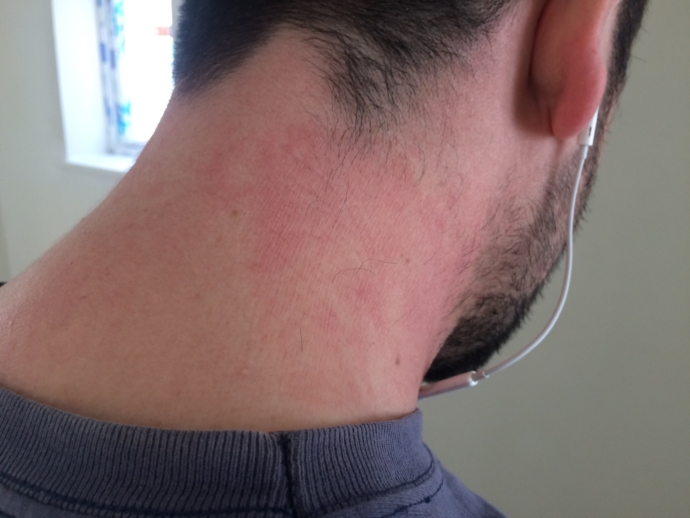
Staph infection can be transmitted by:
- Touching a person who has staph on their skin
- Being near a person who has staph when they cough or sneeze
- Touching a surface such as a table or door knob that has the bacteria on it
- If staph bacteria are on your skin and you cut yourself or have another injury with an open wound, you can get a staph infection
What is staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome?
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome (SSSS) is a serious skin infection. The infection causes peeling skin over large parts of the body. It looks like the skin has been scalded or burned by hot liquid.
How do you get staph infection?
You can get staph from breathing in infected breath droplets, touching contaminated surfaces including an infected person’s skin, or getting the bacteria in a cut.
Can a staph infection cause a rash to break off?
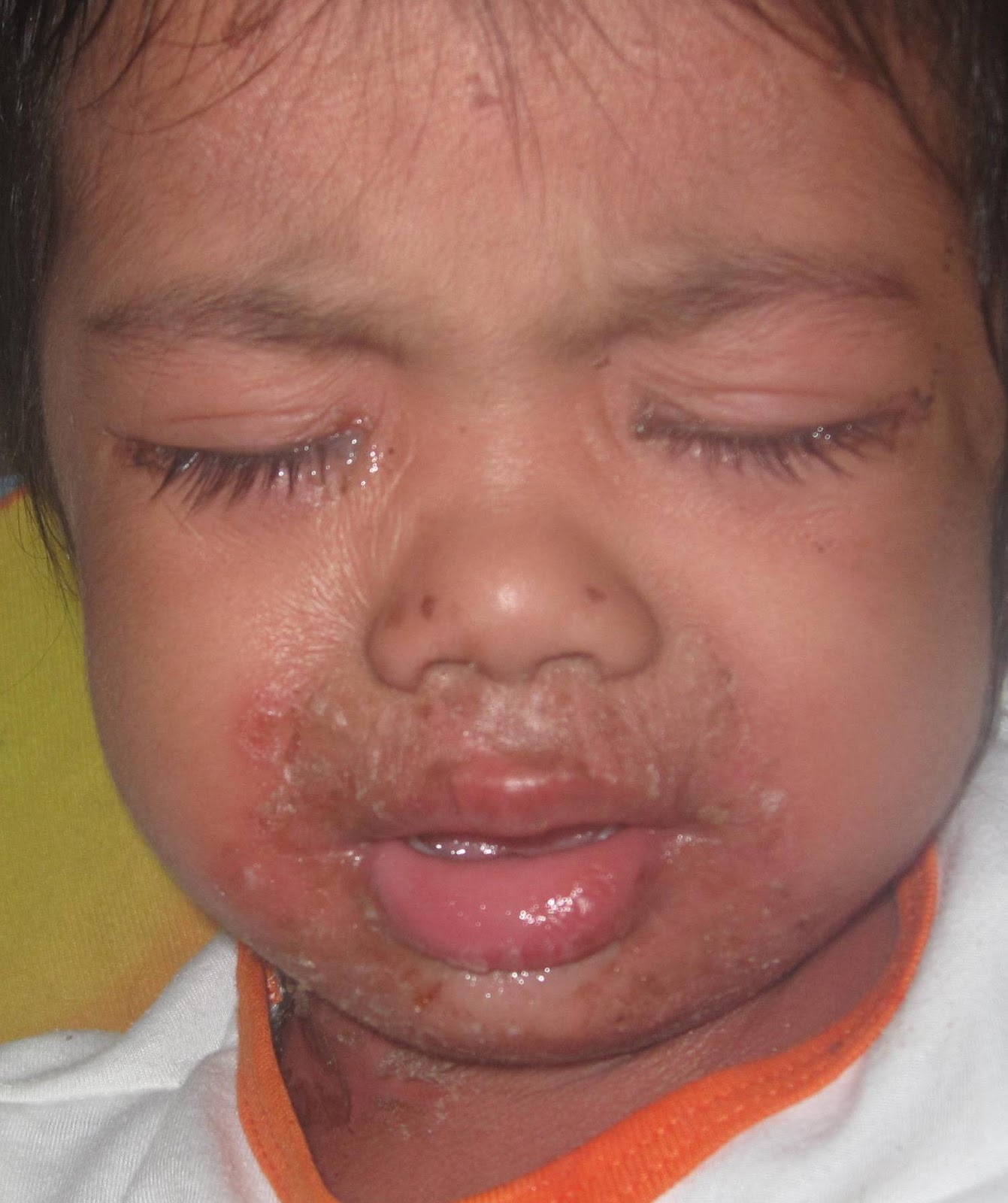
Toxins produced as a result of a staph infection may lead to staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome. Affecting mostly babies and children, this condition features a fever, a rash and sometimes blisters. When the blisters break, the top layer of skin comes off — leaving a red, raw surface that looks like a burn.
Can you get a staph infection from a cut?
If staph bacteria are on your skin and you cut yourself or have another injury with an open wound, you can get a staph infection How Is a Staph Infection Diagnosed?
What causes staph scalded skin?
It's usually caused by an infection with a type of Staphylococcal aureas bacteria. The bacteria release poison (toxins) that cause the skin to blister and peel.
Is staph scalded skin contagious?
SSSS is not a common condition. The Staph bacterium that causes SSSS can be passed from person to person (contagious).
What is the main cause of staph infection?
The cause of a staph infection is staph bacteria entering the body. They can enter through an open wound or when a person ingests food that has become contaminated with the bacteria. Staph bacteria might enter a person's body as a result of them: picking or scratching at pimples, sores, or bumps on the skin.
