How to Calculate Dependent Probability?
- Get the compound probability of an event and any one dependent probability.
- Divide the compound probability by the known event probability.
- The value is called the dependent probability.
What is the formula for dependent probability?
Give the formula to find the probability of occurrence of A and B, when A and B are dependent events. The probability of occurrence of A and B is given by the formula, P(A and B) = P(A) · P(B|A).
How will you solve the probability dependent events?
To find the probability of dependent events, one uses the formula for conditional probability given below: If the probability of events A and B is P(A) and P(B) respectively then the conditional probability of event B such that event A has already occurred is P(B/A).
How do you find the probability of dependent and independent events?
1:576:44Probability of Independent and Dependent Events (6.2) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd all we have to do is multiply them together 1 over 6 times 1 over 2. Give an answer of 1 over 12MoreAnd all we have to do is multiply them together 1 over 6 times 1 over 2. Give an answer of 1 over 12 as a result the probability of rolling a 5 and getting heads is equal to 1 over 12 or 0.08 33.
How do you find the probability of multiple dependent events?
Just multiply the probability of the first event by the second. For example, if the probability of event A is 2/9 and the probability of event B is 3/9 then the probability of both events happening at the same time is (2/9)*(3/9) = 6/81 = 2/27.
How do you find the probability of three dependent events?
0:253:16Probability of Dependent Events | MathHelp.com - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo let's first find the probability that Andrew chooses a brown sock. Since there are four brownMoreSo let's first find the probability that Andrew chooses a brown sock. Since there are four brown socks in the drawer. And there are eight plus four or 12 total socks in the drawer.
What is the example of dependent event?
More formally, we say that when two events are dependent, the occurrence of one event influences the probability of another event. Simple examples of dependent events: Not paying your power bill on time and having your power cut off. Being the first person to enter a movie theater and finding a good seat.
How do you calculate probability?
Probability is calculated by dividing the number of ways the event can occur by the total number of outcomes. Probability and odds are different concepts. Odds are the probability that something happens divided by the probability that it doesn't happen.
How do you find the probability of A or B?
If events A and B are mutually exclusive, then the probability of A or B is simply: p(A or B) = p(A) + p(B).
How do you calculate probability example?
Using the example of the rolling dice, you'd calculate your total probability by multiplying the 1/6 chances you calculated: P(A and B) = 1/6 x 1/6 = 1/36. Using these results, there's a 1/36 chance of rolling "6" on one die at the same time you roll a "6" with the other.
How do you find the probability of A and B not independent?
If Events A and B are not independent, then P(A and B) = P(A) x P(B|A). Applying this to the problem of two aces, the probability of drawing two aces from a deck is 4/52 x 3/51 = 1/221.
How do you find the probability of A or B or C?
P(A ∪ B ∪ C) = P(A) + P(B) + P(C) − P(A ∩ B) − P(A ∩ C) − P(B ∩ C) + P(A ∩ B ∩ C).
How do you solve independent probability?
Events A and B are independent if the equation P(A∩B) = P(A) · P(B) holds true. You can use the equation to check if events are independent; multiply the probabilities of the two events together to see if they equal the probability of them both happening together.
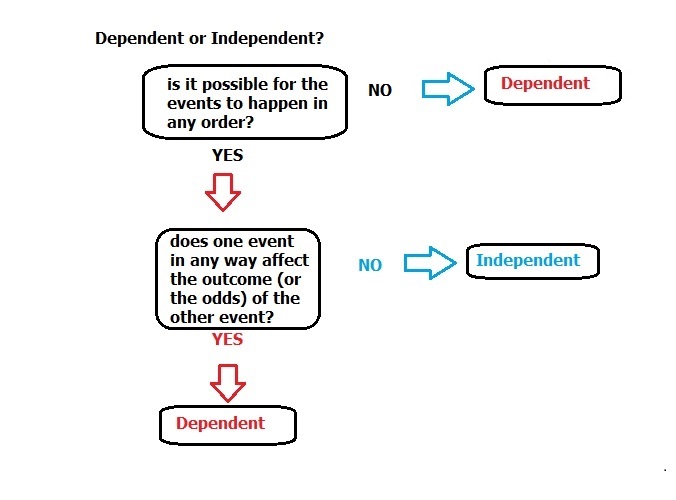
How do you know if two events are dependent?
