How is this medicine (Procainamide) best taken?
- It is given as a shot into a vein.
- It is given as an infusion into a vein over a period of time.
How do you administer procainamide hydrochloride?
Alternatively, a loading infusion containing 20 mg of Procainamide Hydrochloride per mL (1 g diluted to50 mL with 5% Dextrose Injection, USP) may be administered at a constant rate of 1 mL per minute for 25 to 30 minutes to deliver 500 to 600 mg of PA.
What are the ingredients in procainamide hydrochloride?
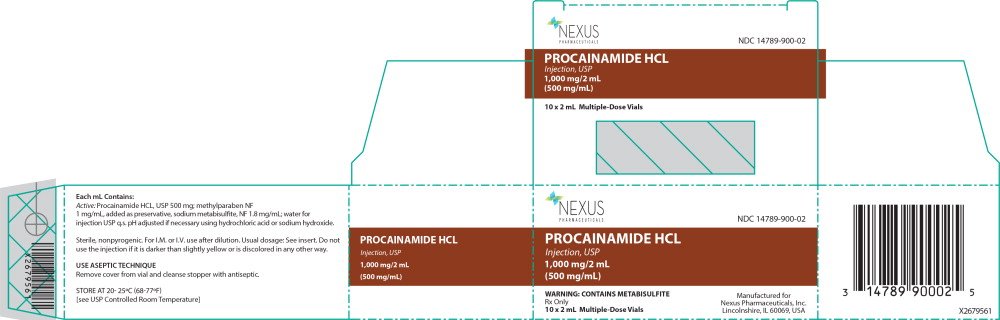
Each milliliter of the 10 mL vial contains Procainamide hydrochloride 100 mg; methylparaben 1 mg and sodium metabisulfite 0.8 mg added in water for injection. In both formulations, the solution may contain hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide for pH adjustment.
How many milligrams of Procainamide can you take?
Oral: ORAL procainamide is not available in the US but is available in Canada. Immediate-release: 250 mg orally every 3 hours. Sustained-release: 500 mg every 6 hours. Twice daily formulation: 1000 mg every 12 hours. Immediate-release: 375 mg every 3 hours. Sustained-release: 750 mg every 6 hours. Twice daily formulation: 1500 mg every 12 hours.
How does procainamide work?
Procainamide works by slowing the nerve impulses in the heart and reducing the sensitivity of heart tissues. This medicine is available only with your doctor's prescription. The oral dosage forms of this medicine are no longer available in the United States. This product is available in the following dosage forms:

What should you check before administering procainamide?
Check apical pulse, BP, and cardiac monitor prior to administration of procainamide. Monitor blood pressure, QRS duration, and QT interval frequently for patients receiving procainamide. Serum procainamide levels should be between 3 – 10 mcg/ml.
How often is procainamide given?
Procainamide comes as a capsule and tablet to take by mouth. Immediate-acting procainamide usually is taken every 3 or 4 hours. The long-acting product is usually taken every 6 or 12 hours.
When would you use procainamide?
Procainamide injection is used to treat irregular heartbeats and to slow an overactive heart. When the heart has a normal heartbeat (rhythm), it will work more efficiently. Procainamide works by slowing the nerve impulses in the heart and reducing the sensitivity of heart tissues.
What is a contraindication to procainamide?
Complete Heart Block: Procainamide should not be administered to patients with complete heart block because of its effects in suppressing nodal or ventricular pacemakers and the hazard of asystole.
Does procainamide lower blood pressure?
As outlined above, procainamide loading decreased arterial and central venous pressures and increased heart rate. Both the frequency and amplitude of sympathetic burst dis- charges in the neurogram decreased, and in this subject, SNA decreased from 155 units/min to 63 units/min after procainamide infusion.
What is the most common adverse effect of procainamide?
Common side effects of Pronestyl (procainamide hydrochloride) include nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, diarrhea, bitter taste in the mouth, dizziness, tired feeling, flushing (warmth, redness, or tingly feeling), and itching or rash.
When do you use amiodarone vs procainamide?
Interpretation: The results of this trial indicate that procainamide is better tolerated and more efficacious acutely than amiodarone in the treatment of hemodynamically stable wide complex tachycardia (presumably VT), including in patients with structural heart disease.
When do you stop procainamide infusion?
The indications for stopping infusion were: 1. reversion to sinus rhythm, 2. hypotension with a greater than 20% fall in systolic blood pressure, 3. QRS widening> 130% of normal, or 4.
