Can You give Me list of oxidizing agents?
There are hundreds of different oxidizing agents, including various chromates, dichromates, halogens, bromates and nitrites. There are two different classes of oxidizing agents, organic and inorganic, both of which are considered hazardous materials.
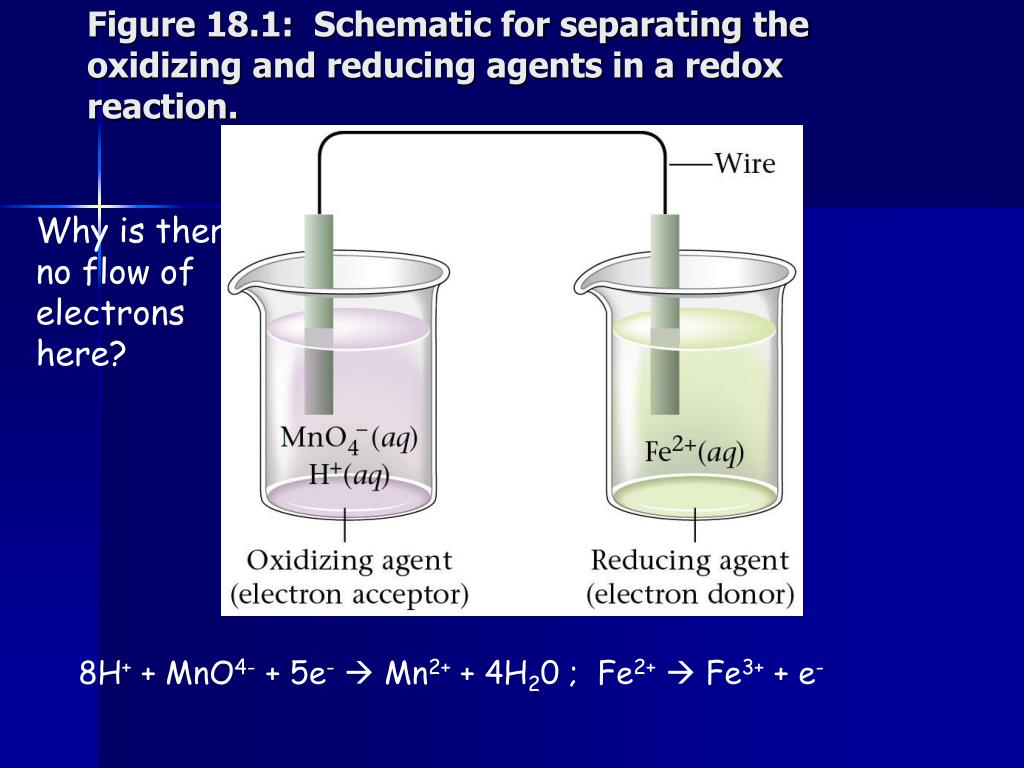
Can KMnO4 act as an oxidizing and reducing agent?
The oxalic acid acts as a reducing agent, and the KMnO4 acts as an oxidizing agent. KMnO4 acts as an indicator of where the permanganate ions are a deep purple colour. In this redox titration, MnO4– is reduced to colourless manganous ions (Mn2+) in the acidic medium. In which medium oxidising power of KMnO4 is Max?
Is NADH is reducing or oxidizing agent?
NADH is a reducing agent because it REDUCES something AND IN TURN gets oxidized. An oxidizing agent OXIDIZES something and in turn gets reduced. So NADH in its reduced form can donate a H (AKA reduce something else), thus getting oxidized because it lost an electron--reducing agent thank you so much! This confused me for a long time too.
Is oxalic acid an oxidizing or reducing agent?
The permanganate ion removes electrons from oxalic acid molecules and thereby oxidizes the oxalic acid. Thus, the MnO 4- ion acts as an oxidizing agent in this reaction. Oxalic acid, on the other hand, is a reducing agent in this reaction.

What is reducing agent in chemistry?
A reducing agent in chemistry is a compound that easily loses electrons, thus increasing its oxidation state and being oxidized.
What is a oxidizing agent in chemistry?
An oxidizing agent in chemistry is a compound that easily gains electrons, thus decreasing its oxidation state and being reduced.
How do you identify oxidizing and reducing agents?
Oxidizing and reducing agents are identified by looking at the starting and ending oxidation charges of compounds in a reaction. Oxidizing agents d...
Oxidizing Agent
An oxidizing agent is a compound that oxidizes other compounds. Oxidizing agents can also be called oxidants or oxidizers. The process of oxidation occurs when the oxidizing agent accepts electrons from another compound, called the reducing agent.
What is a Reducing Agent?
Now that we've looked at oxidizing agents, what is a reducing agent? A reducing agent is the opposite (or the compound causing the reaction to go the opposite direction) of the oxidizing agent, and it reduces other compounds. It does this by giving up electrons to the oxidizing agent, and the reducing agent itself becomes oxidized in the process.
Oxidizing Agent vs Reducing Agent
Oxidizing and reducing agents always occur in the same reactions, because if one compound releases an electron then there must be another compound to receive it. The main differences between oxidizing agents versus reducing agents include the following:
Identifying Oxidizing and Reducing Agents
In order identify oxidizing and reducing agents, we need to look at specific examples of chemical reactions. An oxidizing agent will:
Which compounds are good oxidizing agents?
