
What are the treatment options for neurofibroma?
Treatment 1 Monitoring. Your doctor may recommend observation of a tumor if it's in a place that makes removal difficult or if it's small and causes no problems. ... 2 Surgery to remove the tumor. Symptoms can be relieved by removing all or part of a neurofibroma that's pressing on nearby tissue or damaging organs. ... 3 Clinical trials. ...
How do you get rid of NF2 tumors?
Surgery to remove tumors. Symptoms can be relieved by removing all or part of tumors that are compressing nearby tissue or damaging organs. If you have NF2 and have experienced hearing loss, brainstem compression or tumor growth, your doctor might recommend surgery to remove acoustic neuromas that are causing you problems.
What are the treatment options for symptom-related neuromas?
Symptoms can be relieved by removing all or part of tumors that are compressing nearby tissue or damaging organs. If you have NF2 and have experienced hearing loss, brainstem compression or tumor growth, your doctor might recommend surgery to remove acoustic neuromas that are causing you problems.
Is there a cure for Neurofibromatosis or schwannomatosis?
There is no known treatment or cure for neurofibromatosis or schwannomatosis. Medication can be prescribed to help with pain. In some cases, growths may be removed surgically or reduced with radiation therapy. Although surgery in these areas can cause further injury to nerves and additional neurological problems, it is usually well tolerated.

How do you stop neurofibromas from growing?
There is no medication that can prevent neurofibromas from growing. And, there is nothing you can do that would make more neurofibromas develop. Neurofibromas often appear or grow in size during times of hormone changes such as puberty (which you can't avoid) and pregnancy.
Can you remove neurofibromas?
There are many ways to remove neurofibromas. Usually a neurofibroma is “excised”, meaning “cut out”, by a scalpel or other means; or they are “destroyed” by electrosurgery. The tumors may also be destroyed (ablated) by desiccation (dehydration or drying), or vaporized using electrosurgery.
How do you control neurofibroma?
Your doctor might recommend surgery or other procedures to treat severe symptoms or complications of neurofibromatosis....Surgery and other proceduresSurgery to remove tumors. ... Stereotactic radiosurgery. ... Auditory brainstem implants and cochlear implants.
How do neurofibromas start?
Neurofibromatosis is caused by genetic defects (mutations) that either are passed on by a parent or occur spontaneously at conception. The specific genes involved depend on the type of neurofibromatosis: NF1 . The NF1 gene is located on chromosome 17.
What is inside a neurofibroma?
Neurofibromas are comprised of Schwann cells, fibroblasts, perineural cells, and mast cells in a variably myxoid background. [1] A mutation in the NF1 gene causes neurofibromas. There are three main types of neurofibromas: localized (most common), diffuse, and plexiform.
Can neurofibromas become cancerous?
A neurofibroma is usually noncancerous (benign). Rarely, it can become cancerous (malignant).
Is a neurofibroma serious?
Neurofibromas are benign tumors that rarely cause serious medical issues. People who have many neurofibromas or noticeably large neurofibromas sometimes feel self-conscious about their appearance, though. Surgery might be an option.
Does neurofibromatosis worsen with age?
In many cases, neurofibromatosis symptoms worsen as a patient ages. There is no cure for neurofibromatosis. However, many symptoms can be treated and managed. Children with more severe symptoms will naturally require more medical attention than children who have mild symptoms.
Can a neurofibroma burst?
As neurofibroma is highly vascular, vessel rupture can occur spontaneously or with trivial trauma.
What can be mistaken for neurofibromatosis?
Legius syndrome also is called a neurofibromatosis 1-like syndrome because its symptoms are similar to NF1. Individuals with Legius syndrome have skin problems including brown birthmarks, called cafe-au-lait spots, and freckling, as well as mild learning problems and a larger head.
Do neurofibromas grow back?
It is important to discuss your expectations prior to surgery, as some neurofibromas may grow back after surgery. Plexiform neurofibromas are another type of neurofibroma. However, these tumors are frequently larger and involve multiple nerves.
Are neurofibromas common?
Intramuscular neurofibromas grow on small nerves in the muscles. This type can cause pain. Spinal neurofibromas grow on the nerves exiting the spine. They are more common in adults than children, and if they grow large enough, spinal neurofibromas can compress nerves and cause pain, numbness or weakness.
Can a dermatologist remove neurofibromas?
From a dermatological standpoint, smaller, raised neurofibromas can be removed with simple excision or electrodessication.
Do neurofibromas grow back?
It is important to discuss your expectations prior to surgery, as some neurofibromas may grow back after surgery. Plexiform neurofibromas are another type of neurofibroma. However, these tumors are frequently larger and involve multiple nerves.