How do staph infections start out?
Staph infection MRSA infections start out as small red bumps that can quickly turn into deep, painful abscesses. Staph skin infections, including MRSA , generally start as swollen, painful red bumps that might look like pimples or spider bites. The affected area might be: Warm to the touch.
What kills staph infection on skin?
Antibiotics commonly prescribed to treat staph infections include cefazolin, nafcillin, oxacillin, vancomycin, daptomycin and linezolid. For serious staph infections, vancomycin may be required. This is because so many strains of staph bacteria have become resistant to other traditional antibiotics.
Can adults get scalded skin syndrome?
Adults rarely develop the syndrome because of antibodies to the exotoxin. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome can be mistaken for bullous impetigo. Both cause blistering skin lesions caused by the staphylococcus exotoxin, but in the latter, the exotoxins remain localized to the site of infection.
How long is staph contagious?
Each case of staph infection is different, but most often staph will resolve in 1-3 weeks. Once you complete your antibiotic treatment, you'll no longer be contagious, but you should keep any skin infection clean and covered until it is completely gone.
How do I clean my house after staph infection?
Disinfect hard, nonporous surfaces2Wash and rinse surface with water.Mix 1/2 cup of Clorox® Regular Bleach2, with 1 gallon of water.Wipe surface area with bleach solution and let stand for 5 minutes.Rinse well and air dry.
Does staph stay in your body forever?
As a result, the body does not develop long-term immunity and remains vulnerable to that particular staph infection throughout life. While certain staph bacteria cause mild skin infections, other strains of staph bacteria can wreak havoc in the bloodstream and bones, sometimes leading to amputations.
How long can staph live on bedding?
Symptoms of a Staph infection include redness, warmth, swelling, tenderness of the skin, and boils or blisters. How do Staph skin infections spread? Staph/MRSA lives on the skin and survives on objects for 24 hours or more.
What happens if staph is left untreated?
