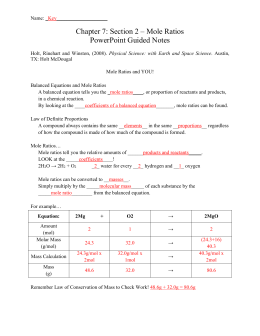
The limiting reagent (or reactant) in a reaction is found by calculating the amount of product produced by each reactant. The reactant that produces the least amount of product is the limiting reactant.
How do you determine limiting reagent?
Strategy:
- Write the balanced chemical equation.
- Convert from mass of reactants and product to moles using molar masses and then use mole ratios to determine which is the limiting reactant.
- Calculate the percent yield by dividing the actual yield by the theoretical yield and multiplying by 100.
What is a real life example of a limiting reactant?
You will places tires on all of the cars and then when all of the cars have tires, if there are excess tires, then the cars are the limiting reagent as shown below. Another real life example would be shoes and people. Lets say there are 25 people and 48 shoes. Each person needs two shoes.
How to solve a limiting reagent problem?
this step-by-step guide and you will be able to calculate limiting reagent, theoretical yield, and percent yield. 1. Write a balanced equation for the reaction 2. Calculate the molecular weight of each reactant and product 3. Convert all amounts of reactants and products into moles 4. Figure out the limiting reagent 5. Calculate the theoretical yield 6.
How do you find excess reactants?
Super Simple Trick to identify Limiting & Excess Reagent:
- Calculate the number of moles of each reactant.
- Then calculate the total number of moles for each reactant using balanced chemical equation.
- The reactant /reagent that gives the least amount of product is the limiting reactant & the reactant /reagent that gives the greater amount of product is the excess reactant ...

How do you find the limiting reagent in a solution?
17:0118:52Limiting Reactant Practice Problems - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIt's going to be the smaller of the two values. It's going to be 40.5. That's the answer to part bMoreIt's going to be the smaller of the two values. It's going to be 40.5. That's the answer to part b the reactant that gave us the lower theoretical yield of 40.5 grams of water is o2. So once again o2
What is the formula for limiting?
Limits formula:- Let y = f(x) as a function of x. If at a point x = a, f(x) takes indeterminate form, then we can consider the values of the function which is very near to a. If these values tend to some definite unique number as x tends to a, then that obtained a unique number is called the limit of f(x) at x = a.
How do you find the limiting and excess reactant?
9:0020:11Stoichiometry - Limiting & Excess Reactant, Theoretical & Percent YieldYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo what you want to do is start with the limited reactant. And convert it to the excess reactant. SoMoreSo what you want to do is start with the limited reactant. And convert it to the excess reactant. So the limit of reactant is the eight moles of o2. And let's convert it to the moles of protein. The
What is the rate limiting reactant?
The limiting reactant (or limiting reagent) is the reactant that gets consumed first in a chemical reaction and therefore limits how much product can be formed.
What is the function formula?
Functions is an important branch of math, which connects the variable x with the variable y. Functions are generally represented as y = f(x) and it states the dependence of y on x, or we say that y is a function of x.
What is the limiting reagent?
A reactant in a chemical reaction that determines the amount of product that is produced is the limiting reactant or limiting reagent. The reason f...
What is the difference between limiting reactant and limiting reagent?
A reactant is a substance that reacts directly when the reaction is initiated, whereas a reactant is a substance that participates in a chemical re...
Why is the limiting reactant important?
The limiting reagent/reactant is important because it can tell a chemist that only x moles of compounds can form when the perfect quantity is used...
Are limiting reactants present in all reactions?
The limiting reactant determines the maximum amount of product that can be formed from the reactants when reactants are not present in stoichiometr...
What is the benefit of having a limiting reagent?
In a chemical reaction, the task of limiting reagent or reactant is significant because it can help the chemist predict the maximum quantity of rea...
What is a limiting reactant?
The limiting reactant is the reactant from which the minimum amount of product is formed. Also, if we calculate the amount of one reactant needed to react with another reactant, then the reactant which is in shortage would be the required limiting reactant. Thus, the required limiting reagent for the reaction can be identified using ...
How to find Limiting Reagent?
The limiting reactant or reagent can be determined by two methods .
What determines when a reaction will stop?
This reactant generally determines when the reaction will stop. The exact amount of reactant which will be needed to react with another element can be calculated from the reaction stoichiometry. The limiting reagent depends on the mole ratio, not on the masses of the reactants present.
How many moles of hydrogen gas are needed to form ammonia?
