
The working rule for obtaining the negation of a statement is given below:
- 1. Write the given statement with “not”. For example, the sum of 2 and 2 is 4. The negation of the given statement is “the sum of 2 and 2 is not 4”.
- 2. Make suitable modifications, if the statements involve the word “All” and “Some”.
How to obtain the negation of a statement?
The working rule for obtaining the negation of a statement is given below: 1 Write the given statement with “not”.#N#For example, the sum of 2 and 2 is 4. The negation of the given statement is... 2 Make suitable modifications, if the statements involve the word “All” and “Some”. More ...
How do you write the negation of P?
If “P” is a statement, then the negation of statement P is represented by ~P. The symbols used to represent the negation of a statement are “~” or “¬”. For example, the given sentence is “Arjun’s dog has a black tail”.
What is the negation of a proposition?
The negation of a proposition (¬q) means “it is not the case that q”. The truth value of the negation is the opposite of the truth value of the proposition. If the truth value of q is True, then the truth value of the negation of q (denoted as ¬q) is False.
What is negation in maths?
Sometimes in Mathematics, it is necessary to find the opposite of the given mathematical statement. The process of finding the opposite of the given statement is called “Negation”. In this article, we are going to learn the negation of a statement with many solved examples.
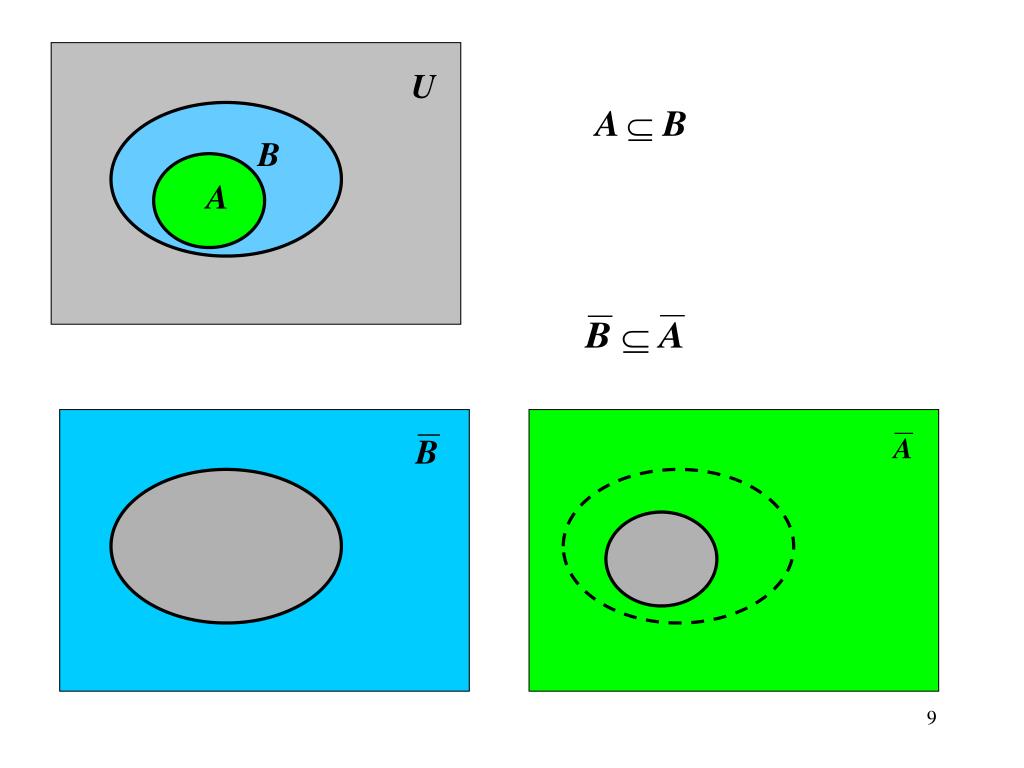
What is the negation of the proposition example?
Examples of negation. Proposition: The earth is round. Negation: It is not the case that the earth is round. Negation in simple English: The earth is not round.
What is the negation of P → Q?
p∨(∼q)
What is the negation of A or B?
Not A and Not B.In general, we have the same statement: The negation of "A or B" is the statement "Not A and Not B."
What is the converse of P → Q?
The converse of p → q is q → p. The inverse of p → q is ∼ p →∼ q. A conditional statement and its converse are NOT logically equivalent. A conditional statement and its inverse are NOT logically equivalent.
How do you negate a negative statement?
To negate complex statements that involve logical connectives like or, and, or if-then, you should start by constructing a truth table and noting that negation completely switches the truth value. The negation of a conditional statement is only true when the original if-then statement is false.
What is the negation of I walk or I chew gum?
I don't walk and I don't chew gum.
What's the negation of a statement?
In math, a negation of a statement can be thought of as another statement that has the opposite truth value of that statement.
Is negation and inverse the same?
The negation is (p∧∼(∼q)), and could be read as "It is raining and the sun shining". The inverse is ∼p⟹∼(∼q) and could be read "If it is not raining, then the sun is shining." (Bonus) The converse is (∼q)⟹p which can be read "if the sun is not shining, then it is raining."
Which is logically equivalent to P ∧ Q → R?
Solution. (p ∧ q) → r is logically equivalent to p → (q → r).
What is P -> Q?
P→Q means If P then Q. ~R means Not-R. P ∧ Q means P and Q. P ∨ Q means P or Q. An argument is valid if the following conditional holds: If all the premises are true, the conclusion must be true.
What is the truth value of P ∨ Q?
So because we don't have statements on either side of the "and" symbol that are both true, the statment ~p∧q is false. So ~p∧q=F. Now that we know the truth value of everything in the parintheses (~p∧q), we can join this statement with ∨p to give us the final statement (~p∧q)∨p....Truth Tables.pqp∨qTFTFTTFFF1 more row
What does P and Q stand for in logic?
The proposition p is called hypothesis or antecedent, and the proposition q is the conclusion or consequent. Note that p → q is true always except when p is true and q is false.
What does it mean when a mathematical logic is two-valued?
As this logic is two-valued (binary) and it means the negation of a false statement must be true and vice versa.
Can you find three-valued logic?
In addition, you can find three-valued logic and more like temporal logic. However, I don't think you are seeking about them.
What is the negation of p?
Definition: The negation of statement p is "not p." The negation of p is symbolized by "~p." The truth value of ~p is the opposite of the truth value of p.
Can we negate a negation?
We can also negate a negation. For example, the negation of ~p is ~ (~p) or p. This is illustrated in the example below.
Is the product of two negative numbers a positive number?
The product of two negative numbers is not a positive number. false. We can construct a truth table to determine all possible truth values of a statement and its negation. Definition: A truth table helps us find all possible truth values of a statement. Each statement is either True (T) or False (F), but not both.
Is the third sentence false?
Note that the third sentence is false since 2 is a prime number. It is possible that a closed sentence will have different truth values at different times. This is demonstrated in Example 2 below.
What is Meant by Negation of a Statement?
In Mathematics, the negation of a statement is the opposite of the given mathematical statement. If “P” is a statement, then the negation of statement P is represented by ~P. The symbols used to represent the negation of a statement are “~” or “¬”.
Is the negation of the negated sentence the original sentence?
It is observed that the “negation of the negated sentence is the original sentence”. Now, let us understand this with the help of an example.