Two events are dependent if the outcome of the first event affects the outcome of the second event, so that the probability is changed.
What is conditional probability of dependent events?
When the occurrence of one event affects the occurrence of another subsequent event, the two events are dependent events. The concept of dependent events gives rise to the concept of conditional probability.
How do you calculate probability?
Probability is calculated by dividing the number of ways the event can occur by the total number of outcomes. Probability and odds are different concepts. Odds are the probability that something happens divided by the probability that it doesn't happen.
What is dependent event?
Dependent events are those which depend upon what happened before. These events are affected by the outcomes that had already occurred previously. i.e. Two or more events that depend on one another are known as dependent events. If one event is by chance changed, then another is likely to differ.
What is the probability of a sure event?
An event whose chances of happening is 100 % is called a sure event . The probability of such an event is 1. In a sure event, one is likely to get the desired output in the whole sample experiment. On the other hand, when there are no chances of an event happening, the probability of such an event is likely to be zero. This is said to be an impossible event.
What is the probability of drawing a red ball followed by a blue ball?
1/ 7 will be the probability value of drawing a red ball followed by a blue ball.
What affects the probability of the second draw?
The result of the first draw will affect the probability of the second draw.
What is probability theory?
Probability theory is an important concept that is quite familiar to the students who study mathematics in higher classes. For example Weather forecast of some area says that there is a twenty percent probability that it will rain tomorrow. The probability is a chance of some event to happen.
What is total event?
Total events are defined as all the outcomes which may possibly occur relevant to the experiment asked in the question. Also, the events of interest are known as favorable events. More elaborately, in the branch of probability, an event is defined to be the set of all the possible outcomes for an experiment.
How to calculate probability of two events occurring for each player?
Now, calculate the probability of both events occurring for each player by multiplying the probability of the first event and second event together.
What is dependent event?
These events are called dependent events since the outcome of the second (or third) event depends on the outcome of the first event.
Which principle allows us to calculate the probability of two or more events occurring?
The principle that allows us to calculate the probability of two or more events occurring is also called the Multiplication Rule and is written as follows:
What is the ratio of the number of desired outcomes?
Probability is formally defined as the ratio of the number of desired outcomes (what you want to happen) to the number of total possible outcomes (what could possibly happen). Probability is a ratio, so it can be expressed as a fraction, a decimal, or a percent.
Why do we use probability?
You’ve used probability to describe the likelihood of events occurring. In this lesson, you will investigate how you can calculate the probability of two or more events. Probability is used to describe how likely something is to happen. For example, you may have heard the weather forecaster describe the chances that it will rain today.
Is the second spin dependent on the first spin?
That is, the results of the second spin do not depend on the results of the first spin. Since that is the case, we can call these events independent events.
What is dependent event?
If the occurrence of event A affects the occurrence or non-occurrence of event B , the events are termed as dependent events. For example: A coloured ball is drawn from a bag. If another ball is drawn from the bag before replacing the first ball, the probability of drawing the second ball will be affected by the probability of drawing the first ball.
What is the probability of simultaneous happening of two events?
The probability of simultaneous happening of two events A and B is equal to the probability of B multiplied by the conditional probability of A with respect to B.
What is the probability that the first ball is white and the second ball is blue when the first ball drawn is not replaced?
Therefore, the probability that the first ball is white and the second ball is blue when the first ball drawn is not replaced is 7/40.
Can conditional probability be zero?
For conditional probability of event A with respect to event B, probability of event B can never be zero. Conversely, for conditional probability of event B with respect to event A, probability of event A can never be zero.