The second deriviatve is just the derivative of the first derivative. Step 1: The critical points (maximums and minimums) of y’ are where y” = 0. Plot those points. Step 2: Where the slope is positive in y’, y” is positive. Draw the positive parts of the y” graph with the maximums being where points of inflection were in y’. Step 3: Where the slope is negative in the y’, y” is negative. Draw the negative parts of the y” graph with the minimums being where points of ...
How do you find the second derivative?
The Second-Derivative Test. Let c be a critical value of a function f at which f ′ ( c) = 0 which is differentiable on some open interval containing c and where f ″ ( c) exists. Then, if f ″ ( c) < 0, then f has a local maximum at x = c; if f ″ ( c) > 0, then f has a local minimum at x = c.
What is the purpose of the second derivative?
- x > 1 For all x > 1, [f” (x) = 6 (x – 1)] > 0. The function is Concave Up.
- x < 1 For all x < 1, [f” (x) = 6 (x – 1)] < 0. The function is Concave Down.
- x = 1 [f” (x) = 6 (x – 1)] = 0. Thus, (1, f (x = 1)) is a Point of Inflection of the given function.
How do you find a derivative from a graph?
How do you find a derivative from a graph? Choose a point on the graph to find the value of the derivative at. Draw a straight line tangent to the curve of the graph at this point. Take the slope of this line to find the value of the derivative at your chosen point on the graph.
How to calculate the second derivative of the determinant?
Second Derivative. A derivative basically gives you the slope of a function at any point. The derivative of 2x is 2. Read more about derivatives if you don't already know what they are! The "Second Derivative" is the derivative of the derivative of a function. So: Find the derivative of a function. Then find the derivative of that.
What does the second derivative look like on a graph?
The second derivative tells whether the curve is concave up or concave down at that point. If the second derivative is positive at a point, the graph is bending upwards at that point. Similarly if the second derivative is negative, the graph is concave down.
How do you represent the second derivative?
In functional notation, the second derivative is denoted by f″(x). In Leibniz notation, letting y=f(x), the second derivative is denoted by d2ydx2.
How do you graph the derivative of another graph?
3:4314:48Sketching the Derivative of a Function - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipPoint it says for that corresponding x-coordinate on the original graph whatever that y-coordinateMorePoint it says for that corresponding x-coordinate on the original graph whatever that y-coordinate is that's the slope of the tangent line. Okay as I move from this x-coordinate. Over to my my.
What does 2nd derivative tell you?
The second derivative measures the instantaneous rate of change of the first derivative. The sign of the second derivative tells us whether the slope of the tangent line to f is increasing or decreasing.
How do you do the second derivative on Desmos?
Use f′′(x) to find the second derivative and so on. If the derivative evaluates to a constant, the value is shown in the expression list instead of on the graph. Note that depending on the complexity of f(x) , higher order derivatives may be slow or non-existent to graph.
How do you find the graph of a function from its derivative?
0:127:38Draw the Function given Graph of Derivative - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo if the derivative if the graph of the derivative is below the x-axis that's negative itsMoreSo if the derivative if the graph of the derivative is below the x-axis that's negative its decreasing on the original function or the original function is decreasing.
How do you read a first and second derivative graph?
2:074:27Ex 1: Interpret the Graph of the First Derivative Function - Degree 2YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipChanges from decreasing to increasing at x equals negative three and therefore there would be a lowMoreChanges from decreasing to increasing at x equals negative three and therefore there would be a low point or a relative minimum. So we have a relative minimum at x equals negative three.
How do you graph the second derivative on a TI 84?
Press 2nd CALC and select maximum or minimum. The maximum or minimum point on the interval you selected will appear. To find the 2nd derivative at a single point, from the home screen enter nDeriv Y2 , X , and the x-coordinate you want to evaluate at. To graph the 2nd derivative, enter nDeriv(Y2,X,X) in Y3 and graph.
Why do we write D 2y dx 2?
