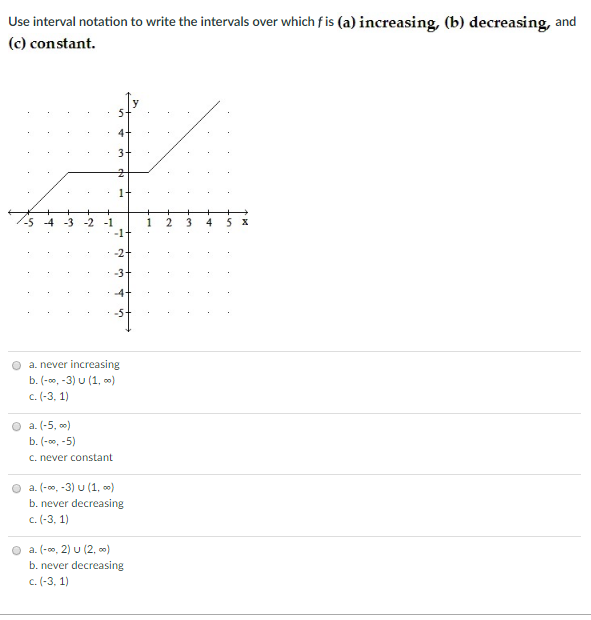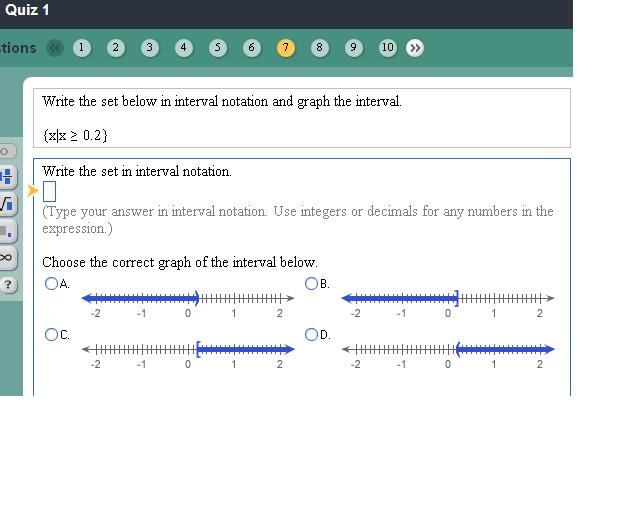
What is the sample interval?
Sampling interval is the distance or time between which measurements are taken, or data is recorded. In research terms, also referred to as 'nth selection', this is when we select every nth participant (sampling unit) in the list; this sampling interval produces a random selection from throughout the total population.
What is interval sampling in research?
a form of random sampling in which participants at uniformly separated points are selected for study and the starting point for selection is arbitrary. An example is choosing every 10th name from a list of candidates.
What should I set my sampling interval to?
A good starting sample interval is 15 seconds (which happens to be the default), but avoid longer than 1 min.
What is sample size formula?
Sample Size n = N * [Z2 * p * (1-p)/e2] / [N – 1 + (Z2 * p * (1-p)/e2] Source: Sample Size Formula (wallstreetmojo.com)
How do you find the sampling fraction?
The sampling fraction is the proportion of a population to be included in a sample . The sampling fraction is equal to the sample size divided by the population size, n/N.
What is sampling interval AMD?
Sampling Interval: The time between each update of performance data. Sampling intervals can range from 1 to 10 seconds and can be adjusted in increments of 1 sec. Log Performance to File: Indicates where performance logs are saved to – Performance logs are saved as CSV files.
How do I optimize AMD settings for gaming?
3:5416:36How to Optimize AMD Radeon Settings For GAMING ... - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipOn tessellation mode is going to be set to either amd. Optimized. Or if you would like anMoreOn tessellation mode is going to be set to either amd. Optimized. Or if you would like an experimental tweak head down to override. Application settings set the maximum.
How do I set my AMD graphics card settings to get max performance?
