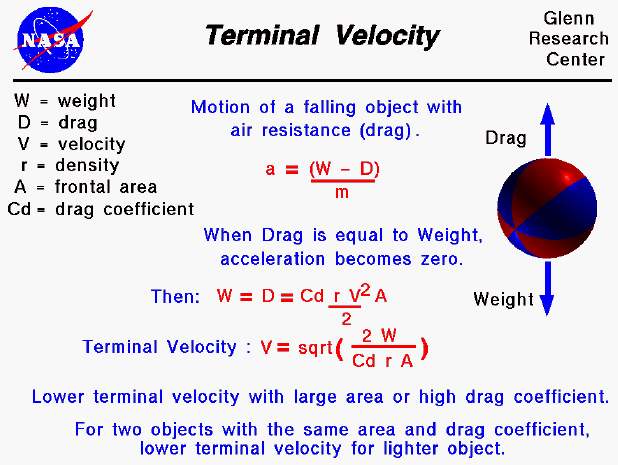
How to Calculate Terminal Velocity
- Method 1 Solving for Terminal Velocity. Use the terminal velocity formula, v = the square root of ( (2*m*g)/ (ρ*A*C)). ...
- Method 2 Find the Gravitational Force. Find the mass of the falling object. This should be measured in grams or kilograms, in the metric system. [3]
- Method 3 Determine the Drag Force. Get the density of the medium. ...
How long does it take to reach terminal velocity?
With air resistance acting on an object that has been dropped, the object will eventually reach a terminal velocity, which is around 53 m/s (195 km/h or 122 mph) for a human skydiver. One may also ask, how long does it take for a bowling ball to reach terminal velocity? two hours and 20 minutes
How to calculate terminal velocity.?
To calculate terminal velocity:
- Multiply the mass of the object by the gravitational acceleration.
- Divide the resultant by the product of drag coefficient and projected area.
- Multiply the number in the previous step by 2.
- Divide the product by the density of fluid.
- Obtain the square root of the result to get the terminal velocity of the object.
What is the equation for terminal velocity?
Things to Remember
- The highest constant velocity attained by a body while falling during a thicker medium is called terminal velocity.
- The maximum velocity of a body travelling through a viscous fluid is called terminal velocity.
- It is achieved when the medium's force of resistance equals and opposes the force of gravity.
What is the equation for terminal speed?
Using mathematical terms, terminal speed—without considering buoyancy effects—is given by. V t = 2 m g ρ A C d {displaystyle V_ {t}= {sqrt {frac {2mg} {rho AC_ {d}}}}} where. V t {displaystyle V_ {t}} represents terminal velocity, m {displaystyle m} is the mass of the falling object, g {displaystyle g}

What is terminal velocity calculate the terminal velocity?
Use the terminal velocity formula, v = the square root of ((2*m*g)/(ρ*A*C)). Plug the following values into that formula to solve for v, terminal velocity. g = the acceleration due to gravity. On Earth this is approximately 9.8 meters per second.
What is the terminal velocity of a falling object?
Terminal velocity is defined as the highest velocity that can be achieved by an object that is falling through a fluid, such as air or water. When terminal velocity is reached, the downward force of gravity is equal to the sum of the object's buoyancy and the drag force.
How do you calculate terminal velocity in physics?
3:185:21Terminal Velocity - A Level Physics - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThis kind of a stage here the gradient would be equal to a value of about nine point eight oneMoreThis kind of a stage here the gradient would be equal to a value of about nine point eight one meters. Per second squared which is acceleration G due to gravity as time.
Where is the terminal velocity?
Terminal velocity is the maximum velocity (speed) attainable by an object as it falls through a fluid (air is the most common example). It occurs when the sum of the drag force (Fd) and the buoyancy is equal to the downward force of gravity (FG) acting on the object.
How do you find terminal velocity in an experiment?
1:1310:33Terminal Velocity Experiment - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipI'll then use that to work out the velocity using the constant velocity equation s equals V T.MoreI'll then use that to work out the velocity using the constant velocity equation s equals V T.
How do you find terminal velocity from a graph?
3:1915:59What is Terminal Velocity? How Do We Find It? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipBy setting the acceleration of the object in the y. Direction equal to zero. And add theMoreBy setting the acceleration of the object in the y. Direction equal to zero. And add the acceleration due to gravity to both sides solve for terminal velocity squared.
What is the terminal velocity of a ball?
Terminal Velocity ExamplesFalling objectMassTerminal velocityBaseball (3.66cm radius)145 gm74 mi/hrGolf ball (2.1 cm radius)46 gm72 mi/hrHail stone (0.5 cm radius).48 gm31 mi/hrRaindrop (0.2 cm radius).034 gm20 mi/hr1 more row
What is terminal velocity GCSE physics?
At terminal velocity, the object moves at a steady speed in a constant direction because the resultant force acting on it is zero.
How is terminal value calculated?
Terminal value is calculated by dividing the last cash flow forecast by the difference between the discount rate and terminal growth rate. The terminal value calculation estimates the value of the company after the forecast period.
How do you calculate terminal velocity from a distance time graph?