Let us consider the following reaction of formation of ammonia: In the reaction given above, 3 moles of Hydrogen gas are required to react with 1 mole of nitrogen gas to form 2 moles of ammonia. But what if, during the reaction, only 2 moles of hydrogen gas are available along with 1 mole of nitrogen. In that case, the entire quantity of nitrogen ...
What is the name of the reactant that is completely used up in a chemical reaction?
The reactant that is entirely used up in a reaction is called as limiting reagent . Limiting reagents are the substances that are completely consumed in the completion of a chemical reaction. They are also referred to as limiting agents or limiting reactants .
What is the limiting reagent for zinc chloride?
Zinc chloride is formed in excess so the limiting reagent here is hydrochloric acid.
Why can't a reaction continue?
From the illustration shown above, it can be observed that the limiting reactant is the reason the reaction cannot continue since there is nothing left to react with the excess reactant. it is the reactant that entirely consumed over the course of the reaction.
Excess Reactant
Consider going grocery shopping for a meal that must be prepared for dinner. There will always be some ingredients left over and some that will be totally consumed once the dish is created, no matter how well planned it is. This situation can be compared to chemical processes that occur all around us.
Limiting and Excess Reactants
In the above example of assembling a bicycle, it can be seen that while one frame was left over, all of the wheels were used up in the process. As a result, the number (or quantity) of wheels determined how many final products (bicycles) could be manufactured, i.e. the wheels set the limit.
How to Find Excess Reactant
Assume a reaction that commences with 10 moles of hydrogen gas (H2) and 7 moles of oxygen gas (O2). The coefficients of a balanced equation for water formation, {eq}2H_2 + O_2 \rightarrow 2H_2O {/eq} , reveal that one mole of H2 and half a mole of O2 are spent for every one mole of water produced.
What is the limiting reactant?
The idea of limiting reactant is essential in the examination of stoichiometry of reactions between solutes and solvents in chemical reactions. The limiting reactant is the substrate that administrates the amount of recuperation of a solute in a process. This is attributed to the premise that once the limiting reactant has been exhausted; there can be no additional chemical reactions (Sumanaskera et al. 4293).
How to determine the extent of a chemical reaction?
A method of examining the extent of the chemical reaction in a process is to supervise the thermal energy that is within the reaction systems . Chemicalreactions are usually endothermic of or exothermic as they either absurd energy or liberate thermal energy as they are taking place. The quantity of heat energy that is transmitted is correlated to the amount of precipitate that has formed. The objective of this experiment is to apply a thermometer in order to assess the changes that take place in the temperature as indicators of the extent of the chemical reaction (Sumanaskera et al. 4293).
What is the stoichiometric proportion of NaOH to HCl at the intersecting point of?
The stoichiometric proportion of NaOH to HCl at the intersecting point of the graph is 1: 1. The balanced chemical equation for the reaction between NaOH and HCl is:
How to dilution 1.0 M HCl?
Applying the 600ml flasks, measure all of the recommended quantities of 1.0 M HCl and NaOH. The dilution was achieved by adding water. Use the plastic form cup as a vessel for fascinating the reaction. Measure and pour 45 ml of the 1.0 M HCl. Take the temperature and record it to the nearest ±0.2° C. Next assess, measure and pour 5.0 ml of NaOH into the graduate cylinder. Ensure the simultaneous pouring of the 1.0 M HCl and 1.0 NaOH.
What is the limiting reactant in the reaction between an acid and a base?
In this case, the limiting reactant was the H 2 SO 4. The amount and the proportion of H 2 SO 4 was the limiting reactant in this experiment. The use of H 2 SO 4 as a reagent has been verified. The ratios of the reagent to the substrate were 1: 2. The hypothesis that was proposed was validated by the results of the experiment.
How many M solutions are there in NaOH?
There were three separate3.0 M solutions of NaOH, HCl (hydrochloric acid), H 2 SO 4 (sulphuric acid).These solutions were diluted to a 1.0 M concentration and mixed in aPlastic Foam Cup. The exothermic qualities of the chemical reactions between NaOH, HCl (hydrochloric acid), H 2 SO 4 (sulphuric acid) were evaluated by using a thermometer. The 10 ml graduate, stirring rod and the 600 ml flasks were applied in the laboratory experiment.
What is the stoichiometry of HCl and NaOH?
The stoichiometry of the reaction between HCl (hydrochloric acid), H 2 SO 4 (sulphuric acid) and NaOH (sodium hydroxide) will be as certained and the perspective of limiting reactants will be reviewed in this laboratory experiment. The hypothesis that will be tested in this laboratory is that the reagent H 2 SO 4 administrates the reaction of the chemical process between an acid and a base. This hypothesis is in accordance with the work that was conducted by Sumanasekera, Allen, Fang, Loper, Rao and Eklund (1999).