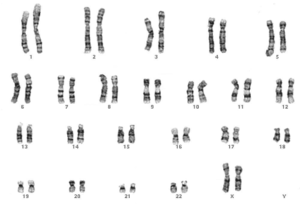
- Male karyotype: The male karyotype has one X and one Y chromosomes with 22 pairs of autosomes. ...
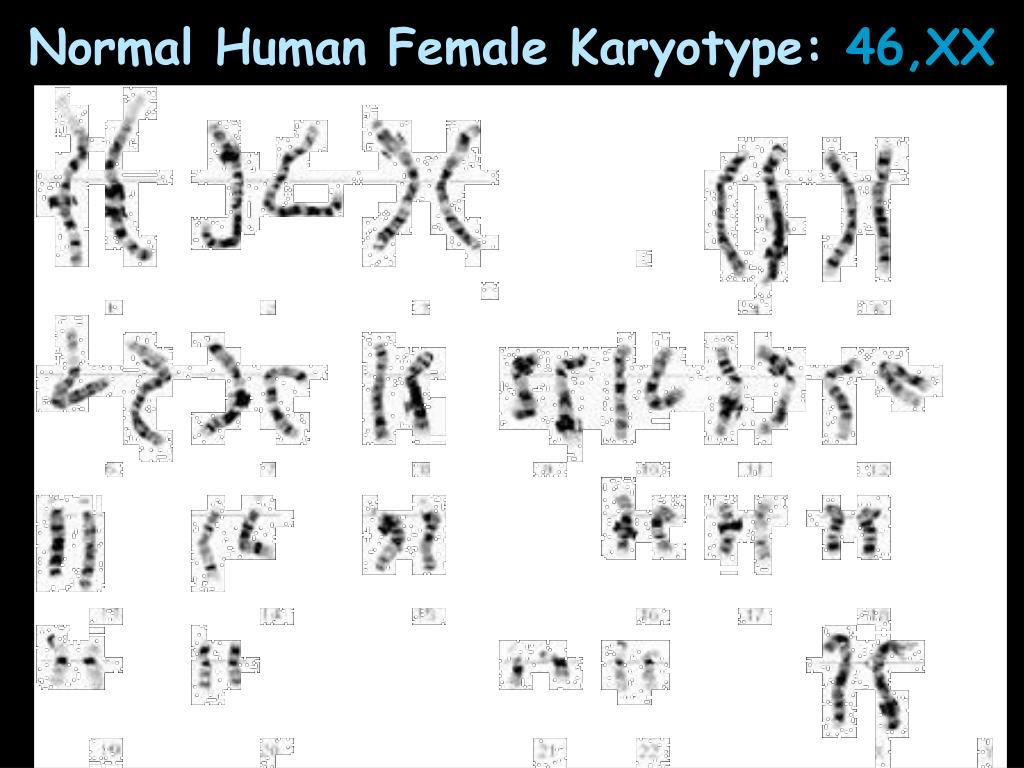
- Female karyotype: Females have two X chromosomes instead of X and Y of males. Both the X chromosomes are the same in size and are metacentric.
- Conclusion: Using other techniques like PCR, DNA sequencing and DNA microarray SNPs and other small copy number variations can be reported.
What is the difference between male and female karyotypes?
What is the Difference Between Normal and Abnormal Karyotyp
- Karyotype: A standard arrangement of the chromosome complement prepared for chromosome analysis. ...
- e the prognostic impact of monosomal karyotype (MK) in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in the context of the current World Health Organization Male 406 (55) 176 (55) Female 333 (45) ...
- Define diploid karyotype. ...
- g a karyotype is to collect a sample. ...
What is the difference between male and female karyotype?
What is the normal female karyotype? Females have two X chromosomes, while males have one X and one Y chromosome. A picture of all 46 chromosomes in their pairs is called a karyotype. A normal female karyotype is written 46, XX, and a normal male karyotype is written 46, XY.
What is a normal female karyotype?
- If you’ve had trouble getting pregnant or have had several miscarriages, the doctor may want to check whether you or your partner have a chromosome problem.