Staph can cause serious infections if it gets into the blood and can lead to sepsis or death. Staph is either methicillin-resistant staph (MRSA) or methicillin-susceptible staph (MSSA). Staph can spread in and between hospitals and other healthcare facilities, and in communities.
Can staph go away on its own?
Staph infections are caused by bacteria called staphylococcus. They most often affect the skin. They can go away on their own, but sometimes they need to be treated with antibiotics.
When is staph no longer contagious?
As long as a staph infection is active, it is contagious. Most staph infections can be cured with antibiotics, and infections are no longer contagious about 24 to 48 hours after appropriate antibiotic treatment has started.
When does staph stop being contagious?
Each case of staph infection is different, but most often staph will resolve in 1-3 weeks. Once you complete your antibiotic treatment, you'll no longer be contagious, but you should keep any skin infection clean and covered until it is completely gone.
How long does staph scalded skin syndrome last?
The prognosis for staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome is excellent, with full healing usually occurring within 10 days with no scarring. However, possible complications can lead to scarring, disability, and death. These complications include: Shock.
How long can staph live on bedding?
Symptoms of a Staph infection include redness, warmth, swelling, tenderness of the skin, and boils or blisters. How do Staph skin infections spread? Staph/MRSA lives on the skin and survives on objects for 24 hours or more.
What is the treatment for staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome?
What is the treatment of staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome? Treatment of SSSS usually requires hospitalisation, as intravenous antibiotics are generally necessary to eradicate the staphylococcal infection. A penicillinase-resistant, anti-staphylococcal antibiotic such as flucloxacillin is used.
Where do bullae blisters appear?
Tissue paper-like wrinkling of the skin is followed by the appearance of large fluid-filled blisters ( bullae) in the armpits, groin and body orifices such as the nose and ears. Rash spreads to other parts of the body including the arms, legs and trunk.
What is the name of the disease that causes red blisters on the skin?
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome (SSSS) is an illness characterised by red blistering skin that looks like a burn or scald, hence its name staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome . SSSS is caused by the release of two exotoxins ( epidermolytic toxins A and B) from toxigenic strains of the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus.
What is the role of desmosomes in skin?
Desmosomes are the part of the skin cell responsible for adhering to the adjacent skin cell. The toxins bind to a molecule within the desmosome called Desmoglein 1 and break it up so the skin cells become unstuck. SSSS has also been called Ritter disease or Lyell disease when it appears in newborns or young infants.
Is a staphylococcus aureus infection a SSSS?
However, staphylococcal skin infections are seen commonly in infants and younger children, thus an obvious increased risk of SSSS. Staphylococcus aureus is also commonly found in infections of the throat, ears and eyes.
How do children get it?
In children, the bacteria may enter the body through a minor break in the skin, such as a cut, the umbilical stump, or diaper rash that breaks the skin. Older children may develop SSSS on their faces. In anyone, the toxin can travel through the bloodstream to reach other areas.
Risk factors
Newborns are particularly susceptible because they do not have the antibodies to fight off the infection, and their kidneys cannot help clear the infection from the body.
What is a scalded skin?
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome (SSSS) is a serious skin infection caused by the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus. This bacterium produces an exfoliative toxin that causes the outer layers of skin to blister and peel, as if they’ve been doused with a hot liquid. SSSS — also called Ritter’s disease — is rare, ...
Why does SSSS peel?
Problems arise when the bacteria enter the body through a crack in the skin. The toxin the bacterium produces damages the ability of the skin to hold together. The upper layer of skin then breaks apart from the deeper layers, causing the hallmark peeling of SSSS.
What causes SSSS?
Causes of SSSS. The bacterium that causes SSSS is common in healthy people. According to the British Association of Dermatologists, 40 percent of adults carry it (usually on their skin or mucous membranes) with no ill effects. Problems arise when the bacteria enter the body through a crack in the skin. The toxin the bacterium produces damages the ...
How to diagnose SSSS?
Diagnosis of SSSS is usually made via a clinical exam and a look at your medical history. Because the symptoms of SSSS can resemble those for other skin disorders such as bullous impetigo and certain forms of eczema, your doctor may perform a skin biopsy or take a culture to make a more definitive diagnosis.
How do you know if you have SSSS?
Early signs of SSSS usually begin with the hallmark symptoms of an infection: fever. irritability. fatigue. chills. weakness. lack of appetite. conjunctivitis (an inflammation or infection of the clear lining that covers the white portion of the eyeball) You may also notice the appearance of a crusty sore.