Open AMD Radeon Settings or control center. Select Preferences, then Radeon Additional Settings. Expand Power and click Switchable Graphics Global Settings. Select High performance for the Graphic Setting.
What are the two categories of samples?
There are two types of sampling methods:Probability sampling involves random selection, allowing you to make strong statistical inferences about the whole group.Non-probability sampling involves non-random selection based on convenience or other criteria, allowing you to easily collect data.
What is systematic sampling and example?
Systematic sampling is a probability sampling method where researchers select members of the population at a regular interval – for example, by selecting every 15th person on a list of the population. If the population is in a random order, this can imitate the benefits of simple random sampling.
What is snowball sampling?
Snowball sampling is a recruitment technique in which research participants are asked to assist researchers in identifying other potential subjects.
What is a sampling interval in audit?
The systematic sampling is also referred as 'interval' sampling. This sampling technique involves the auditor to take the number of sampling units in the population and segregate this into the sample size so as to provide a sampling interval.
What happens if the analysis interval is less than the sample interval?
If an analysis interval is selected that is less than the sample interval in which the counter log was collected, then the tool will revert the analysis interval to the same as the sample interval. This isn't ideal, but will still work ( Figure 12.4 ).
How long should a sample interval be for a latency counter?
Therefore, when sampling the “latency” counters, try to find the “Goldilocks” range of not too often and not too long. A good starting sample interval is 15 seconds (which happens to be the default), but avoid longer than 1 min.
How many samples can you collect in Perfmon?
If you are still not sure of what sample interval to use, then start with an interval that will collect about 1000 samples though the duration of the data collection. The reasoning for this is Perfmon's line chart can only display up to 1000 data points at a time and the extra samples are hidden in an equal distribution. Limiting the counter log to 1000 or less samples prevents Perfmon from needing to hide some of the data.
How to avoid input/output identification in step 4?
Note that the input/output identification performed in Step 4 could be avoided by taking for Rd any of the D-T models Rds, Rdr or Rdb obtained in Step 2 by discretizing the given C-T model Rc. Algorithm IDMV is explained in Appendix A9.
How to obtain presampling filter?
To obtain a presampling filter that rejects potential aliases, we need to pass low frequencies, up to almost half the sample rate, and reject frequencies above it. We need a frequency response that is constant at unity up to just below 0.5 fS, whereupon it drops to zero. We need a filter function whose frequency response – not time response – resembles a boxcar.
Can we minimize loop time?
There are two main options: We can either minimize loop time (sample period) or minimize the resources. Figure 7.16 illustrates the first case—the loop time is decreased to two.
What is the confidence interval in statistics?
In statistics, confidence intervals usually go hand-in-hand with a confidence level and margin of error. Basically, the confidence interval tells you how confident you can be that a statistic from poll or survey results would be reflected within that same range if the entire population were surveyed.
Why are confidence levels and intervals used?
Confidence levels and intervals are used because there’s no way to be 100% sure that the results for an entire population will match the data represented in the sample. There will always be deviations and margins of error.
How to find alpha value of confidence level?
Just like the t-distribution example above, we’ll calculate the alpha value by subtracting our confidence level in decimal form from “one” and then dividing that result by “two.” Subtracting .95 from 1 gives us .05, divided by 2 for a total of .025.
How to find the standard error of a t-value?
Now that we’ve found the T-value, we need to calculate the standard error. To do this, we’ll divide the standard deviation by the square root of our sample size. In this example, $250 will be divided by the square root of 20, which gives us 55.9016994375.
What is the formula for normal distribution?
The formula we’ll be using is x̄ ± z (σ / (√n)). For our values, x̄ is the mean, z is the z-score, σ is the standard deviation of the sample, and n is the number of items in the sample.
What is the formula for t score?
The formula we’ll be using is x̄ ± t* σ / (√n). For our values, x̄ is the mean, t is the t-score, σ is the standard deviation of the sample, and n is the number of items in the sample.
How to find the mean of a number?
To find the mean (x̄), add all of the numbers together and divide by 12 since there are a total of tw elve numbers in this sample. Our mean is 64.75.