Can NF type 1 tumors be removed?
There are no currently available medical or pharmacological treatments for cutaneous and subcutaneous tumors of NF1. Surgery is the only treatment option for cutaneous and subcutaneous tumors. High Quantity (HQ) surgical removal by several methods has been used.
What is the life expectancy of someone with neurofibromatosis?
If there are no complications, the life expectancy of people with NF is almost normal. With the right education, people with NF can live a normal life. Although mental impairment is generally mild, NF1 is a known cause of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.
What is a neurofibroma?
Neurofibromas are benign (noncancerous) tumors that grow on nerves in the body. Most neurofibromas occur in association with a genetic disorder. Solitary neurofibromas can also occur in otherwise healthy people; these are called sporadic neurofibromas. Neurofibromatosis type 1, or NF1, is a genetic disorder characterized by multiple neurofibromas, ...
How to diagnose neurofibroma?
A pathologist can make a definitive diagnosis of a neurofibroma by looking at a piece of the tumor under a microscope.
What causes neurofibromas?
Neurofibromatosis is a genetic disease caused by a mutation in a gene responsible for a protein that regulates nerve tissue growth, and can be inherited.
Where do neurofibromas grow?
Neurofibromas can grow on nerves in the skin (cutaneous neurofibroma), under the skin (subcutaneous) or deeper in the body, including in the abdomen, chest and spine. Neurofibromas can grow sporadically. Sporadic neurofibromas typically grow on the skin. People with NF1 are predisposed to developing multiple neurofibromas.
Can NF1 cause pain?
People with NF1 are predisposed to developing multiple neurofibromas. Most of these tumors do not hurt or cause problems, but some may itch or be painful. Treatment consists of observation and, if necessary, surgical removal. Researchers are looking into various medicines to shrink neurofibromas in patients with NF1.
Can neurofibroma be removed without surgery?
Most sporadic neurofibromas do not cause pain and can be managed without surgery. Sometimes after consulting with their doctor, people will choose to have sporadic neurofibromas surgically removed for cosmetic reasons or because the neurofibroma is growing in a location where it is bothersome.
Can neurofibroma be removed?
If a tumor begins to cause significant pain, is associated with loss of neurological function, compresses a nearby structure or shows rapid growth on imaging, the doctor may recommend removing the neurofibroma surgically.
What is the treatment for neurofibromatosis?
Malignant tumors and other cancers associated with neurofibromatosis are treated with standard cancer therapies, such as surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Early diagnosis and treatment are the most important factors contributing to a good outcome.
How to assess a child for neurofibromas?
Assess your child's skin for new neurofibromas or changes in existing ones. Check for signs of high blood pressure. Evaluate your child's growth and development — including height, weight and head circumference — according to growth charts available for children who have NF1. Check for signs of early puberty.
How to find a neurofibromatosis specialist?
Find a primary care doctor you can trust and who can coordinate your child's care with other specialists. The Children's Tumor Foundation has an online tool to help you find a neurofibromatosis specialist in your area.
What tests are needed to diagnose NF1?
If additional tests are needed to diagnose NF1, NF2 or schwannomatosis, your doctor might recommend: Eye exam. An eye doctor can detect Lisch nodules, cataracts and visual loss. Hearing and balance exams. A test that measures hearing (audiometry), a test that uses electrodes to record your eye movements (electronystagmography) ...
What is the best medication for schwannomatosis?
Your doctor might recommend: Drugs for nerve pain such as gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) or pregabalin (Lyrica) Tricyclic antidepressants such as amitriptyline.
Can a genetic test detect schwannomatosis?
Ask your doctor about genetic counseling. Genetic tests won't always identify schwannomatosis because other, unknown genes may be involved with the disorder.
Can NF1 be treated early?
Contact your doctor promptly if you notice any changes in signs or symptoms between visits. Many complications of NF1 can be treated effectively if therapy starts early.
How small is a neurofibroma tumor?
Neurofibroma treatment usually isn't needed for a single, small — less than an inch (about 2 centimeters) — tumor under the skin. Neurofibroma treatment usually involves monitoring or surgery.
How old do you have to be to get neurofibroma?
These tumors are most often found in people ages 20 to 40 years . Your doctor will diagnose a neurofibroma based on a physical examination, a discussion with you about your medical history, or the results of an imaging test such as a CT or MRI scan.
What is the best way to see if a tumor is growing?
Observation includes regular checkups and imaging tests to see if your tumor is growing. Surgery to remove the tumor.
Can neurofibroma be malignant?
A neurofibroma is usually noncancerous (benign). Rarely, it can become cancerous (malignant).
