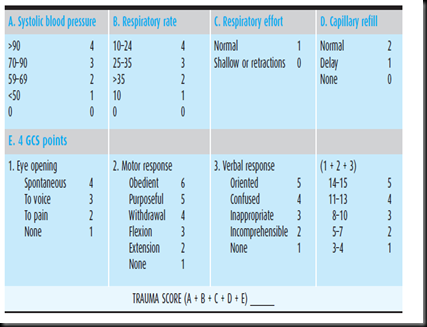
The revised trauma score in this case is calculated as follows:
- Step 1. Transform the values given in points according to the RTS table: - GCS of 12 means 3 - SBP of 86 means 3 - RR of...
- Step 2. Apply the points in the RTS formula:
How do you calculate the Revised Trauma Score?
Revised Trauma Score = (0.9368 x Glasgow Coma Scale coded value) + (0.7326 x Systolic Blood Pressure coded value) + (0.2908 x Respiratory Rate coded value). The Revised Trauma Score range is 0-12.
Does the Revised Trauma Score (RTS) correlate with survival chances?
There is a strong correlation between the RTS and the survival chances as shown below: Revised Trauma Score (RTS) Survival probability 0 2.7 % 1 7.1 % 2 17.2 % 3 36.1 % 5 more rows ...
What are the different types of trauma scoring?
There are other physiological trauma scoring methods, such as APACHE II or the acute trauma index. The RTS scores range between 0 and 7.8408, where the higher the score, the higher the chances of survival following the traumatic or non-traumatic injury.
What is the Pediatric Trauma Score (PTS)?
The Pediatric Trauma Score (PTS) is a system for children and is similar to the RTS. It has six components: weight, airway, systolic blood pressure, central nervous system, open wound, and skeletal injury.

What is normal Revised Trauma Score?
Use in triage The score range is 0–12. In START triage, a patient with an RTS score of 12 is labeled delayed, 11 is urgent, and 3–10 is immediate. Those who have an RTS below 3 are declared dead and should not receive certain care because they are highly unlikely to survive without a significant amount of resources.
What components make up the Revised trauma Scale?
[1] Components of the TS include respiratory rate, respiratory effort, systolic blood pressure, capillary refill time, and the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS).
What parameters include triage Revised trauma?
The T-RTS, which uses the physiological parameters of respiratory rate, blood pressure and the level of consciousness according to the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS), is used in ambulance care to classify patients in terms of the severity of their injuries (see Table 2, T-RTS).
How do you use ISS scores?
The ISS score takes values from 0 to 75. A score of 1 represents a minor injury and a score of 75 represents a fatal injury. By definition, any AIS body region score of 6 results automatically in an ISS of 75. An ISS score of 1 is possible if only one body region is injured.
What is the purpose of the Revised Trauma Score?
The Revised Trauma Score (RTS) is one of the more common scores aimed to measure the functional consequences of an injury. It uses three specific physiologic parameters: (1) the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS); (2) systemic blood pressure; and (3) the respiratory rate.
How many points are assigned to each element of the Revised Trauma Score?
It has six components: weight, airway, systolic blood pressure, central nervous system, open wound, and skeletal injury. Each component is given a score ranging from −1 to +2. Generally, patients with a PTS of less than 8 will benefit from transfer to a pediatric trauma center.
What is trauma scoring system?
The Revised Trauma Score (RTS) is one of the more common physiologic scores in use. It combines 3 specific, commonly assessed clinical parameters, as follows: (1) Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS), (2) systolic blood pressure (SBP), and (3) respiratory rate (RR).
What is modified trauma in ER?
Modified Trauma Team Activation allows for initial activation of a portion of the trauma team (usually excluding the general-trauma surgeon) with subsequent activation of the full team if necessary.
What is the revised trauma score?
The revised trauma score (RTS) is a physiologic-based triage score (Table 30-2 ). The RTS was derived from two earlier versions of a triage scores, the Triage Index and the Trauma Score ( Champion et al., 1980, 1981, 1989). The RTS has three variables—respiratory rate, systolic blood pressure, and GCS. The RTS is the sum of each variable multiplied by a weighted coefficient.
What is the RTS score?
The Revised Trauma Score (RTS) is one of the more common scores aimed to measure the functional consequences of an injury. It uses three specific physiologic parameters: (1) the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS); (2) systemic blood pressure; and (3) the respiratory rate. RTS is heavily weighted toward the GCS to compensate for major head injury without multisystem injury or major physiological changes and correlates well with the probability of survival.
What is the RTS of a coma scale?
The RTS is the sum of each variable multiplied by a weighted coefficient. where GCS is the Glasgow Coma Scale; SBP is systolic blood pressure; and RR is respiratory rate. These variables were determined to correlate statistically with survival and mortality. A higher RTS is associated with a better chance of survival.
What is the Glasgow Coma Score?
