
How many dominant a alleles are there in our population?
The total number of dominant A alleles in our population equals 600, which is the sum of: - the number of AA individuals times 2 (the number of A alleles per individual) = 180 x 2 = 360 - the number of Aa individuals (times 1, the number of A alleles per individual) + 240 600
How do you find the frequency of an allele?
The frequency of an allele is defined as the total number of copies of that allele in the population divided by the total number of copies of all alleles of the gene.
How do you find the number of homozygous alleles?
If in a given sample of N individuals of which D are homozygous for one allele (A 1 A 1 ), H are heterozygous (A 1 A 2 ), and R are homozygous for the allele (A 2 A 2 ), then N D + H + R. Since each of the N individuals are diploid at this locus, there are 2N alleles represented in the sample. Each A 1 A 1 genotype has two A 1 alleles.
How are alleles counted in a two-allele system?
When codominant alleles are present in a two-allele system, each genotype has a characteristic phenotype. The numbers of each allele in both homozygous and heterozygous conditions may be counted in a sample of individuals from the population and expressed as a percentage of total number of alleles in a sample.
How do you determine the number of alleles and genotypes?
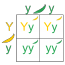
Number of genotypes for a given number of alleles Given n alleles at a locus, the number genotypes possible is the sum of the integers between 1 and n: With 2 alleles, the number of genotypes is 1 + 2 = 3. 3 alleles there are 1 + 2 + 3 = 6 genotypes. 4 alleles there are 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 = 10 genotypes.
What are the alleles in a population?
The fact that genes exist in alternate forms, called alleles, forms the basis for the study of population genetics. Populations are made up of members of the same species that interbreed.
How many alleles are in a group?
Alleles are the pairs of genes occupying a specific spot called locus on a chromosome. Typically, there are only two alleles for a gene in a diploid organism.
What formula is used to determine the frequency of alleles?
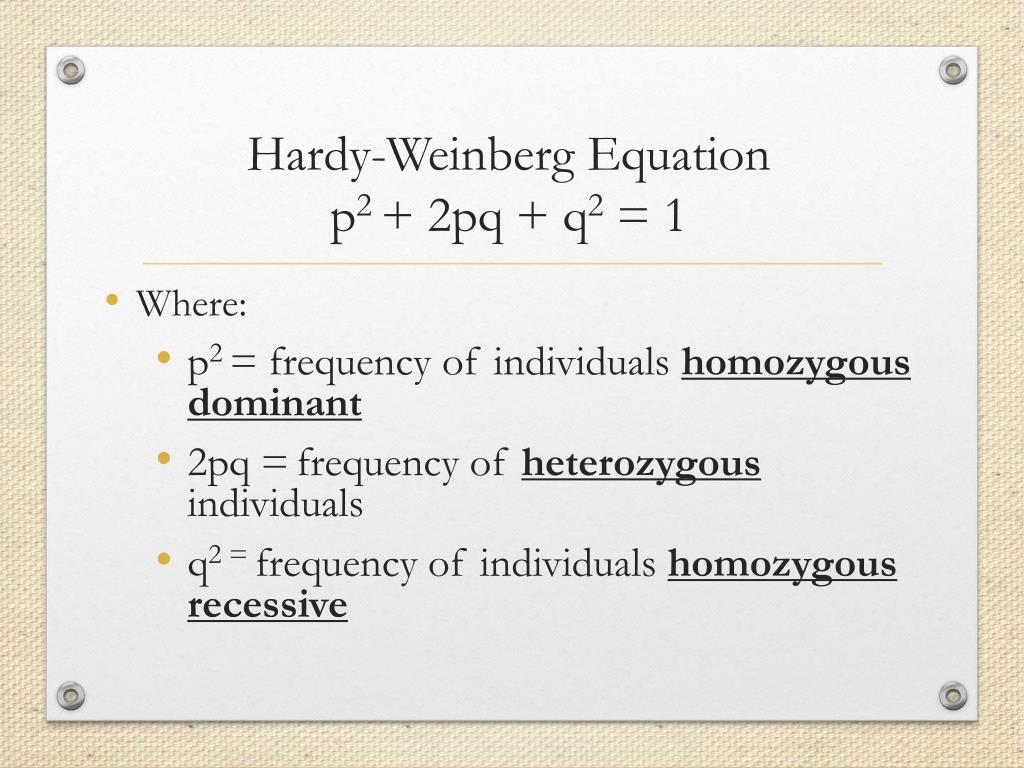
How do you calculate allele frequencies? Allele frequencies can be calculated by using the Hardy-Weinberg model using the formula p² + 2pq + q² = 1. P = frequency of dominant alleles and q is the frequency of recessive alleles.
