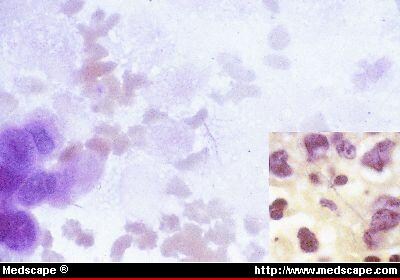
It can be found in natural and processed water, sewage, and dirt. Healthy people usually do not get Mycobacterium
Mycobacterium
Mycobacterium is a genus of Actinobacteria, given its own family, the Mycobacteriaceae. Over 190 species are recognized in this genus. This genus includes pathogens known to cause serious diseases in mammals, including tuberculosis and leprosy in humans. The Greek prefix myco- mean…
How do healthy people get Mycobacterium fortuitum infections?
Feb 22, 2017 · It can be found in natural and processed water, sewage, and dirt. [1] [2] Healthy people usually do not get Mycobacterium fortuitum infections; however, they may occur after surgery, in people with an impaired immune system, or after exposure to a contaminated medical device (such as an endoscope). It is uncommon for this condition to cause lung disease, but …
Where does Mycobacterium fortuitum come from?
Nov 10, 2021 · It can be found in natural and processed water, sewage, and dirt. Healthy people usually do not get Mycobacterium fortuitum infections; however, they may occur after surgery, in people with an impaired immune system, or after exposure to a contaminated medical device (such as an endoscope).
Which medications are used in the treatment of Mycobacterium fortuitum infection?
How do you get Mycobacterium fortuitum? Surgical sites may become infected after the wound is exposed directly or indirectly to contaminated tap water. Other possible sources of M. fortuitum infection include implanted devices such as catheters, injection …
Why is Mycobacterium fortuitum red in color?
Apr 12, 2011 · Mycobacterium fortuitum can be a hospital-acquired disease; surgical-site infections due to this bacteria are well-documented. Surgical sites may become infected after the wound is exposed directly or indirectly to contaminated tap water.
Is Mycobacterium fortuitum contagious?
Compared to M. tuberculosis they are weak pathogens, and infected patients are not considered contagious. Disease is probably acquired from environmental sources by direct entry of the organisms through traumatized skin or mucous membranes or by aspiration into previously abnormal lungs.
How do you get infected with Mycobacterium?
Infection with M. abscessus is usually caused by injections of substances contaminated with the bacterium or through invasive medical procedures employing contaminated equipment or material. Infection can also occur after accidental injury where the wound is contaminated by soil.
How do you prevent Mycobacterium fortuitum?
M fortuitum is a ubiquitous organism. Avoiding exposure to tap water in the operating room and during cosmetic skin procedures helps to prevent infection. M fortuitum is resistant to chlorine disinfection.Nov 18, 2019
How did I get Mycobacterium?
You may develop a nontuberculous mycobacterial infection if you drink contaminated water. Bacteria can also enter the body through a break in the skin, such as a puncture wound that gets contaminated with water or soil. Inhaling the bacteria also puts you at risk for infection.
Where is Mycobacterium fortuitum found?
It can be found in natural and processed water, sewage, and dirt. Healthy people usually do not get Mycobacterium fortuitum infections; however, they may occur after surgery, in people with an impaired immune system , or after exposure to a contaminated medical device (such as an endoscope).
How serious is Mycobacterium?
Nontuberculous mycobacteria are tiny germs found in soil, water, and on both tame and wild animals. They're harmless to most people. But sometimes when these bacteria get into your body, they can cause a serious lung disease.Jul 28, 2021
What does Mycobacterium fortuitum cause?
Mycobacterium fortuitum is frequently associated with skin, soft tissue, and bone infections while it rarely causes pulmonary or disseminated diseases. Skin and soft tissue infections are common after mammoplasty and similar plastic surgery interventions or cardiac surgery (sternal wound infections).
Is Mycobacterium fortuitum rare?
ABSTRACT. The Mycobacterium fortuitum group of rapidly growing nontuberculous mycobacteria is an uncommon cause of renal infection, particularly in otherwise healthy hosts.May 1, 2007
How common is Mycobacterium Marinum?
Frequency. M marinum infections are rare but well described in the literature. The estimated annual incidence is 0.27 cases per 100,000 adult patients. The infection is typically limited to the skin, mostly involving limbs, but spread to deeper structures has been reported.Jun 4, 2019
Is Mycobacterium contagious?
