How to Solve for a Missing Right Triangle Length
- Replace the variables in the theorem with the values of the known sides. 48 2 + 14 2 = c2
- Square the measures and add them together.
How to find a missing side length?
Find the missing side lengths of the figure:
- Identify the missing sides of the figure. The sides labeled {eq}x {/eq} are our missing sides.
- Find side lengths that are parallel to the missing sides. ...
- Use arithmetic and the given information to solve for the missing side.
How do you find the unknown length of a triangle?
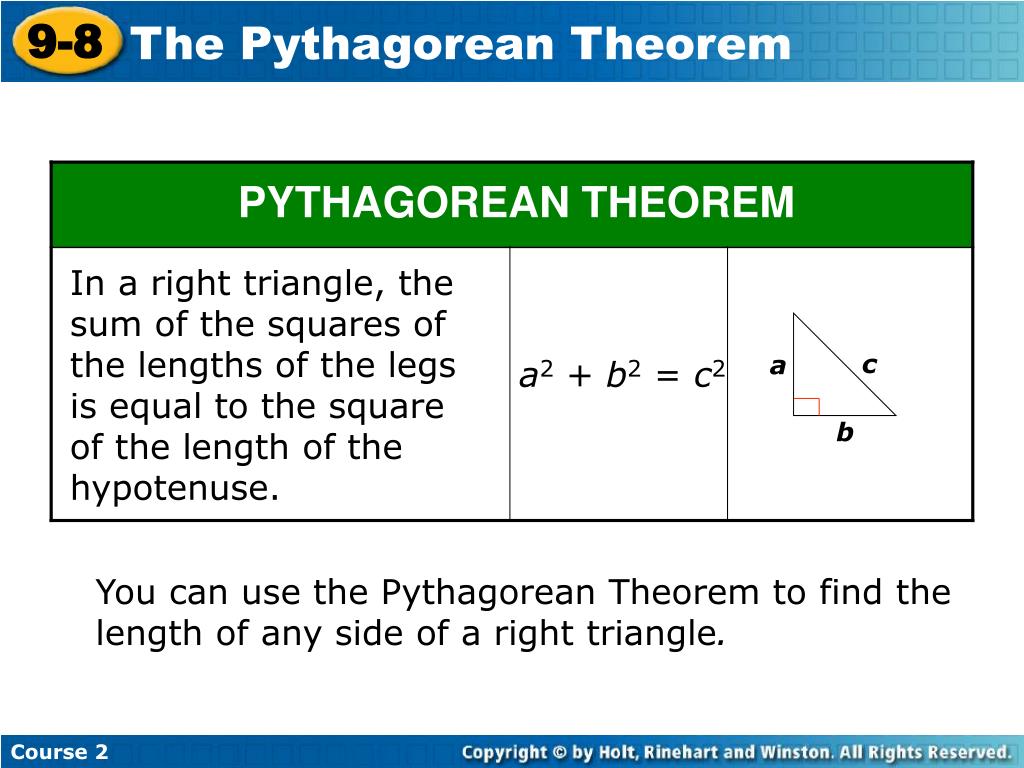
How do you find the unknown length of a triangle? The Pythagorean theorem states that a2 + b2 = c2 in a right triangle where c is the longest side. You can use this equation to figure out the length of one side if you have the lengths of the other two.
How do you find the missing side of a right triangle?
Step by step guide to finding missing sides and angles of a Right Triangle
- By using Sine, Cosine or Tangent, we can find an unknown side in a right triangle when we have one length, and one angle (apart from the right angle).
- Adjacent, Opposite and Hypotenuse, in a right triangle is shown below.
- Recall the three main trigonometric functions: SOH – CAH – TOA, sin θ = opposite hypotenuse θ = o p p o s i t e h y p o ...
How do you determine the length of a right triangle?
b = √ (c² - a²) for hypotenuse c missing, the formula is. c = √ (a² + b²) Given angle and hypotenuse. Apply the law of sines or trigonometry to find the right triangle side lengths: a = c * sin (α) or a = c * cos (β) b = c * sin (β) or b = c * cos (α) Given angle and one leg.
How do you find the length of a special right triangle?
0:191:20How to use special right triangles to find the missing side lengthsYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe relationship is whatever the side length is times the square root of 2.. So this is as simple asMoreThe relationship is whatever the side length is times the square root of 2.. So this is as simple as five square root of 2..
How do you find the missing sides of a special right triangle 30 60 90?
0:123:2730-60-90 Special Right Triangles - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipYou divide by 2 to get back to the shorter leg. And then multiply by the square root of 3 to get theMoreYou divide by 2 to get back to the shorter leg. And then multiply by the square root of 3 to get the longer leg the toughest one often is when they give you this longer leg.
How do you find the missing sides of a special right triangle 45 45 90?
0:122:4245-45-90 Special Right Triangles - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipTimes longer so this is the ratio you want to remember X X and X square root of 2 4 45-45-90MoreTimes longer so this is the ratio you want to remember X X and X square root of 2 4 45-45-90 triangles so let's look at some examples. Say this one over here they give us the leg length is X.
How do you find the length of a 90 degree triangle?
0:072:07Find the Missing Length of a Right Triangle - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe Pythagorean theorem states that for every right triangle. The sum of the squares of the lengthsMoreThe Pythagorean theorem states that for every right triangle. The sum of the squares of the lengths of the legs equals. The square of the length of the hypotenuse. If you know the lengths of two of
What is the special right triangle rule?