The Glasgow Coma Score (GCS) is a commonly used index for evaluating the level of consciousness and overall status of the central nervous system ( Table 5-1 ). Three physiologic categories (eye-opening, verbal response, and motor response) are assessed and the total score (3 to 15) is determined by the sum of the highest value the patient achieves in each category. The GCS is helpful because it can be rapidly calculated in the field, and it correlates with mortality.
What is the third generation of severity scoring system?
Third-generation models of severity scoring systems include simplified acute physiology score (SAPS) 3, APACHE IV, and mortality probability model (MPM)-III. APACHE IV predictions of hospital mortality have good discrimination and calibration, and should be useful for benchmarking performance in ICUs. The SAPS 3 admission score is able to predict vital status at hospital discharge with the use of data recorded at ICU admission and conceptually dissociates evaluation of the individual patient from evaluation of the ICU, thus allows them to be assessed at their respective reference levels. Finally, MPM-III provides more accurate comparisons of actual versus expected ICU outcomes.
What is the APACHE I score?
APACHE II was introduced as a simplified modification of the original APACHE. The APACHE II score consisted of three parts: 12 acute physiological variables, age, and chronic health status. The APACHE III system was designed to predict an individual's risk of dying in a hospital. It compares each individual's medical profile against nearly 18 000 cases in its memory before reaching a prognosis that is, on average, 95% accurate.
Is injury severity scoring still in use?
Injury severity scoring is still in a prolonged infancy. Although over 30 years old, the first-generation summary predictors (ISS, GCS, RTS, and TRISS) are still the standard scores in general use. The development of large trauma databases (e.g., NTDB) and better statistical software have now allowed us to see clearly the shortcomings of these early scoring techniques. In particular, the “summed subscores” approach to summary measures used in ISS, RTS, and GCS, as well as the overall survival predictor TRISS, uniformly results in probability of survival functions that are nonlinear, and, more problematically, often not monotonically related to mortality. Newer scoring systems that both better discriminate survivors from nonsurvivors and have better statistical properties have been developed (e.g., ICISS), but have failed to replace the first-generation scores. In part this is because the second generation of scores has not performed dramatically better than the older scores, and in part this is because the older scores are so firmly entrenched. Perhaps the most important reason for this inertia is that scores have as yet found no real use except in the arena of trauma research where scores that provide a rough ordering of injury severity have been adequate. However, if provider report cards, patient referrals, center certification, and revenue distribution come to depend on objective measures of the success of trauma care, it is likely that trauma scoring will elicit much greater interest. Even if reliable trauma scores are developed and adopted, the statistical challenge of comparing providers must not be underestimated.
How does this revised trauma score calculator work?
This is a health tool based on the RTS physiological system that is used for on site triage assessing vital signs and in predicting the outcome.
RTS interpretation
This medical scoring system is used to assess the vital signs of the patient in the emergency care unit and indicates the intensity of the injury.
Example calculation
Let’s take the case of a patient with a Glasgow coma scale score of 12, systolic blood pressure of 86 and a respiratory rate of 15. The revised trauma score in this case is calculated as follows:
RTS variables and formula
The on site triage method proposed in the revised trauma score evaluates the severity of the injury based on the Glasgow Coma Scale and two vital signs: Systolic blood pressure (BP) and Respiratory rate.
Revised trauma score interpretation
The RTS scores range between 0 and 7.8408, where the higher the score, the higher the chances of survival following the traumatic or non-traumatic injury.
Other references
1. Gilpin DA, Nelson PG. Revised trauma score: a triage tool in the accident and emergency department. Injury. 1991; 22 (1):35-7.
What is trauma triage?
Trauma triage is the use of trauma assessment for prioritising of patients for treatment or transport according to their severity of injury. Primary triage is carried out at the scene of an accident and secondary triage at the casualty clearing station at the site of a major incident. Triage is repeated prior to transport away from ...
Is there a universal scoring system?
There is, however, no universally accepted scoring system and each system has its own limitations.
Is the NISS a triage tool?
It is not useful as a triage tool. It only considers one injury per body region and therefore may underestimate the severity in trauma victims with multiple injuries affecting one body part. The NISS is a modified version of the ISS developed in 1997.

How Does This Revised Trauma Score Calculator Work?
RTS Interpretation
- This medical scoring system is used to assess the vital signs of the patient in the emergency care unitand indicates the intensity of the injury. RTS ranges from 0 to 7.8408. It is established that 4 is the threshold for treatment in the trauma centre. Values below 3 are considered to be highly unlikely to survive and are declared dead. There is a strong correlation between the RTS and the …
Example Calculation
- Let’s take the case of a patient with a Glasgow coma scale score of 12, systolic blood pressure of 86 and a respiratory rate of 15. The revised trauma score in this case is calculated as follows: Step 1. Transform the values given in points according to the RTS table: - GCS of 12 means 3 - SBP of 86 means 3 - RR of 15 means 4 Step 2. Apply the poin...
References
- 1) Champion HR et al, "A Revision of the Trauma Score", J Trauma 29:623-629, 1989 2) Champion HR et al, "Trauma Score", Crit Care Med 9:672-676, 1981