1:182:50Terminal Velocity Graphs - A level Physics - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo if the net force is equal to zero. Then by Newton's second law by F equals MA or the net forceMoreSo if the net force is equal to zero. Then by Newton's second law by F equals MA or the net force the acceleration will also become 0 and therefore velocity.
How do you find the terminal velocity of a ball in oil?
Analysis of ResultsWhen the ball bearing reaches terminal velocity, the distance it has travelled between each time interval will be the same, and so its velocity can be determined.Use the equation speed = distance / time to find the average velocity of the ball bearing between each set of bands or markers.More items...
What is terminal velocity?
Terminal velocity is defined as the highest velocity which can be attained by an object during its falling through the air. It happens when the sum...
Does terminal velocity exist in a vacuum?
In a vacuum, since there is no drag force, the terminal velocity does not exist.
What does Terminal Velocity depend on?
Terminal velocity is the point at which the drag force equals the force of gravity. Hence, terminal velocity will depend on the mass, cross-section...
Why a flat piece of paper will fall more slowly as compared to the same paper after it has been crum...
The paper weighs the same, but the air drag forces on the ball have decreased because its surface area has decreased. Due to this, the crumpled pap...
Give an application of the terminal velocity in our life?
Parachutes and hang gliders. As it is possible to increase or decrease the terminal velocity by making some changes in your weight or shape, or alt...
What is the terminal velocity equation?
The terminal velocity equation tells us that an object with a large cross-sectional area or a high drag coefficient falls slower than an object with a small area or low drag coefficient. A large flat plate falls slower than a small ball with the same weight.
Is the drag coefficient of a terminal velocity high?
If your drag coefficient includes compressibility effects, then your answer is correct. If your drag coefficient was determined at low speeds, and the terminal velocity is very high, you are getting the wrong answer because your drag coefficient does not include compressibility effects. The terminal velocity equation tells us ...
What is Terminal Velocity?
When the ball is thrown into the sea, It accelerates initially due to gravity. As the velocity increases, the retarding force also increases (by Stokes’s Law). Finally, the net force becomes zero when the viscous force plus buoyant force becomes equal to the force due to gravity, and so does the acceleration.
Terminal Velocity Formula (vt)
Consider a small sphere shown in Fig. (b) is falling from rest through a large column of viscous fluid. The forces acting on the sphere are:
Terminal Velocity Formula– Sample Problems
Q.1. Assume that a spherical body is flowing through the water. The velocity of the body at a particular instant is 2 m s – 1. What will be the drag force on the body due to the fluid? Assume that Stokes’s law is valid.
Summary
The property of a fluid by which an internal frictional force acts between its different layers which oppose their relative motion is called viscosity. The ratio of the shear stress to the time rate of shearing strain is known as the coefficient of viscosity ( η). The coefficient of viscosity ( η) falls when the temperature rises and vice versa.
FAQs on Terminal Velocity Formula
Q.1. What is terminal velocity? Ans: Terminal velocity is defined as the highest velocity which can be attained by an object during its falling through the air. It happens when the sum of the dragged force ( ( F d) and the buoyancy is equal to the downward force of gravity ( F g) acting on the body and the net force acting on the object is zero.
Which object has the largest terminal velocity?
Objects with a large mass and small surface area (like a bowling ball or a person without a parachute) will have the largest terminal velocity, while objects with a small mass and large surface area (like a feather or a person with a parachute) will have the smallest terminal velocity.
Why does dropping a rock have a smaller terminal velocity?
The rock falling through water would have a smaller terminal velocity because the density of water is greater than air.
Why does a parachute lower your velocity?
The parachute has a very large surface area and drag coefficient and a relatively small mass, so it experiences much higher air drag forces than you would without a parachute. Calculating Terminal Velocity.
What is the effect of air drag on velocity?
If any of these increase, the air drag force increases, but the velocity of the object has the biggest effect on the air drag force. As the objects speed up, the drag force increases rapidly until the air drag force is equal to the force of gravity.
What causes an object to fall?
As the object falls, the force of gravity initially causes it to continuously speed up as predicted by Isaac Newton. As it gets faster and faster, the air drag force increases until eventually, the air drag force is exactly equal to the force of gravity, and there is no net force acting on the object.
What force is applied to every falling object?
Drag Force. While it is true that the Earth exerts a gravitational force on every falling object, there is another very important force that also affects the terminal velocity of a falling object. As objects fall through air, they experience drag or air resistance forces that act upward and oppose the force of gravity.
How fast does gravity go when you jump out of an airplane?
Force of gravity = mass * g. So, when you jump out of that airplane, you immediately start speeding up at a rate of 9.8 m/s every second. If there was no air in the atmosphere, you would keep speeding up at that rate until you hit the ground. However, the air you are falling through exerts a force on you, too.
What causes an object to slow down?
As some object falls, the force of gravity initially causes it to continuously speed up. When it gets faster and faster, the air drag force increases until eventually. This air drag force is exactly equal to the force of gravity. If these two forces are exactly balanced, then the object will no longer speed up or slow down ...
When an object is falling under the influence of gravity or subject to some type of constant driving force, what is the answer
This force is subject to a resistance or drag force which increases with velocity. It will at last reach the maximum velocity where the drag force equals the driving force.