What is the total number of alleles in the gene pool?
Allele Frequencies In a sexually reproducing species, each member of the population has two copies of each gene. Therefore, the total number of copies of each gene in the gene pool is 200.
What is an allele example?
An example is the human ABO blood group system; persons with type AB blood have one allele for A and one for B.
How are alleles named?
Allele designations begin with a letter and contain alphanumeric characters. Punctuation marks occur in certain cases where they convey meaning. Allele designations appear as superscripted short alphanumeric strings following the gene symbol of which they are an allele and serve as an acronym for the allele name.
How many alleles of a gene are present on each chromosome?
Hence, each chromosome carries one allele of a gene in a diploid individual.
What is allele frequency in a population?
An allele frequency is calculated by dividing the number of times the allele of interest is observed in a population by the total number of copies of all the alleles at that particular genetic locus in the population. Allele frequencies can be represented as a decimal, a percentage, or a fraction.
What is allele in biology?
An allele is one of two or more versions of DNA sequence (a single base or a segment of bases) at a given genomic location. An individual inherits two alleles, one from each parent, for any given genomic location where such variation exists. If the two alleles are the same, the individual is homozygous for that allele.
What is allele frequency example?
Allele frequency refers to how frequently a particular allele appears in a population. For instance, if all the alleles in a population of pea plants were purple alleles, W, the allele frequency of W would be 100%, or 1.0.
How is allele frequency related to population size?
So, while allele frequencies are almost certain to change in each generation, the amount of change due to sampling error decreases as the population size increases. Perhaps the most important point is that the direction of the change is unpredictable; allele frequencies will randomly increase and decrease over time.
How to find the number of alleles in a population?
To find the number of alleles in a given population, you must look at all the phenotypes present. The phenotypes that represent the allele are often masked by dominant and recessive alleles working in conjunction. To analyze the allele frequency in a population, scientists use the Hardy-Weinberg (HW) equation.
What is the definition of allele frequency?
The allele frequency is the number of individual alleles of a certain type, divided by the total number of alleles of all types in a population. In simple terms, the allele frequency describes how common an allele is within a population.
How to find the allele frequency of Q2?
The white rabbits account for 16 of the 100 total rabbits. In a percentage, this is exactly 16%, or 0.16. This number is equivalent to q 2. Taking the square root, we find that the allele frequency of q (white) is 0.4, or 40%.
What is the lethal allele of a plant?
1. In a population of flowers, a certain allele is lethal to the plant if the plant is homozygous recessive for the genotype. A single recessive allele with a dominant allele, a heterozygote, will produce a totally health plant, indistinguishable from a homozygous dominant plant. A scientist fertilizes 100 seeds, of which only 75 sprout. The scientist thinks the plants that didn’t sprout all had the lethal homozygous recessive genotype. What is the allele frequency of the recessive allele in the population?
How does allele frequency change over time?
Allele frequency can change over time as evolution acts upon a population and the population adapts by increasing or decreasing the frequency of certain alleles. Calculating allele frequencies is a complex topic, which combines aspects of math and genetics. In general, all of the alleles in a population add up to 100%.
How is the allele frequency different from the phenotypic ratio?
The allele frequency is different from the phenotypic ratio in that it accounts for all alleles, even if they are recessive and are “hidden” within carrier organisms. The phenotypic ratio only describes the phenotypes, or actual physical features that are present within a population.
What is the sum of allele frequencies of p and q?
If this is the case, the sum of the allele frequencies of p and q must equal 1 because with only two alleles the combined frequency must equal 100%.
Abstract
Previously reported methods for estimating the number of different alleles at a single locus in a population have not described a useful general result. Using the number of alleles observed in a sample gives an underestimate for the true number of alleles.
METHOD
Suppose there are M different alleles for a locus in a population. A random sample of n alleles is drawn from the population. Let Xi be the number of the i th type of allele observed in the sample and D the number of different observed allele types. Furthermore, let fj be the number of alleles that have j representatives in the sample.
SIMULATION STUDY
Simulation studies were performed under the following three mutation models:
EXAMPLES AND APPLICATIONS
Estoup et al. ( 1995) published a set of microsatellite data from nine populations of honey bee ( Apis Mellifera L.) subspecies. The adequacy of two mutation models usually used for microsatellite, IAM and RMM, are tested by comparing the observed and theoretical number of alleles.
DISCUSSION
A drawback of the sample coverage method is that, when the allele number is large but the sample size is relatively small and all the alleles in the data are different ( i.e., D = f1 = n ), we have ˆc = 0 and hence ˆM = ∞. Although in this case we would expect there are many alleles in the population, this estimate is not useful.