Originally Answered: Why is the second derivative of “y” notated by “d^2y/dx^2”? The first derivative is denoted as dy/dx. The second derivative is a derivative, with respect to x, of the first. Therefore we denote it as d/dx(dy/dx).
How do you write y double prime?
Using prime notation, this is f″(x) or y″. You can read this aloud as "f double prime of x" or "y double prime." Using Leibniz notation, the second derivative is written d2ydx2 or d2fdx2. This is read aloud as "the second derivative of y (or f)."
What is d2y dx2?
The second derivative, d2y. dx2 , of the function y = f(x) is the derivative of dy. dx. .
Summary
Points of inflection become critical points. Critical points become zeros.
Want more?
For students of the Los Angeles South Bay, you can sign up for one of our in-home tutors. If you live outside the area, we are happy to work with you via video chat! Just click on the schedule a tutor button. You can also like us on Facebook, find more study tools, or follow us on Instagram by clicking on the corresponding icon.
GRAPHING OF FUNCTIONS USING FIRST AND SECOND DERIVATIVES
The following problems illustrate detailed graphing of functions of one variable using the first and second derivatives. Problems range in difficulty from average to challenging.
Click HERE to return to the original list of various types of calculus problems
Your comments and suggestions are welcome. Please e-mail any correspondence to Duane Kouba by clicking on the following address :
What is a Second Derivative?
The second derivative (f ′′ ), is the derivative of the derivative (f ′ ). In other words, in order to find it, take the derivative twice.
Examples
Example question 1: Find the 2nd derivative of 2x3. Step 1: Take the derivative: f′ 2x 3 = 6x 2 Step 2: Take the derivative of your answer from Step 1: f′ 6x 2 = 12x
Find the Second Derivative Implicitly
Like the “usual” way of finding second derivatives, finding the second derivative implicitly involves two steps: implicitly differentiating twice.
Finding the Second Derivative Implicitly: Example
Example question: Find the second derivative implicitly of x 2 + 4y 2 = 1.
Part One: Finding the First Derivative Implicitly
Step 1: Take the derivative (s) of the left hand side. We have two parts to differentiate: x2 and 4 y2:
Part Two: Finding the Second Derivative Implicitly
You could jump right in at this point and re-run the steps above to get the second derivative.
Second Derivative Test
This test is used to find intervals where a function has a relative maxima and minima. You can also use the test to determine concavity.
What Is The Second Derivative Of A Function?
The second derivative of a function f (x) is the derivative of the derivative of f (x). In other notation:
What Does Second Derivative Tell You?
The second derivative f’’ (x) tells you how fast the first derivative f’ (x) is changing. However, there is a lot more that the second derivative can tell us, such as:
Conclusion
Now you know what the second derivative tells you and what it is. You also have some examples of how it is used to give us more information about a function and its shape.
What Is The Second Derivative? Second Derivative Definition
Taking a derivative of a function means making an algebraic manipulation of the function to study its instantaneous rate of change. There is no limit to how many times this can be done. The first time this manipulation is made from the original function it is called the first derivative.
How To Find The Second Derivative
Finding a second derivative really means taking the derivative of a first derivative, and this process is best illustrated with an example.
Differentiating Functions Step-by-step To Find The Second Derivative
1) Identify the proper method of differentiation for the given function.
Second Derivative Examples
1) The first derivative will require the power rule and the product rule.
1. A cubic
The initial example shows a cubic curve on the left, its derivative in the middle, and the second derivative on the right. The red line is tangent to the cubic and the slope of this curve is the value of the derivative. Move the slide and compare the red line and the red crosshair in the middle graph.
2. A Sine curve
Select the second example from the drop down menu, the sine curve. Move the slider.
3. An exponential
Select the third example, the exponential function. Move the slider. Does it make sense that the second derivative is always positive? Why? What is it about the shape of the original function that tells you the second derivative will always be positive?
4. A hyperbola
Select the fourth example, the hyperbola. Can you relate the concavity of the hyperbola on the left to the second derivative graph on the right?
Explore
You can also type your own function into the "f (x)=" box to explore other derivatives and second derivatives.