How long does it take for a blister to heal?
As the blisters drain and ooze, dehydration can become a problem. You’ll be told to drink plenty of fluids. Healing typically begins 24–48 hours after treatment is started. Full recovery follows just five to seven days later.
How many cases of a syphilis in children?
According to research published in the journal Annals of Internal Medicine, 98 percent of cases occur in children under 6. Adults with weakened immune systems or poor kidney function are also susceptible.
What causes staph scalding on skin?
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome is caused by a Staphylococcus or “Staph” infection. Staphylococcus is a type of bacterium of which there are more than 30 different varieties. Staphylococcus aureus is the most common form associated with disease. Staphylococcus aureus is commonly found on human skin and begins colonization immediately after birth. Usually, this bacterium resides on the skin and mucous membranes of humans but does no harm. However, it does predispose an individual to infection, especially when given the opportunity to break through the skin. Staphylococcus aureus is the underlying infection in individuals with staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome. However, in many healthy children no underlying bacterial infection can be detected clinically.
How common is staph scalded skin?
The incidence, which has doubled in the last decade (based on national hospitalization data), is estimated to be between .09 and .56 per 1,000,000 individuals in the general population. However, these estimates may reflect cases reported in the medical literature and the disorder most likely is more common in the United States than estimated, particularly in infants and young children. The majority of cases are in children under the age of 6. Newborns (neonates) are at particular risk because they do not have fully developed immune systems, do not have neutralizing antibodies for the toxin, and their kidneys cannot fully clear toxins from the body yet. For similar reasons certain adults, specifically adults with a compromised immune system or poor kidney function, are at a greater risk than the general population of developing the disorder.
What is scalded skin syndrome?
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome (SSSS) is a disorder that develops because of a toxin produced by a staphylococcal infection. A toxin is a harmful substance that causes disease when it enters tissues of the body. In SSSS the toxin spreads to the skin through the blood stream and specifically binds to a target protein very high in ...
How does staph infection affect the skin?
Symptoms develops because a Staphylococcus aureus infection (or often only colonization when the Staph germ does not cause infection but makes toxin) releases toxins into the blood at the primary site of infection or colonization. These toxins spread to the skin and damage the upper part of the epidermis (outer part of the outer layer of the skin). Specifically, the toxins damage desmoglein 1, a molecule essential for epidermal cells to stick together (adhere) and form a protective barrier. Damaged desmoglein 1 prevents epidermal cells from sticking together causing the upper level of the epidermis to break apart and eventually pull away (detach) from the rest of the epidermis and the dermis (the layer of the skin beneath the epidermis which attaches to the underlying fat). Local release of the toxin into the skin results in bullous impetigo (see Related Disorders below) at the site of primary infection or colonization. When these toxins enter the bloodstream and spread to affect the skin in other areas of the body, staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome develops.
How to diagnose staphylococcal scalded skin?
A diagnosis of staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome is based upon identification of characteristic symptoms, a thorough clinical evaluation, and a detailed patient history. Although not usually necessary, in some cases, a skin biopsy, in which a tiny piece of affected skin is removed and studied under a microscope, may be performed. A biopsy can reveal non-inflammatory superficial splitting of the epidermis, which is indicative of the disorder and can differentiate it from similar disorders.
What are the symptoms of a scalded skin?
Affected individuals may also experience nonspecific symptoms such as fever (usually low grade), chills, and weakness. Unlike similar disorders that cause a scalded skin appearance, the mucous membranes are not affected.
What is the top layer of the epidermis?
The top layer of the epidermis, which is the top layer of the skin, may separate (detach) from the underlying layers resulting in loose blisters and shallow erosions (sores). Affected skin may slough off in sheets. Sloughing results in the exposure of moist, reddish tissue very close to the top of the epidermis and gives ...
How do you get a staphylococcus aureus infection?
Staphylococcus aureus infections are normally spread from skin-to-skin contact. However, they can also be spread by touching objects that are contaminated with the bacteria, like towels or other personal items. They can also be spread from one area of the body to another through dirty hands or fingernails.
How Is Scalded Skin Syndrome Diagnosed?
They may be able to diagnose scalded skin syndrome based on an examination alone, or your child may need additional tests. A small piece of skin may be removed and studied under a microscope. This is called a biopsy.