The great majority of NTM lung disease in the U.S. is caused by Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC). Everyone comes into contact with NTM, but it usually only causes infection in people with underlying lung disease, such as bronchiectasis or COPD, a weakened immune system or older age. NTM disease is not contagious.Nov 6, 2020
Can Mycobacterium be cured?
A complete cure can be expected with some NTM strains but not with others. Reinfection is common. To avoid becoming infected again, you may need to make some lifestyle changes.Apr 22, 2021
How does Mycobacterium affect the body?
Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by a bacterium called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The bacteria usually attack the lungs, but TB bacteria can attack any part of the body such as the kidney, spine, and brain. Not everyone infected with TB bacteria becomes sick.
Where can I find mycobacterium fortuitum?
It can be found in natural and processed water, sewage, and dirt.
What infection was developed after mastectomy?
Following surgery for a mastectomy with a subsequent implant of a tissue expander and alloderm, I developed an infection which was identified as mycrobacterium fortuitum. Could this be a hospital acquired infection and does this type of infection get reported to the department of health?
Can mycobacterium fortuitum cause eye disease?
It is uncommon for this condition to cause lung disease, but Mycobacterium fortuitum infection can lead to skin disease, osteomyelitis (inflammation of the bone), joint infections, and eye disease. The signs and symptoms of infection differ depending on the infection site.
Can you get Mycobacterium fortuitum after surgery?
Healthy people usually do not get Mycobacterium fortuitum infections; however, they may occur after surgery, in people with an impaired immune system, or after exposure to a contaminated medical device (such as an endoscope).
Can mycobacterium fortuitum be a surgical site infection?
Mycobacterium fortuitum can be a hospital-acquired disease; surgical-site infections due to this bacteria are well-documented. Surgical sites may become infected after the wound is exposed directly or indirectly to contaminated tap water. Other possible sources of mycobacterium fortuitum infection include implanted devices (such as catheters ), ...
What is mycobacterium fortuitum associated with?
Mycobacterium fortuitum is frequently associated with skin, soft tissue, and bone infections while it rarely causes pulmonary or disseminated diseases. Skin and soft tissue infections are common after mammoplasty and similar plastic surgery interventions or cardiac surgery (sternal wound infections).
What is the treatment for Mycobacterium fortuitum?
Mycobacterium fortuitum infections can usually be treated with a two-drug regimen based on in vitro susceptibility testing. This may include fluoroquinolones, doxycycline, amikacin, or sulfonamides. Mycobacterium fortuitum contains an inducible erythromycin methylase erm gene that confers resistance to macrolides.
What causes a cat to have a mycobacterial infection?
Atypical or rapidly growing mycobacterial infections 52 are caused by the Mycobacterium fortuitum group, which grow within 7 days on appropriate culture medium. In cats the most common clinical presentation is a nonhealing wound in the inguinal area, often at the site of a cat bite abscess. The infection invades the surrounding skin and subcutaneous tissue. Affected areas are alopecic and have fistulous tracts and a watery discharge. Diagnosis can be made by cytologic examination of exudates and culture of exudates, but histologic confirmation may be needed. Treatment involving a combination of surgical excision and antimicrobial therapy with drugs such as clarithromycin may be required, although some species are susceptible to more routine antibiotics such as doxycycline or fluoroquinolones.
What is the name of the bacteria that causes boils?
Atypical mycobacteria (AMB), including Mycobacterium marinum, Mycobacterium fortuitum, and Mycobacterium chelonae ( Fig. 13.5) can produce boil-like lesions in the skin. These AMB are ubiquitous in nature and are often found in soil, water, and decaying organic matter.
What is the most common RGM causing extrapulmonary infections?
M. fortuitum is the most common RGM causing extrapulmonary infections. It usually causes nosocomial infection of the skin and soft tissues. It only exceptionally causes pulmonary disease. Its presence in pulmonary specimens usually represents either laboratory contamination or nonpathogenic colonization.
What is the name of the bacteria that colonizes the central line catheter?
Mycobacterium fortuitum is a rapidly growing Mycobacterium ubiquitous in nature that is known to form biofilms and colonize the in situ central line catheters. Catheter-associated mycobacteremia is a rare condition caused by rapidly growing Mycobacteria in central venous devices (TID).
How long does it take for mycobacterium fortuitum to grow?
Atypical or rapidly growing mycobacterial infections 52 are caused by the Mycobacterium fortuitum group, which grow within 7 days on appropriate culture medium. In cats the most common clinical presentation is a nonhealing wound in the inguinal area, often at the site of a cat bite abscess.