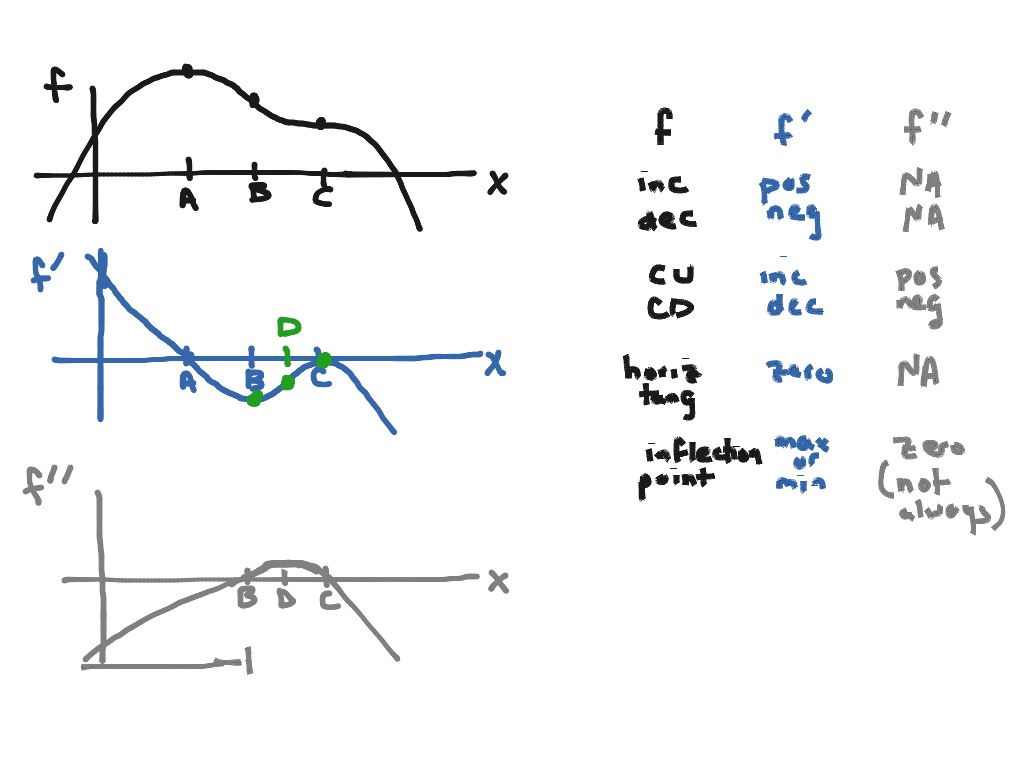
Derivative Graph Rules
Below are three pairs of graphs. The top graph is the original function, f (x), and the bottom graph is the derivative, f’ (x).
How To Read Derivative Graphs
Alright, this seems simple enough, but what do we do if we are given the derivative graph, and we want to find the original function?
Original Equation
- Critical Points: These occur where the slope is 0. They are the minimums and maximums of your graph. Points of Inflection:These occur where concavity changes in the original.
First Derivative
- The first derivative is the graph of the slopes of the original equation. How to Graph Step 1: Critical points (maximums and minimums) of the original equation are where the zeros are now the zeros (y’ = 0). Plot those points. Step 2:Where the slope is positive in the original, y’ is positive. Draw the positive parts of the y’ graph with the maximums being where points of inflection were …
Second Derivative
- The second derivative is a graph of the slope of the first derivative. How to Graph Follow the same steps as for graphing the first derivative, except use the first derivative graph like it was the original. The second deriviatve is just the derivative of the first derivative. Step 1: The critical points (maximums and minimums) of y’ are where y” =...
Summary
- Points of inflection become critical points. Critical points become zeros. Asymptotesstay in the same spots.
Want More?
- For students of the Los Angeles South Bay, you can sign up for one of our at-your-home tutors. If you live outside the area, we are happy to work with you via video chat! Just click on the schedule a tutor button. You can also find more free math resources and our favorite study tools for other subjects by clicking on the corresponding buttons.