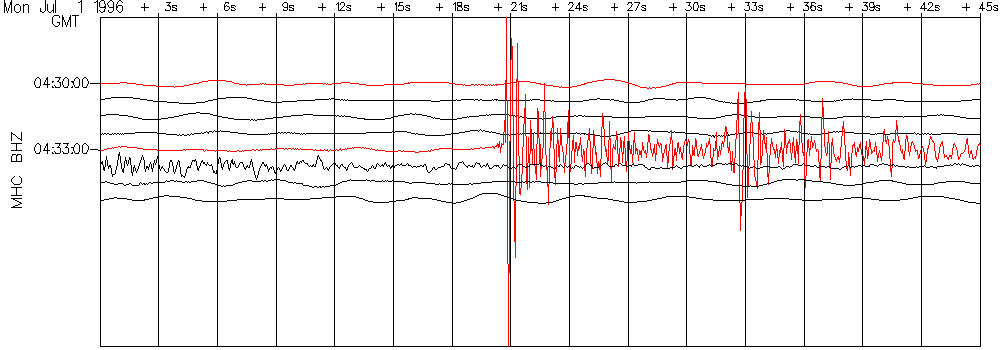
The P wave will be the first wiggle that is bigger than the background signals). Because P waves are the fastest seismic waves, they will usually be the first ones that your seismograph records. The next set of seismic waves on your seismogram will be the S waves. These are usually bigger than the P waves.
How do seismograph stations help determine an earthquakes epicenter?
Three seismographs are needed. A circle is drawn from each of the three different seismograph locations, where the radius of each circle is equal to the distance from that station to the epicenter. The spot where those three circles intersect is the epicenter (Figure 13.12).
How many seismograph stations are needed to locate the epicenter of an earthquake A 1 B 2 C 3 D 4?
Total 3 seismograph stations are used to locate the epicentre of an earthquake of all directions.
How do you find the distance to the epicenter of an earthquake?
To determine the distance of the earthquake epicenter, you can use the steps in the previous section.Determine the arrival times of the P-wave and the S-wave: Arrival time of P-wave: 1.0 min. ... Calculate the difference between the arrival time of the P-wave and the S-wave. ... Refer to the Earthquake Time Travel Graph.
How do you compute the distance of the epicenter from each of the stations using this formula?
Compute the distance of the epicenter from each of the stations using this formula: d time difference x 100 km 8 seconds where: d= distance (km) td = time difference in the arrival time of P-wave and S-wave (seconds) This formula is suited because 8 seconds is the interval between the times of arrival of the P-wave and ...
How do scientists find the epicenter of an earthquake quizlet?
How do geologists locate the epicenter of an earthquake? They use seismic waves to locate an earthquake's epicenter. Scientists measure the difference between the arrival time of the P and S waves to the seismograph. The farther away an earthquake the greater the distance between arrival time.
What are P and S waves?
In P or compressional waves, the vibration of the rock is in the direction of propagation. P waves travel fastest and are the first to arrive from the earthquake. In S or shear waves, rock oscillates perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation.
What are the three types of earthquakes?
Three Kinds of EarthquakesShallow fault earthquakes. A fault is a break in the rock beneath our feet. ... Subduction zone earthquakes. The largest earthquakes ever recorded are subduction zone earthquakes. ... Deep earthquakes. Deep earthquakes occur in the subducting ocean slab, deep beneath the continental crust.
What is the Richter scale?
The Richter magnitude scale, also known as the local magnitude (M) scale, assigns a number to quantify the amount of seismic energy released by an earthquake. It is a base-10 logarithmic scale.
What does a seismogram measure?
A seismogram is the recording of the ground shaking at the specific location of the instrument. On a seismogram, the HORIZONTAL axis = time (measured in seconds) and the VERTICAL axis= ground displacement (usually measured in millimeters).