What Are the Symptoms of Scalded Skin Syndrome?
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome usually starts out with redness of the skin and fever. Blisters may appear and then rupture, leaving moist skin behind. Other symptoms can include:
How long does it take for scalded skin to heal?
What Are the Possible Complications of Scalded Skin Syndrome? The prognosis for staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome is excellent, with full healing usually occurring within 10 days with no scarring. However, possible complications can lead to scarring, disability, and death.
Why do my blisters get red?
Some strains of the bacteria staphylococcal aureus bacteria release a toxin that travels through the bloodstream and binds with a protein on the outer layer of the skin. This causes the skin to get red all over and blisters to break out.
Where is the bacterial infection found?
It's found in the nose, groin, armpit, and other areas . Most of the time, the bacteria doesn't cause problems or causes only minor skin infections. However, if the bacteria gets deeper inside your body it can cause life-threatening infections of your blood, joints, lungs, bones, and heart.
Can you share towels with someone with staph?
Don't share towels, sheets, or personal items if someone in your family has a staph infection.
How does staph spread?
Contact sports. Staph bacteria can spread easily through cuts, abrasions and skin-to-skin contact. Staph infections may also spread in the locker room through shared razors, towels, uniforms or equipment.
What causes staph on nose?
Staph infections are caused by staphylococcus bacteria, types of germs commonly found on the skin or in the nose of even healthy individuals. Most of the time, these bacteria cause no problems or result in relatively minor skin infections.
What is the most common type of staph infection?
Skin infections caused by staph bacteria include: Boils. The most common type of staph infection is the boil, a pocket of pus that develops in a hair follicle or oil gland. The skin over the infected area usually becomes red and swollen. If a boil breaks open, it will probably drain pus.
What is the name of the disease that occurs when staph bacteria enters the bloodstream?
Also known as a bloodstream infection, bacteremia occurs when staph bacteria enter a person's bloodstream. A fever and low blood pressure are signs of bacteremia. The bacteria can travel to locations deep within your body, to produce infections affecting:
What is the treatment for staph infection?
Treatment usually involves antibiotics and drainage of the infected area. However, some staph infections no longer respond to common antibiotics.
How long does it take for a staph infection to go away?
Symptoms come on quickly, usually within hours of eating a contaminated food. Symptoms usually disappear quickly, too, often lasting just half a day. A staph infection in food usually doesn't cause a fever.
How do you know if you have MRSA?
Symptoms. MRSA infections start out as small red bumps that can quickly turn into deep, painful abscesses. Staph infections can range from minor skin problems to endocarditis, a life-threatening infection of the inner lining of your heart (endocardium).
What Causes a Staph Infection?
The bacterium Staphylococcus aureus causes staph infections. Staph infections are commonly spread in the community by contact with infected people or with surfaces or objects that have the bacteria on them. Contact with a contaminated wound, or contact with personal items such as towels or razors that have touched infected skin can spread the bacteria.
How Is a Staph Infection Diagnosed?
Staph infection is diagnosed with a physical exam and patient history, along with blood tests and imaging tests in some cases.
What are the symptoms of staphylococcal infection?
Symptoms of staph skin infections, including MRSA include: A bump or infected area on the skin that is. Red.
What is the name of the bacteria that can cause sepsis?
Staphylococcus aureus (“staph” infection) is common bacteria found on the skin and inside the nasal cavity that can cause serious infections if it gets into the blood, leading to sepsis or death.
What to do if you have a MRSA?
Discard bandages and tape in the trash. Do not share personal items that contact skin, such as clothing, towels, razors, and needles. Tell all your healthcare providers if you have been diagnosed with a resistant staph infection (MRSA)
Is staph infection contagious?
Staph infection is quite contagious, including both methicillin-resistant staph (MRSA) and methicillin-susceptible staph (MSSA). You can get staph from breathing in infected breath droplets, touching contaminated surfaces including an infected person’s skin, or getting the bacteria in a cut.
What is scalded skin?
Scalded skin syndrome or staphylococcal scalded syndrome is a severe skin infection caused by manifestation of a class of bacteria called as Staphylococcus aureus. This condition is characterized by peeling and blistering of the skin giving it the appearance as the skin had second degree burns. It is important to know whether scalded skin syndrome is contagious and whether you can get it twice?
Why are children more prone to scalded skin?