Acknowledgement
The authors thank anonymous reviewers for their help. This work was supported in part by National Institutes of Health grant GM 45344.
Where are alleles located in a cell?
c) alleles of a given gene are located on only one pair of chromosomes among the many chromosomes in each cell, and
How many alleles can a diploid have?
a) a given diploid individual can possess only one combination of these alleles,
What do students learn about genes?
Students of biology are usually very eager to learn about genes, the molecular units that carry biological information from one generation to the next. At the undergraduate level they grasp that genes are made up of long stretches of DNA present in chromosomes. They have no trouble agreeing that the subtle differences in the DNA sequence across individuals brings about the variations of a trait, say human eye colour. They are happy to realise that most of these variations arise due to viable mutations, possibly from the same original variety or allele. Mention that the population harbors several alleles of gene A — and several concepts assimilated until then seem to evaporate in a bunch.
Can DNA be identical across individuals?
First of all, it is important to remember that the DNA sequence of a gene need not be identical across individuals. Subtle differences in DNA sequences give rise to gene variants, referred to as alleles of the gene. Since the alleles of the same gene in individual 1 may be different from the alleles present in individuals 2 or 3, and so on, the population as a whole may contain any number of alleles of that gene. Some alleles may occur more frequently than others.
Can gene A be found on both chromosomes?
Answer: False. The locus for gene A can be present on only one of those chromosomes, not on both. 2. Siblings Vidya, Ankita and Sneha all have one allele for gene B in common, but the second allele is shared only by Vidya and Sneha.
What is the frequency of each allele?from varsitytutors.com
Therefore, we know that the frequency of each allele is equal to 0.5.
What percentage of alleles are recessive?from varsitytutors.com
This value tells us that 60% of all the alleles in the population are recessive ( b ).
How to determine the tail length of an aardvark?from varsitytutors.com
Tail length in a population of aardvarks is determined by one gene, where L =long tails and l =short tails. If the frequency of L in the population is 0.4, determine the expected frequencies of each possible genotype: homozygous dominant ( LL ), heterozygous ( Ll ), and homozygous recessive ( ll ).
How many alleles are in a population in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?from varsitytutors.com
Consider a population in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. A gene in the population has two alleles. The gene pool shows a distribution of 80% of the dominant allele and 20% the recessive allele.
How many percent of the population is homozygous recessive?from varsitytutors.com
16% of the population is homozygous recessive. We then take the square root of to find :
Is the brown allele dominant or recessive?from varsitytutors.com
We know that the black allele ( B) is dominant and the brown allele ( b) is recessive.
Full text
Full text is available as a scanned copy of the original print version. Get a printable copy (PDF file) of the complete article (453K), or click on a page image below to browse page by page. Links to PubMed are also available for Selected References.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
What is the probability that each parent transmits a given allele to an offspring?
Table 4 demonstrates Hardy’s and Weinberg’s key insight, that with random mating, the probability that each parent transmits a given allele to an offspring is equal to that allele’s frequency in the population.
When a population is in equilibrium, genotype frequencies can be calculated from allele frequencies?
The key insight is that with random mating, the probability that each parent transmits a given allele to an offspring is equal to that allele’s frequency in the population.
Allele Frequency Definition
Allele Frequency Overview
- The allele frequency is different from the phenotypic ratioin that it accounts for all alleles, even if they are recessive and are “hidden” within carrier organisms. The phenotypic ratio only describes the phenotypes, or actual physical features that are present within a population. To find the allele frequency, scientists must consider heterozygous individuals, which may be hiding a recessive a…
How to Calculate Allele Frequency
- To find the number of alleles in a given population, you must look at all the phenotypes present. The phenotypes that represent the allele are often masked by dominant and recessive alleles working in conjunction. To analyze the allele frequency in a population, scientists use the Hardy-Weinberg (HW) equation.The Hardy-Weinberg equation is written ...
Allele Frequency Example
- In a simplified scenario, p and q are the only alleles in the population, and the population is not developing any mutations.If this is the case, the sum of the allele frequencies of p and q must equal 1 because with only two alleles the combined frequency must equal 100%.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Trying to Find p First
One mistake that students commonly make is trying to calculate p by observing the population, then taking the square root. This does not work in typical recessive/dominant allele relationships, simply because a dominant allele can hide a recessive allele. For instance, if we were to calculat… - Relating Allele Frequency to Fitness
A common misconception of allele frequency is that it is directly related to the evolutionary fitness of a particular allele. Just because an allele is frequent or infrequent has no bearing on the fitness of that allele.For example, many recessive traits that are deleterious “hide” in a population. This …