Which is a contraindication to the use of procainamide infusion in the management?
Procainamide is contraindicated in patients with torsades de pointes, second- or third-degree AV block without a functioning pacemaker, or systemic lupus erythematosus and in patients hypersensitive to the anesthetic procaine.
What does procainamide do to the heart?
Procainamide injection is used to treat irregular heartbeats and to slow an overactive heart. When the heart has a normal heartbeat (rhythm), it will work more efficiently. Procainamide works by slowing the nerve impulses in the heart and reducing the sensitivity of heart tissues.
Does procainamide cause bradycardia?
The adverse effects of procainamide include cardiac toxicity, bradycardia, hypotension, drug-induced lupus erythematosus-like syndrome, and blood dyscrasias. QRS, QTc, and PR prolongation are the most potentially harmful cardiac side effects of procainamide and may become worse when levels of procainamide rise.
What kind of drug is procainamide?
Procainamide (PCA) is a medication of the antiarrhythmic class used for the treatment of cardiac arrhythmias. It is classified by the Vaughan Williams classification system as class Ia; thus it is a sodium channel blocker of cardiomyocytes.
When do you check procainamide levels?
When procainamide levels become supratherapeutic, the risk of the drug's side effects becomes increased (see Background). Levels of both procainamide and NAPA are typically checked before the administration of the second dose.
When do you use amiodarone vs procainamide?
Interpretation: The results of this trial indicate that procainamide is better tolerated and more efficacious acutely than amiodarone in the treatment of hemodynamically stable wide complex tachycardia (presumably VT), including in patients with structural heart disease.
Why is procainamide used in WPW?
The use of intravenous procainamide is a reliable and rapid method of identifying patients with the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome who may be at risk for circulatory insufficiency or sudden death in case of atrial fibrillation.
When do you stop procainamide infusion?
The indications for stopping infusion were: 1. reversion to sinus rhythm, 2. hypotension with a greater than 20% fall in systolic blood pressure, 3. QRS widening> 130% of normal, or 4.
Where should procainamide be used?
Initiation of Procainamide treatment, as with other antiarrhythmic agents used to treat life-threatening arrhythmias, should be carried out in the hospital.
What is the purpose of procainamide hydrochloride injection?
Procainamide hydrochloride injection is indicated for the treatment of documented ventricular arrhythmias, such as sustained ventricular tachycardia, that, in the judgement of the physician, are life-threatening. Because of the proarrhythmic effects of Procainamide, its use with lesser arrhythmias is generally not recommended. Treatment of patients with asymptomatic ventricular premature contractions should be avoided.
What is procainamide hydrochloride used for?
Procainamide Hydrochloride Injection is useful for arrhythmias which require immediate suppression and for maintenance of arrhythmia control. Intravenous therapy allows most rapid control of serious arrhythmias, including those following myocardial infarction; it should be carried out in circumstances where close observation and monitoring of the patient are possible, such as in hospital or emergency facilities. Intramuscular administration is less apt to produce temporary high plasma levels but therapeutic plasma levels are not obtained as rapidly as with intravenous administration. Oral Procainamide dosage forms are preferable for less urgent arrhythmias as well as for long-term maintenance after initial parenteral PA therapy.
How long does it take for procainamide to be absorbed?
Following intramuscular injection, Procainamide is rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream, and plasma levels peak in 15 to 60 minutes, considerably faster than orally administered Procainamide hydrochloride tablets or capsules which produce peak plasma levels in 90 to 120 minutes. Intravenous administration of Procainamide Hydrochloride Injection can produce therapeutic Procainamide levels within minutes after infusion is started. About 15 to 20 percent of PA is reversibly bound to plasma proteins, and considerable amounts are more slowly and reversibly bound to tissues of the heart, liver, lung, and kidney. The apparent volume of distribution eventually reaches about 2 liters per kilogram body weight with a half-time of approximately five minutes. While PA has been shown in the dog to cross the blood-brain barrier, it did not concentrate in the brain at levels higher than in plasma. It is not known if PA crosses the placenta. Plasma esterases are far less active in hydrolysis of PA than of procaine. The half-time for elimination of PA is three to four hours in patients with normal renal function, but reduced creatinine clearance and advancing age each prolong the half-time of elimination of PA.
Can Procainamide be used for heart block?
