How do you find the frequency of a piano?
Starting at any note the frequency to other notes may be calculated from its frequency by: Freq = note x 2 N/12, where N is the number of notes away from the starting note. N may be positive, negative or zero.
What is the frequency of piano keys?
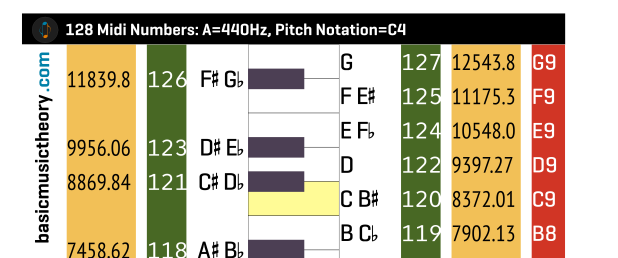
The piano has 88 keys which span the frequency range 27.5 Hz (A0) to 4186 Hz (C8). The strings are sounded by hammer mechanisms which are activated by the keys.
What frequency is A4 on a piano?
440 HzA440 (sometimes called A4) is the 440 Hz tone that serves as the internationally recognized standard for musical pitch.
What frequency is middle C on a piano?
around 261.63 HzHistorically, concert pitch has varied. For an instrument in equal temperament tuned to the A440 pitch standard widely adopted in 1939, middle C has a frequency around 261.63 Hz (for other notes see piano key frequencies).
What key is 432 Hz?
What note is 432 Hz? A sound played at 432 Hz is technically the note "A" ("A4," more specifically). Compared to A4 = 440 Hz, however, the pitch of 432 Hz will sound a bit flat.
What key is 639 Hz?
key of B naturalThe frequency of 639Hz brings us back to the key of B natural with the tuning of : A# – B – C# – D# – E – F# – G#.
What key is 440 Hz?
A440 (also known as Stuttgart pitch) is the musical pitch corresponding to an audio frequency of 440 Hz, which serves as a tuning standard for the musical note of A above middle C, or A4 in scientific pitch notation.
What piano key is 528 Hz?
C-Note528 hertz is a C-Note…. In western music, that 528hz tone would be considered a high “C” note.
What note on the piano is 432 Hz?
A4Frequencies of Musical Notes, A4 = 432 Hz.
Is middle C C3 or 4?
It depends on the number of keys on your keyboard. A standard keyboard or piano has 88 keys. Middle C is C4. On digital keyboards with fewer keys Middle C can also be referred to as C3.
What frequency is the note a?
The International Standards Organization (ISO) has standardized the pitch at A-440.
What frequency is F sharp?
F♯ (F-sharp; also known as fa dièse or fi) is the seventh semitone of the solfège. (E-double sharp). When calculated in equal temperament with a reference of A above middle C as 440 Hz, the frequency of the F♯ above middle C (or F♯4) is approximately 369.994 Hz.
Is 432hz a piano?
The current reference frequency for tuning musical instruments is 440 Hz, which corresponds to the musical note A4 (LA3) in the central octave of the piano. This frequency value was established in the 1950s5 and confirmed in 1975 as the standard tuning for music worldwide.
Which frequency is best for piano?
If an acoustic piano is required to play with other instruments tuned to concert pitch then it will be better to tune the piano to 440 Hz.
What does 432 Hz do?
Music tuned to 432 Hz is softer and brighter, and is said to provide greater clarity and is easier on the ears. Meditation music tuned to 432 Hz is relaxing for the body and mind and also more harmonic and pleasant than 440 Hz which is the frequency that most of the modern day music we listen to is tuned at.
What note on the piano is 432 Hz?
A4Frequencies of Musical Notes, A4 = 432 Hz.
How many notes are there on a piano?
On any piano, only 8 notes (out of the 88 notes on a piano) are actually tuned exactly right. Those are all the A notes, from A-27.5 (which means it has a frequency of 27.5 Hz) up to A-3520 (with frequeny 3,520 Hz). All the other notes are actually slightly "off" - a compromise so that pianos can sound OK when playing in any key.