Another place to look for good oxidizing agents is among compounds with unusually large oxidation states, such as the permanganate (MnO 4- ), chromate (CrO 42- ), and dichromate (Cr 2 O 72-) ions, as well as nitric acid (HNO 3 ), perchloric acid (HClO 4 ), and sulfuric acid (H 2 SO 4 ). These compounds are strong oxidizing agents because elements become more electronegative as the oxidation states of their atoms increase.
What is the oxidizing agent of oxalic acid?
The permanganate ion removes electrons from oxalic acid molecules and thereby oxidizes the oxalic acid. Thus, the MnO 4- ion acts as an oxidizing agent in this reaction.
What are some good reducing agents?
Good reducing agents include the active metals, such as sodium, magnesium, aluminum, and zinc, which have relatively small ionization energies and low electro-negativities. Metal hydrides, such as NaH, CaH 2, and LiAlH 4, which formally contain the H - ion, are also good reducing agents. Some compounds can act as either oxidizing agents ...
Which element is the strongest oxidizing agent?
Elemental fluorine, for example, is the strongest common oxidizing agent. F 2 is such a good oxidizing agent that metals, quartz, asbestos, and even water burst into flame in its presence. Other good oxidizing agents include O 2, O 3, and Cl 2, which are the elemental forms of the second and third most electronegative elements, respectively.
Is oxidizing acid a reducing agent?
Oxalic acid, on the other hand, is a reducing agent in this reaction. By giving up electrons, it reduces the MnO 4- ion to Mn 2+. Atoms, ions, and molecules that have an unusually large affinity for electrons tend to be good oxidizing agents. Elemental fluorine, for example, is the strongest common oxidizing agent.
Where are the strongest reducing agents?
The strongest reducing agents will be found at the corner of the table where sodium and potassium metal are listed.
Is hydrogen gas an oxidizing agent?
Some compounds can act as either oxidizing agents or reducing agents. One example is hydrogen gas, which acts as an oxidizing agent when it combines with metals and as a reducing agent when it reacts with nonmetals.
What is the difference between oxidizing and reducing agents?
Reducing agents are the element (s) that are oxidized (oxidation state increases) and oxidizing agents are the element (s) that are reduced oxidation state decreases).
Is nitrogen a redox reaction?
So, look for the two (or more) elements in an equation whose reaction change requires a CHANGE in their oxidation state. If no change is found, the reaction is not a redox reaction (there are many more types). a) Nitrogen is being reduced from an oxidation state of 0 to -3, so it is the oxidizing agent.
Is nitrogen a reducing agent?
b) Nitrogen is being oxidized from an oxidation state of 0 to +1, so it is the reducing agent. Oxygen is being reduced from an oxidation state of 0 to -2, so it is the oxidizing agent. Answer link.
What is Oxidation and Reduction?
Reduction is loss of oxygen atoms and gain of electrons and hydrogen. While oxidation is gain of oxygen and loss of electrons and hydrogen. Thus, we can say when an element gets oxidized, its oxidation state increases while in reduction it decreases. Same thing is explained in concise way in the table given below –
What are the reactions in which oxidation and reduction both take place?
The reactions in which oxidation and reduction both take place are called redox reactions.
How does iron react with copper?
In the above reaction iron is losing 2 electrons thus, acting as a reducing agent. Oxidation state of iron as a reactant is 0 while +2 as a product in the reaction. Thus, the oxidation state of iron is increasing, so oxidation is taking place. While another reactant copper is gaining two electrons and working as an oxidizing agent. The oxidation state of copper is +2 as reactant in the reaction while 0 as product so reduction is taking place. Thus, iron is acting as a reducing agent but getting oxidized itself while copper is acting as an oxidizing agent but reduced.
What are some examples of weak reducing agents?
Strong reducing agents are weak oxidizing agents. Sodium, hydrogen, and lithium are examples of strong oxidizing agents. While weak reducing agents cannot lose electrons easily. Fluorine, chlorine, iron etc. are weak reducing agents. We can know the strength of reducing agents by electrochemical series as well. As we move upwards from hydrogen in the electrochemical series then the strength of reducing agents decreases. While if we move downwards from hydrogen then the strength of reducing agents increases. (image will be uploaded soon).
What happens when we move upwards from hydrogen?
As we move upwards from hydrogen in the electrochemical series then the strength of reducing agents decreases. While if we move downwards from hydrogen then the strength of reducing agents increases. (image will be uploaded soon).
What is reducing agent?
Reducing agent is an element (or compound) that –. Loses its electron/s to an electron recipient group and. Itself gets oxidized in a redox chemical reaction. Thus, reducing agent reduces others while itself gets oxidized by losing electrons.
Which oxidizing agent is the strongest?
Sodium, hydrogen, and lithium are examples of strong oxidizing agents. While weak reducing agents cannot lose electrons easily. Fluorine, chlorine, iron etc. are weak reducing agents. We can know the strength of reducing agents by electrochemical series as well.
