How Can You Hedge Using Futures?
- Identify the Futures Contract
- Get the value of the contract
- Maintain the position (rollover) 1. Identify the Futures Contract As there aren’t futures contracts for all securities, you will have to either use a market that’s tracked by a futures contract, or find a correlating futures market. Now, in case you’re trying to use a stock for hedging, it could become a little difficult. ...
How to hedge a portfolio of stocks?
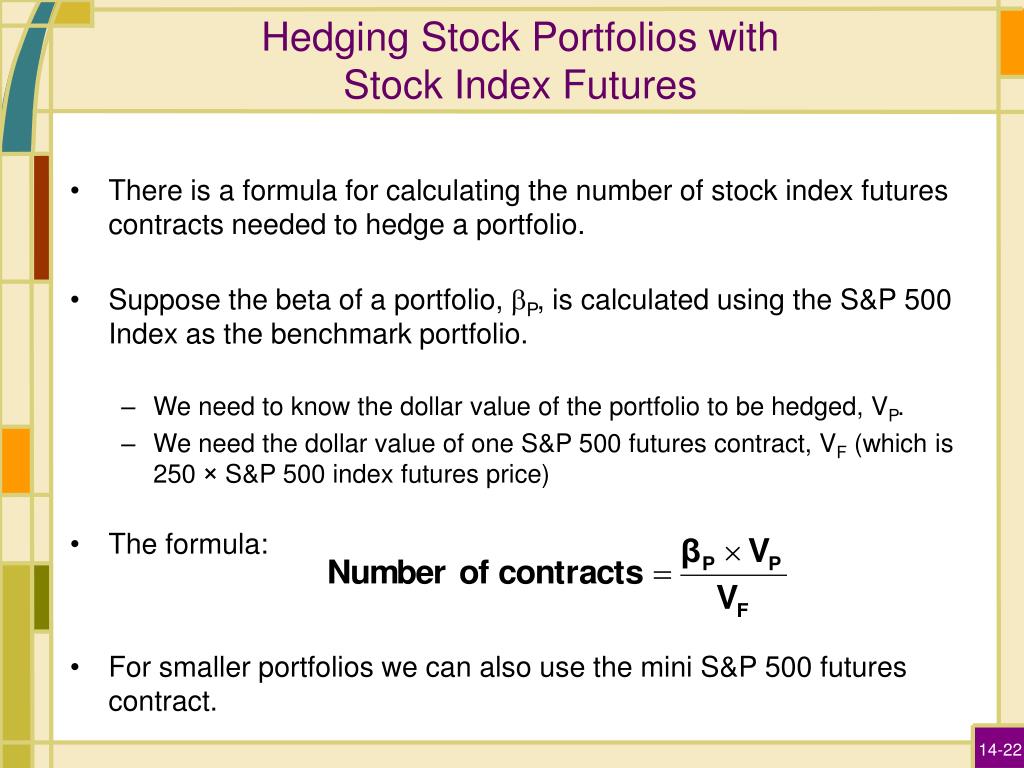
One of the best ways to hedge a portfolio of stocks is to use an index future. Many large cap stocks move in tandem with an index when a large adverse move happens in the stock market.
What is hedging in stocks?
If an investor owns a portfolio of stocks, his exposure is to a downward move in stock prices. Hedging can be accomplished with many different types of financial instruments -- including a stock index that represents a proxy for a portfolio of stocks.
Where are futures contracts traded?
The S&P 500 index contract is the most widely traded U.S. futures contract. The contract is traded on the Chicago Mercantile Exchange.
Why do investors reduce risk?
Investors at points during their investment life may decide to reduce risk. This can occur as they become more conservative or if they change their view on which way the stock market will go. Hedging risk has a number of benefits and can be accomplished by using stock index futures.
How much does it cost to buy a futures contract if the index is at 1,000?
So, if the index is at 1,000, you would pay $250,000 to buy one futures contract. This is why the S&P e-mini contract was created in 1997. Its multiplier is $50, so one futures contract if the index was at 1,000 would cost $50,000 -- much more affordable for the retail investor who wants to hedge portfolio risk.
When were index futures created?
In 1982 , stock index futures were created to allow portfolio managers to control this risk by hedging their investments using futures contracts like commodity producers hedge the value of their production..
How much is an S&P E-mini futures contract?
If you own an S&P e-mini futures contract that you bought when the S&P was at 1,000, and the index rises to 1,500, the value of your contract rises from $50,000 to $75,000. If the index drops to 500, your contract's value is $25,000. The S&P contract is the most popular because the S&P index is considered reflective of the broad market, and many index mutual funds and hedge funds as well as S&P-based exchange traded funds are widely used ways of investing in the diversified broad market.
How Can You Hedge Using Futures?
As we explained earlier, it’s common for companies to use futures to hedge against unexpected price fluctuations in the assets they use for their daily operations. However, still being a viable option it’s less common that individual investors or market players use futures to hedge their positions. For those purposes, options contracts are better in most cases.