A special right triangle is a right triangle with some regular feature that makes calculations on the triangle easier, or for which simple formulas exist. For example, a right triangle may have angles that form simple relationships, such as 45°–45°–90°. This is called an "angle-based" right triangle.
How do you work out the length of a 45 degree angle?
1:103:04Examples: Solve a 45-45 Right Triangle - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo we know this angle here would be 45 degrees notice that we're given the length of one of the legsMoreSo we know this angle here would be 45 degrees notice that we're given the length of one of the legs is equal to 12 feet well both of the legs of a 45-45-90 triangle would be equal to x.
What is the 45 45 90 triangle formula?
45°−45°−90° triangle is a commonly encountered right triangle whose sides are in the proportion 1:1:√2 . The measures of the sides are x , x , and x√2 . In a 45°−45°−90° triangle, the length of the hypotenuse is √2 times the length of a leg.
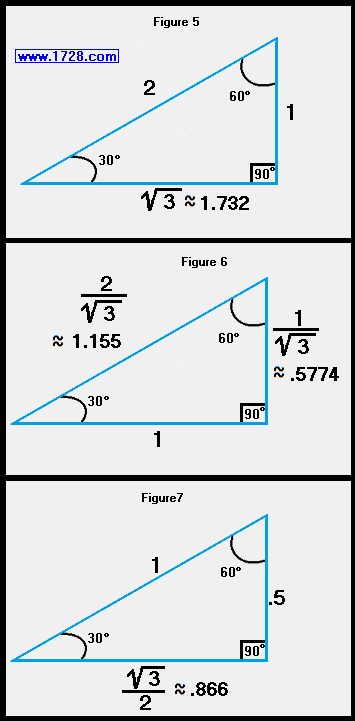
What are the sides of 30 60 90 triangle?
Sides of a 30 60 90 TriangleThe basic 30-60-90 triangle sides ratio is:The side opposite the 30° anglexThe side opposite the 60° anglex * √3The side opposite the 90° angle2x
How do you solve a 30 60 90 triangle with only the hypotenuse?
0:092:44How to determine the legs of a 30 60 90 triangle when given ... - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo if you're given the hypotenuse to find the short leg you have to divide by two. So guys all thisMoreSo if you're given the hypotenuse to find the short leg you have to divide by two. So guys all this is is 52 square root of three divided.
What are the side lengths of a 30 60 90?
30°-60°-90° Triangles There is a special relationship among the measures of the sides of a 30°−60°−90° triangle. A 30°−60°−90° triangle is commonly encountered right triangle whose sides are in the proportion 1:√3:2. The measures of the sides are x, x√3, and 2x.
How to find the missing side of a right triangle?
If you know two other sides of the right triangle, it's the easiest option; all you need to do is apply the Pythagorean theorem: a² + b² = c².
How to find area of a triangle?
As we remember from basic triangle area formula, we can calculate the area by multiplying triangle height and base and dividing the result by two . A right triangle is a special case of a scalene triangle, in which one leg is the height when the second leg is the base, so the equation gets simplified to:
How do you solve a right angle triangle with only one side?
To solve a triangle with one side, you also need one of the non-right angled angles. If not, it is impossible:
How to find side adjacent to angle?
Alternatively, multiply the hypotenuse by cos (θ) to get the side adjacent to the angle .
What is the symmetry of a right triangle?
If a right triangle is isosceles (i.e., its two non-hypotenuse sides are the same length) it has one line of symmetry. Otherwise, the triangle will have no lines of symmetry.
How are right angled triangles similar?
They are similar if all their angles are the same length, or if the ratio of 2 of their sides is the same.
How to find the hypotenuse of an angle?
If you have an angle and the side opposite to it, you can divide the side length by sin (θ) to get the hypotenuse. Alternatively, divide the length by tan (θ) to get the length of the side adjacent to the angle.
How to solve a triangle with 2 sides?
Step 1. Since we know 2 sides and 1 angle of this triangle, we can use either the Pythagorean theorem (by making use of the two sides) or use sohcahtoa (by making use of the angle and 1 of the given sides). Step 2. Step 2. Chose which way you want to solve this problem. There are several different solutions.
What is the name of the triangle with 1 side and 1 angle?
Since we know 1 side and 1 angle of this triangle, we will use sohcahtoa .
How to find the length of a hypotenuse?
Step 1. Step 1. Since we know 1 side and 1 angle of this triangle, we will use sohcahtoa . Step 2. Step 2. Set up an equation using the sine, cosine or tangent ratio Since we want to know the length of the hypotenuse, and we already know the side opposite of the 53° angle, we are dealing with sine.
What is the only thing you can't use to solve a sine problem?
The only thing you cannot use is sine, since the sine ratio does not involve the adjacent side, x, which we are trying to find.
How to solve for x in Pythagorean theorem?
Step 1. Step 1. Since we know 2 sides of this triangle, we will use the Pythagorean theorem to solve for x. Step 2. Rest of Steps. Substitute the two known sides into the Pythagorean theorem's formula : a 2 + b 2 = c 2 8 2 + 6 2 = x 2 100 = x 2 x = 100 x = 10.
Which theorem is used to solve for side t?
Since we know 2 sides of this triangle, we will use the Pythagorean theorem to solve for side t .