What does a combined signal sound like on a piano?
These two notes are right next to each other on the piano, and sound discordant (bad) when played together. The combined signal gives some insight why. You can see a regular combined signal which is very close to the original two (grey) signals, resulting in "beating" - a kind of shimmering which is not always pleasant. (It can be put to good use in music, but that's for another discussion.)
What is the major 3rd on a piano?
A-220 and C#-275. The major 3rd is one of the most common and "pleasing" sounds in music. On a piano tuned by equal temperament, however, you can see the 3 curves doen't line up so well (the grey A-220, C#-275 and the green combination of the two) because actually, C# is 277.18, which is too sharp for a totally pleasing sound.
What is the Hz of a 3rd major?
To sound right, a major 3rd "should" have frequency 275 Hz (that is, 5/4 × 220), but is quite "sharp" at 277.18 Hz on a piano.
Can a piano play in any key?
It can't be helped if pianos need to play in any key (which of course, they nearly always need to do).
How to find frequency of note other than A4?
In theory it is easy, to get the frequency of the note other than A4=440Hz you just multiply/divide 440Hz by the proper number . For example, to get A2, you divide by 4 and get A2=110Hz.
How to find the frequency of a note in equal tempered tuning?
In an equal-tempered tuning, the frequency of a note n is x = C4 * 2^ (n/12) Hz. Adding in our adjustment term, we get x = C4 * 2^ ( (n + (s/2) (n/12)^2) / 12) Hz. (Notes below middle C should be flat rather than sharp, so subtract the adjustment term rather than adding it.)
What is the correct frequency for middle C?
For concert pitch (A = 440 Hz), the correct frequency for middle C depends on the choice of stretch factor s. Substitute x = 440 Hz and n = 9 semitones in the above formula, then solve for C4. For s = 0.05, the correct frequency is 261.41 Hz.
What does "a piano" mean?
1. To paraphrase: A piano is meant to sound(to a human) as if it is equal temperament even though, by some measurement, well-tuned pianos tend to demonstrate the railsback phenomenon -- more so for smaller pianos.– nobarDec 31 '19 at 18:18. Add a comment | .
What is a professional piano tuner?
A professional piano tuner knows that the exact tuning that is required will vary with every piano that he or she works with. Tuning each acoustic piano is a time-consuming and interactive process, and it does not depend entirely on a fixed set of exact pitches or frequencies.
Why is my piano tuning stretched?
The problem is that the reason a piano gets stretched tuning in the first place is disharmonicity, meaning that the sine waves constituting the various harmonics travelling the string itself are not simple multiples of the fundamental.
Why do you need several oscillators per key?
In case this question was asked in the context of sound synthesis: you will need several oscillators per key at different frequencies in order to manage disharmonicity properly.

Background
The New Applet
- The new applet follows on from the above considerations and allows you to explore the graphs of piano note frequencies. There is a virtual piano that you can play (one note at a time) and after playing each note, you can see the graph of that note and its frequency. You can find the new applet here: You can also see a composite signal, which is the...
Discussion
- A-440 and A-220
When you play A-440, the graph looks as follows. They grey one is A-220, and the green one is A-440. You'll notice the frequency of A-440 is twice the frequency of A-220, and the wavelength is half as long. The two curves coincide at each major time point (at 1 and 2 on the t-axis). - E - the "perfect 5th"
A perfect 5th above A-220 (in theory) is 220× 3/2 = 330 Hz. On a piano, E is actually 329.63 Hz, just a little bit "flat". You can see in the graph there are 1.5 wavelengths for E (the green curve) in the one wavelength of A-220. It's extremely close, and it appears the two curves coincide at t = …
Signal Combinations
- In the applet, you can also see the combined signal of the fundamental (A-220 in this case), with the note just played.
Conclusion
- Piano note frequencies are an interesitng application of trigonometric graphs, exponential growth and music perception. Once again, here's the link to the applet: Frequencies of Notes on a Piano: Learning object See the 4 Commentsbelow.