Contraindications. Complete Heart Block: Procainamide should not be administered to patients with complete heart block because of its effects in suppressing nodal or ventricular pacemakers and the hazard of asystole.
Is procainamide safe for agranulocytosis?
Because Procainamide has the potential to produce serious hematological disorders (0.5 percent) particularly leukopenia or agranulocytosis (sometimes fatal), its use should be reserved for patients in whom, in the opinion of the physician, the benefits of treatment clearly outweigh the risks. (see WARNINGS and Boxed Warning.)
Does procainamide cause ANA?
WARNING: The prolonged administration of Procainamide often leads to the development of a positive anti-nuclear antibody (ANA) test, with or without symptoms of a lupus erythematosus-like syndrome. If a positive ANA titer develops, the benefit versus risks of continued Procainamide therapy should be assessed
What is procainamide used for?
Procainamide is a medication used to manage and treat ventricular arrhythmias, supraventricular arrhythmias, atrial flutter/fibrillation, and Wolf-Parkinson-White syndrome.
How is procainamide metabolized?
Procainamide is metabolized hepatically via acetylation to form N-acetyl procainamide (NAPA) via a substrate of CYP2D6. This compound is then excreted as NAPA. The half-life of procainamide is 2.5 to 5 hrs, and the maximum dose in current recommendations is 17 mg/kg.
Why is procainamide used in Wolf-Parkinson-White syndrome?
Procainamide is indicated in patients with Wolf-Parkinson-White syndrome as it is important for acute termination of antidromic AV re-entrant tachycardia in stable patients. In particular, because the use of an AV nodal blocking agent in this patient population may enhance conduction down the accessory pathway and therefore induce ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation. [4]
How long does it take for procainamide to work?
Procainamide is given IV or PO with the onset of action in 10 to 30 minutes. The loading dose is of IV procainamide is 10 to 17 mg/kg and administered at a rate of 20 to 50 mg/min. Alternatively, this may be dosed at 100 mg every 5 minutes in adult patients. The administration of this maintenance dose is from 1 to 4 mg/minute; however, the manufacturer labeling recommends 2 to 6 mg/minute.
When was procainamide first approved?
Procainamide was initially approved by the US FDA in 1950 and fell out of favor due to its side effect profile and the development of newer antiarrhythmics. Procainamide usage has increased in recent years, and it is now seen as a viable option for several arrhythmias.
Is procainamide a toxic drug?
Toxicity from procainamide overdose is rare as it is usually given IV in a monitored setting. However, it is plausible to administer a toxic dose accidentally or when a patient with renal impairment receives an inaccurate dose. Consultation of a medical toxicologist and regional poison control center is necessary in cases of oral procainamide overdose. Treatment would theoretically be similar to an overdose of other Class 1A antiarrhythmics, including quinidine and disopyramide, in which the patient receives hypertonic sodium bicarbonate to block sodium channels. [11]
Is procainamide safe for breastfeeding?
Use with caution in patients with heart failure, electrolyte imbalances (particularly hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia), myasthenia gravis patients, and in hepatic or renal impairment. Procainamide also crosses the placenta and may be present in the milk of breastfeeding mothers, and as such, chronic use requires caution in this population. [10]
What are some things I need to know or do while I take Procainamide?
Tell all of your health care providers that you take procainamide. This includes your doctors, nurses, pharmacists, and dentists.
How is this medicine (Procainamide) best taken?
Use procainamide as ordered by your doctor. Read all information given to you. Follow all instructions closely.
What do I need to tell my doctor BEFORE I take Procainamide?
If you have an allergy to procainamide or any other part of procainamide.
How do I store and/or throw out Procainamide?
If you need to store procainamide at home, talk with your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist about how to store it.
How old do you have to be to take procainamide?
If you are 50 or older , use procainamide with care. Talk with your doctor.
What to do if you have an overdose on procainamide?
Some drugs may have another patient information leaflet. Check with your pharmacist. If you have any questions about procainamide, please talk with your doctor, nurse, pharmacist, or other health care provider. If you think there has been an overdose, call your poison control center or get medical care right away.
Can procainamide cause lupus?
Long-term use of procainamide may cause lupus, a disease that causes irritation to joints and other parts of the body. Talk with the doctor. This medicine is only to be used to treat certain types of abnormal heartbeats. Other abnormal heartbeats have happened with procainamide, which in rare cases can be deadly.
What is the best medication for wide complex tachycardia?