Children are more prone to this condition due to lack of antibodies and poor immunity to fight back with the toxins. Also, the kidneys are not well developed in children to flush out the toxins. Hence, they too are at greater risk of experiencing scalded skin syndrome.
What is scalded skin syndrome?
Scalded skin syndrome (SSS), also known as Ritter’s disease, is caused by the exfoliative toxins secreted by the bacteria. These toxins cause the skin to become very fragile and prone to peeling upon light touches. It is a rare condition and affects only about 56 individuals out of 100000 people. This condition is most commonly seen in children below the age of 6. Though rarely, adults with history of renal failure, immune-deficiency and other chronic conditions are prone to scalded skin syndrome.
What is the term for infection of the deeper layer of the skin that extends into the fat and tissues that lie underneath?
Cellulitis , i.e. infection of the deeper layer of the skin that extends into the fat and tissues that lie underneath it.
Is scalded skin contagious?
While scalded skin syndrome is contagious, there are many ways in which it can be prevented and the spread can be controlled. Scalded skin syndrome can be prevented by following the measures mentioned below:
Signs and symptoms
- Initial symptoms can include fever (usually low grade), generalized redness, and tenderness of the skin. Onset of symptoms is usually rapid. Some individuals may experience nonspecific symptoms that develop before the skin symptoms including a sore throat and inflammation of the eyelids known as conjunctivitis. Initially the affected skin may have a sandpaper-like feel before …
Prognosis
- The severity of the disorder is highly variable. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome can cause mild disease or potentially it can progress to cause life-threatening complications. Such severe complications are rare in children, with the mortality rate below 5%. However, the mortality rate is higher in adults, due primarily to additional factors including the presence of other health issues …
Causes
- Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome is caused by a Staphylococcus or Staph infection. Staphylococcus is a type of bacterium of which there are more than 30 different varieties. Staphylococcus aureus is the most common form associated with disease. Staphylococcus aureus is commonly found on human skin and begins colonization immediately after birth. Usua…
Pathophysiology
- Symptoms develops because a Staphylococcus aureus infection (or often only colonization when the Staph germ does not cause infection but makes toxin) releases toxins into the blood at the primary site of infection or colonization. These toxins spread to the skin and damage the upper part of the epidermis (outer part of the outer layer of the skin)....
Epidemiology
- Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome affects males and females in equal numbers. The incidence, which has doubled in the last decade (based on national hospitalization data), is estimated to be between .09 and .56 per 1,000,000 individuals in the general population. However, these estimates may reflect cases reported in the medical literature and the disorder most likely …
Diagnosis
- Symptoms of the following disorders can be similar to those of staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome and should be differentiated from SSSS. Comparisons may be useful for a differential diagnosis. A diagnosis of staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome is based upon identification of characteristic symptoms, a thorough clinical evaluation, and a detailed patient history. Although …
Symptoms
- Other infectious and non-infection related skin disorders can produce symptoms similar to those seen in staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome. Such disorders include epidermolysis bullosa, epidermolytic ichthyosis, peeling skin syndrome, scarlet fever, Kawasaki disease, thermal burns, erythema multiforme, eczema herpeticum, and various nutritional deficiencies. (For more inform…
Society and culture
- Cultures can be taken from areas that harbor the bacterial germ including the conjunctiva (corners of the eyes), nasal passages, umbilicus, the upper area of the throat that connects with the nasal passages (nasopharynx area. Rarely underling serious infections such as pneumonia, meningitis, arthritis, and deep skin infection can trigger SSSS, and cultures may need to be taken from thes…
Treatment
- Treatment Treatment is directed toward the specific symptoms that are apparent in each individual and may require the coordinated efforts of a team of specialists. Hospitalization may be required. However, older infants and children who are still eating and drinking well can often be treated as outpatient with local skin care and oral antibiotics. Rarely, severe cases may require tr…
Resources
- Information on current clinical trials is posted on the Internet at www.clinicaltrials.gov. All studies receiving U.S. government funding, and some supported by private industry, are posted on this government website.
Sources
- https://www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ Stanley JR, Amagai M. Pemphigus, bullous impetigo, and the staphylococcal scalded skin-syndrome. N Engl J Med.2006;355:1800-1810. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17065642
Selected publications
- Mockenhaupt M, Idzko M, Grosber M, Schopf E, Norgauer J. Epidemiology of staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome in Germany. J Invest Dermatol. 2005;124:700-703. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15816826