What is hedge risk?
Hedging is a form of risk management technique where some of the risks that a position carries are offset by entering a position in another, uncorrelated market.
What is the term structure of a futures contract?
1.The Term Structure of Futures Contracts. Since futures contracts are agreements to buy or sell an asset at a future time and date , the price of the contract isn’t only a representation of the price of the underlying, but also things like storage costs and the market’s expectation of the price on the delivery date.
Why do airlines go to the futures market?
In essence, this means that the airline company goes to the futures market to offset any outsize movements in fuel prices. Since standardized futures that track airline fuel aren’t available, they will choose a market that closely follows the price of airline fuel.
Why were futures contracts invented?
In fact, futures contracts were invented for risk management purposes, when farmers started to offset their risk by selling a futures contract to speculators. In effect, this gave speculators the opportunity to speculate in the future developments of price, while the issuer of the contract was guaranteed the amount stated in the contract.
Is there a futures contract for every commodity?
As we covered in the airline example, there aren’t futures contracts for every type of commodity. Sometimes companies will have to go for the next best solution, which means using futures contracts in a correlated asset.
Can you use a stock for hedging?
Now, in case you’re trying to use a stock for hedging, it could become a little difficult. Far from every stock can be accessed through a futures contract, and a broad market index is probably not what you’re looking for. However, most of the bigger stocks can be reached through futures contracts.
Where Notional Value Comes In
There is an old expression, “you can’t manage what you can’t measure.” Risk managers and traders can use Equity Index futures to help manage their equity index risk. It begins with understanding the notional value of the Equity Index futures contract. The notional value of a futures contract represents that contract’s financial equivalent value.
Using Notional Value as Part of a Hedging Strategy
Traders use notional value to compare the current value of the futures price to other futures contracts or highly correlated physical positions. When calculating a hedge ratio, traders and risk managers would want to compare the value of the instrument of portfolio at risk versus the relative value of the futures contract.
How CME Group Can Help
CME Group lists many Equity Index products providing risk-management tools that serve to assist equity portfolio managers in even the most challenging market environments.
Selling Is Not Always the Best Option
If your portfolio is well diversified, then that means your overall stock exposure moves along with the broader market. It means that you have a balanced exposure to all eleven sectors, from basic materials to tech.
Hedging 101 – The Basics You Should (At Least) Know About
What is hedging? Simple: it’s a strategy used to protect your portfolio from downside risk. The market goes down, taking your portfolio values with it…being hedged means reducing your losses by seeking a positive return on the downside using a different asset.
Why Use Index Futures, Specifically Micro E-Mini Futures?
Let’s go over a few basics. A futures contract obliges you to purchase or sell a specific underlying product on a certain date in the future, that is, unless you sell your contract ahead of expiration.
How to Hedge Your Portfolio
Let’s suppose you hold large positions of the SPDR S&P 500 exchange traded fund (SPY) and the Invesco Nasdaq Trust (QQQ). To make things easier, let’s suppose you hold equal dollar amounts for both:
What is hedge risk?
Hedging is a way to reduce risk exposure by taking an offsetting position in a closely related product or security.
What is futures investment?
Futures are a popular asset class used to hedge against risk. Strictly speaking, investment risk can never be completely eliminated, though its impact can be mitigated or passed on. Hedging through future agreements between two parties dates to the 1800s.
What happens if the price declines to $7.50?
If the price declines to $7.50, the buyer will lose on the futures contract ($7.50 - $10.10 = -$2.60). He will buy required soybean at the market price of $7.50, taking his net buy price to -$7.50 - $2.60 = -$10.10.
What happens if the futures market is not efficient?
If the futures market is not efficient and not well regulated, speculators can dominate and impact the futures prices drastically, leading to price discrepancies at entry and exit (expiration), which undo the hedge.
How does a farmer shield his price?
In all three cases, the farmer is able to shield his desired sale price by using futures contracts. The actual crop produce is sold at available market rates, but the fluctuation in prices is eliminated by the futures contract.
Why do companies use futures?
Using futures takes away the higher profit potential in some cases (as cited above). It can lead to different perceptions in cases of large organizations, especially the ones having multiple owners or those listed on stock exchanges. For example, shareholders of a sugar company may be expecting higher profits due to an increase in sugar prices last quarter but may be disappointed when the announced quarterly results indicate that profits were nullified due to hedging positions.
Is hedge risk without costs?
Hedging is not without costs and risks. Assume that in the first above-mentioned case, the price reaches $13, but the farmer did not take a futures contract. He would have benefited by selling at a higher price of $13. Because of futures position, he lost an extra $2.90. On the other hand, the situation could have been worse for him the third case, when he was selling at $7.50. Without futures, he would have suffered a loss. But in all cases, he is able to achieve the desired hedge.