- You can find out if you have a disorder that you could pass down to your child.
- They can test a stillborn baby to see if there was a genetic issue.
What is the karyotype used for?
The karyotype is used to study and identify chromosomes, location of the centromere, the size difference of different chromosomes and to find out various chromosomal abnormalities. To find out minor variations less than 5Mb is determined by the cytogenetic technique like FISH (Fluorescence in situ hybridization) and DNA microarray.
What is the difference between a female and a male karyotype?
A female karyotype reveals the genetic abnormalities associated with males and females while the male karyotype reveals the genetic abnormalities only associated with males. It is only a myth that problems related to X or Y chromosomes only cause reproductive problems.
How many autosomes does a male karyotype have?
The male karyotype has one X and one Y chromosomes with 22 pairs of autosomes. The normal X chromosome is metacentric while the normal Y chromosome is acrocentric and smaller. The karyotype of male is shown in the figure below. See first,
What is the process of arranging chromosomes called?
The process is known as karyotyping while the process of arranging chromosomes is known as a karyotype . A karyotype reveals so many things related to chromosomes. Interesting article: 10 tips and tricks for karyotyping.
What is the Y chromosome?
A normal male karyotype- 46,XY. The Y chromosome is a unique identity for males. In comparison to other chromosomes, the Y chromosomes have fewer genes. An important gene for maleness that is the SRY is located on the Y chromosome. The SRY gene is located on the TDS region on the short arm of the Y chromosome.
What are the common chromosomal abnormalities?
Common chromosomal abnormalities are translocations, duplications, deletions, insertions, and inversions. Besides, a change in the number of chromosomes is also one of them.
How many X chromosomes do females have?
Females have two X chromosomes instead of X and Y of males. Both the X chromosomes are the same in size and are metacentric. The typical normal female karyotype is shown in the figure below, Normal female karyotype- 46,XX. There is an interesting mechanism associated with female chromosomes- the X-chromosome inactivation.
How is a super female developed?
The super female is developed by the presence of one extra X chromosome in a pair due to the event called nondisjunction. Notably, no serious health-related issues are associated with it. Sometimes a large duplication of X chromosome results in X-linked acrogigantism.
What is the difference between male and female karyotypes?
The male karyotype refers to the appearance of the complete set of chromosomes in a somatic cell of a male while the female karyotype refers to the appearance of the complete set of chromosomes in a somatic cell of a female.
What are the characteristics of a male karyotype?
However, the main characteristic feature of a male karyotype is the presence of an X chromosome and a Y chromosome in the sex chromosome pair. In other words, the Y chromosome is one of the two sex-determining chromosomes in humans as well as many other species. It only passes from father to the son.
How many pairs of chromosomes are in a female karyotype?
It contains 22 pairs of autosomal chromosomes and a pair of sex chromosomes including one X and one Y chromosome. In comparison, the female karyotype is the number and appearance of the complete set of chromosomes of a somatic cell of a female. Though it contains a similar number of autosomal chromosome pairs with a similar appearance, ...
How many chromosomes are in a human body?
Generally, all somatic cells of the body of a human contain 46 chromosomes, which can be classified into 22 pairs of autosomes and a pair of allosomes or sex chromosomes. The autosomal pairs of both males as females are similar. However, the main characteristic feature of a male karyotype is the presence of an X chromosome and a Y chromosome in ...
What are the two types of chromosomes in both male and female karyotypes?
The two types of chromosomes in both types of karyotypes are the autosomal and sex chromosomes. Generally, both male and female karyotypes contain autosomal chr omosome pairs similar in both number and appearance.
What is a male karyotype?
What is the Male Karyotype. Male karyotype is basically the appearance of the complete set of chromosomes in a somatic cell of a male. It allows the determination of the number of chromosomes and their physical characteristics.
Why are karyotypes important?
Also, both types of karyotypes allow the identification of the length of chromosomes, the position of the centromere, and the banding pattern. Also, they allow the determination of the physical characteristics of chromosomes. Besides, both are important in the identification of chromosome abnormalities.