Overview
A neurofibroma is a benign tumor that develops along your nerve cells. This tumor is a symptom of a group of rare, inherited conditions called neurofibromatosis. People born with neurofibromatosis may have tumors on their skin, under their skin or deeper in their bodies. Most neurofibromas don’t cause medical problems.
Symptoms and Causes
Neurofibroma symptoms vary depending on the tumor type, size and location. Some people who have neurofibromas may never have symptoms. But sometimes, neurofibromas can cause serious medical issues such as paralysis or blindness. Here’s information about neurofibroma types and related symptoms:
Diagnosis and Tests
Healthcare providers typically use a physical examination to diagnose neurofibromas. They might also use the following imaging tests:
Prevention
Neurofibromas can be a symptom of an inherited disorder. That means you can’t prevent these tumors from developing.
Living With
Neurofibromas are benign tumors that rarely cause serious medical issues. People who have many neurofibromas or noticeably large neurofibromas sometimes feel self-conscious about their appearance, though. Surgery might be an option.
What is NF2 in the brain?
NF2 is primarily characterized by benign tumors of the nerves that transmit sound impulses and balance signals from the inner ears to the brain. Tumors commonly affect both the left and right (bilateral) hearing and balance (vestibulocochlear) nerves. A third related disorder, called schwannomatosis, has been recognized.
What is NF1 caused by?
NF1 is caused by mutations in the gene that controls production of a protein called neurofibromin (neurofibromin 1). This gene is believed to function as a tumor suppressor. In about 50% of people with NF1, the disorder results from gene mutations that occur for unknown reasons (spontaneous mutation).
What is a NF?
Neurofibromatosis (NF), a type of phakomatosis or syndrome with neurological and cutaneous manifestations, is a rare genetic disorder that typically causes benign tumors of the nerves and growths in other parts of the body , including the skin. Some people with this disorder have barely noticeable neurological problems, while others are affected profoundly. There are two major types: neurofibromatosis type I (NF1) and neurofibromatosis type II (NF2).
What is NF1 in children?
Some people with this disorder have barely noticeable neurological problems, while others are affected profoundly. There are two major types: neurofibromatosis type I (NF1) and neurofibromatosis type II (NF2). NF1 manifests itself at birth or during early childhood.
What is NF1 characterized by?
NF1 is characterized by multiple light brown (café-au-lait) spots concentrated in the groin and underarms and benign tumors under the skin. Enlargement and deformity of bones and curvature of the spine ( scoliosis) may also be present.
How often should a child be examined for NF1?
Healthy children with NF1 are usually examined at six or 12-month intervals. Adults with NF1 generally have standard physical evaluations and an examination of the skin for growths, spots, scoliosis, blood pressure, vision and screening for hearing loss.
Is schwannoma a first degree relative?
One pathologically confirmed schwannoma and a first-degree relative who meets the above criteria is also a definitive sign of schwannomatosis
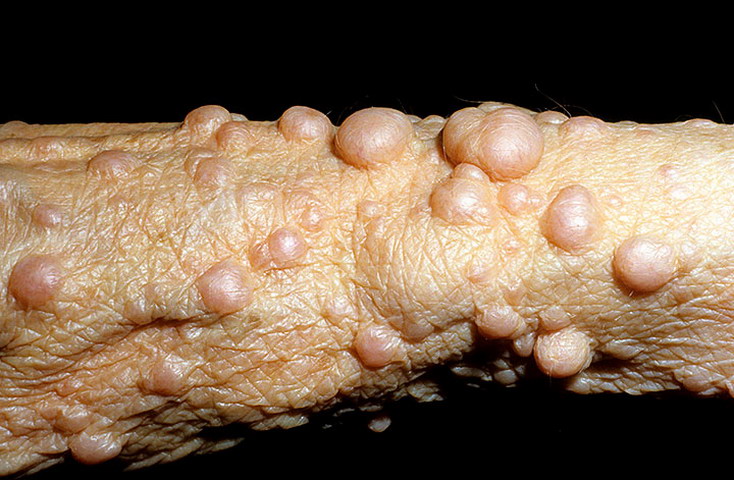
Diagnosis
Treatment
- Changes in an existing neurofibroma
- Numbness or weakness in an area of the body
- The neurofibroma growing in an area where it can be easily injured
- That it is causing problems with your daily life
- Cosmetic problems
Clinical Trials
Coping and Support
Preparing For Your Appointment
- There isn't a cure for neurofibromatosis, but signs and symptoms can be managed. Generally, the sooner someone is under the care of a doctor trained in treating neurofibromatosis, the better the outcome.