The American Heart Association recommends procainamide, amiodarone, or sotalol. In the case of irregular wide-complex tachycardia, management of the condition should be focused on controlling the rapid ventricular rate, the conversion of hemodynamically unstable atrial fibrillation to sinus rhythm, or both.
Can procainamide be used for cardiac arrest?
Alright, so now let’s talk about the adult dosage for procainamide. Remember that the use of procainamide is limited in ACLS for cardiac arrest due to its requirements of slow infusion and its sometimes unknown effectiveness.
Does procainamide slow the conduction of the AV node?
Procainamide is effective at slowing the conduction in the atria, ventricles, and the His-Purkinje system by prolonging the P-R and Q-T intervals and the refractory period of the AV node. Procainamide also slows the refractory period within the atria and ventricles and slows the conduction velocity.
Does procainamide slow the atria?
Procainamide is effective in slowing the conduction in the atria, the ventricles and the Bundle of HIS Purkinje system. It does this by prolonging the P to R and the Q to T intervals and slows the refractory periods of the atria and ventricles as well as the refractory period of the atrioventricular node.
Can procainamide be used for prolonged QT intervals?
Pro Tip #1: The use of procainamide should be avoided in patients with prolonged QT intervals and associated congestive heart failure (CHF).
Is procainamide effective for supraventricular tachycardia?
Now let's take a look at procainamide indications. Procainamide is effective for the treatment of supraventricular tachycardia that returns after vagal maneuvers and adenosine are ineffective. Procainamide is also effective at treating the following: Stable wide complex tachycardia of uncertain origin.
How is procainamide given?
How is procainamide injection given? Procainamide is injected into a muscle or into a vein through an IV. You will receive procainamide injection in a hospital setting where your heart can be monitored in case the medication causes serious side effects.
How is procainamide injection given?
Procainamide is injected into a muscle or vein by a healthcare provider.
What should I avoid while receiving procainamide injection?
Avoid being near people who are sick or have infections. Tell your doctor at once if you develop signs of infection.
Why is procainamide used in the heart?
Procainamide is used to help keep the heart beating normally in people with certain heart rhythm disorders of the ventricles (the lower chambers of the heart that allow blood to flow out of the heart).
What are the side effects of procainamide?
Get emergency medical help if you have any of these signs of an allergic reaction: hives; difficult breathing; swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat. Tell your caregivers at once if you have a serious side effect such as: a new or a worsening irregular heartbeat pattern; ...
What medications interact with procain?
heart rhythm medications such as amiodarone (Cordarone, Pacerone ), quinidine (Quin-G), disopyramide (Norpace), flecaininde ( Tambocor ), mexiletine ( Mexitil ), propafenone, ( Rythmol ), and others. This list is not complete and other drugs may interact with procainamide. Tell your doctor about all medications you use.
Can procainamide cause heart problems?
Procainamide can cause serious side effects and is for use only to treat life-threatening heart rhythm problems. If you receive procainamide during an emergency, make sure any follow-up doctor knows you received procainamide.
What should be examined for before administration of parenteral drug?
Parenteral drug products should be examined visually for particulate matter and discoloration (see HOW SUPPLIED) prior to administration.
How much maintenance infusion is needed for arrhythmia?
The maintenance infusion rates are calculated to deliver 2 to 6 mg per minute, depending on body weight, renal elimination rate, and steady-state plasma level needed to maintain control of the arrhythmia*. The 4 mg/mL maintenance concentration may be preferred if total infused volume must be limited.
Can procainamide hydrochloride be administered intravenously?
Intravenous administration of Procainamide Hydrochlor ide Injection should be done cautiously to avoid a possible hypotensive response. Initial arrhythmia control, under ECG monitoring, may usually be accomplished safely within a half-hour by either of the two methods which follows:
When to follow instructions of AED?
Follow instructions of the AED until the arrival of medical transport.
Can you take procainamide with QT?
Procainamide and sotalol should be avoided in patients with prolonged QT.

Description
Clinical Pharmacology
Indications and Usage
Contraindications
Precautions
Adverse Reactions
Overdosage
Dosage and Administration
How Supplied
- Procainamide Hydrochloride Injection, USP is available in multiple-dose 10 mL vials providing 100 mg Procainamide hydrochloride per mL and 2 mL vials providing 500 mg Procainamide hydrochloride per mL. The solutions, which are clear and colorless initially, may develop a slightly yellow color in time. This does not indicate a change which should pr...