How to calculate confidence interval?
The formula for Confidence Interval can be calculated by using the following steps: Step 1: Firstly, determine the sample mean based on the sample observations from the population data set. It is denoted by. Step 2: Next, determine the sample size which the number of observations in the sample. It is denoted by n.
What is the definition of confidence interval?
In other words, the confidence interval represents the amount of uncertainty expected while determining the sample population estimate or mean of a true population.
What is the confidence interval at 90%?
Therefore, the Confidence Interval at a 90% confidence level is 3.22 to 3.38.
What is the confidence interval at 95% confidence level?
Therefore, the Confidence Interval at a 95% confidence level is 3.20 to 3.40.
How many measurements are needed to find 95% interval?
To achieve 95% interval estimation for the mean boiling point with total length less than 1 degree, the student will have to take 23 measurements.
What is interval estimation?
Interval estimation is the use of sample data to calculate an interval of possible (or probable) values of an unknown population parameter, in contrast to point estimation, which is a single number.
What is the critical value for a 95% confidence interval?
The critical value for a 95% confidence interval is 1.96, where 1 − 0.95 2 = 0.025. A 95% confidence interval for the unknown mean.
Does an increase in sample size decrease the length of the confidence interval?
An increase in sample size will decrease the length of the confidence interval without reducing the level of confidence. This is because the standard deviation decreases as n increases.
What is a class interval?
In a frequency distribution, a class interval represents the difference between the upper class limit and the lower class limit. In other words, a class interval represents the width of each class in a frequency distribution. The following examples show how to calculate class intervals for different frequency distributions.
What is the size of the class interval for the second class?
Similarly, the size of the class interval for the second class is 31 – 35 = 4.
When to use confidence intervals?
One place that confidence intervals are frequently used is in graphs. When showing the differences between groups, or plotting a linear regression , researchers will often include the confidence interval to give a visual representation of the variation around the estimate.
How to find the MSE of a sample?
To find the MSE, subtract your sample mean from each value in the dataset, square the resulting number, and divide that number by n − 1 (sample size minus 1) .
What is the confidence level of a confidence interval?
The confidence level is the percentage of times you expect to reproduce an estimate between the upper and lower bounds of the confidence interval, and is set by the alpha value.
What is the range of values that you expect your estimate to fall between a certain percentage of the time?
The confidence interval is the range of values that you expect your estimate to fall between a certain percentage of the time if you run your experiment again or re-sample the population in the same way.
How to find standard deviation in statistics?
Most statistical software will have a built-in function to calculate your standard deviation, but to find it by hand you can first find your sample variance, then take the square root to get the standard deviation.
Why are confidence intervals useful?
Confidence intervals are useful for communicating the variation around a point estimate.
How many steps are there to find critical value?
There are three steps to find the critical value.
What is a confidence interval in statistics?
In statistics, a confidence interval is an estimated range of likely values for a population parameter, for example 40 ± 2 or 40 ± 5%. Taking the commonly used 95% confidence level as an example, if the same population were sampled multiple times, and interval estimates made on each occasion, in approximately 95% of the cases, the true population parameter would be contained within the interval. Note that the 95% probability refers to the reliability of the estimation procedure and not to a specific interval. Once an interval is calculated, it either contains or does not contain the population parameter of interest. Some factors that affect the width of a confidence interval include: size of the sample, confidence level, and variability within the sample.
What are the factors that affect the width of a confidence interval?
Some factors that affect the width of a confidence interval include: size of the sample, confidence level, and variability within the sample.
What to do if sample size is too big?
If the sample size is too big to manage, you can adjust the results by either. decreasing your confidence level. increasing your margin of error. This will increase the chance forerror in your sampling, but it can greatly decrease the number of responses you need.
What is the most common confidence interval?
This is a separate step to the similarly-named confidence interval in step 2. It deals with how confident you want to be that the actual mean falls within your margin of error. The most common confidence intervals are 90% confident, 95% confident, and 99% confident.