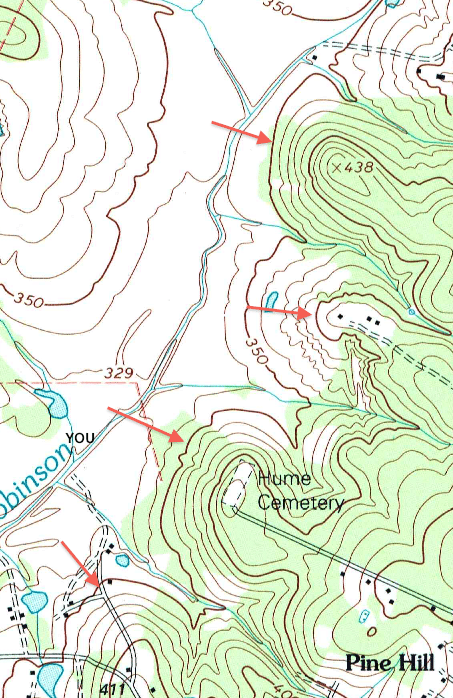
A valley can be “V” or “U” shaped and often can be seen as a “negative” to a ridge. On a map, valleys are represented by the same contour shape as ridges with the difference being the the wide openings are at lower elevation. A gully (or draw) is a narrower valley and a couloir is a gully that is formed on the slope of a ridge.
Which way do the contour lines point on a topographic map?
Bottom left picture shows the contour lines overlaid on the 3D image and the right picture is the topographic map (1:50000) of the same valley. Top of the images and map is toward south direction. A gentle wide valley bottom with higher elevation toward south (contour lines point toward south) is evident.
How do you find the valley bottom of a valley?
Valley bottoms are represented by "U" or "V" shaped contour lines with their closed end pointing towards higher elevation. Bottom left picture shows the contour lines overlaid on the 3D image and the right picture is the topographic map (1:50000) of the same valley.
What is a valley contour line?
Valley Contour Lines A valley is an elongated depression in the landscape that is formed by the action of water (V-shaped) or carved out by glaciers (U-shaped). Valley bottoms are represented by "U" or "V" shaped contour lines with their closed end pointing towards higher elevation.
What does a valley look like on a map?
A valley can be “V” or “U” shaped and often can be seen as a “negative” to a ridge. On a map, valleys are represented by the same contour shape as ridges with the difference being the the wide openings are at lower elevation.
How do valleys look on a contour map?
Valleys are elongated low-lying depressions usually with a river flowing through them. You know that you're looking at a valley bottom when contour lines are V or U-shaped. All rivers flow downhill from higher to lower elevations, perpendicular to the contour line above them.
How do you identify ridges and valleys?
0:109:02Hydrology: Ridges & Valleys - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSomething is a ridge or a valley now that probably made no sense to you so let's do a coupleMoreSomething is a ridge or a valley now that probably made no sense to you so let's do a couple examples. And hopefully that all I can teach you how to identify ridges and valleys very very easily.
What do you notice about the contour lines when they indicate a valley?
When contour lines cross a valley or a stream, they make a sharp pointed V or U-shape. Rivers, of course, are represented by blue lines that will run through the center of the V-shape. Sometimes called draws, the V-shape of this feature always points towards their peak.
How do you draw a valley with contour lines?
0:111:12contours showing a 'V' shaped valley - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo here's that photograph. If we follow a contour along maintaining. The same height on the side ofMoreSo here's that photograph. If we follow a contour along maintaining. The same height on the side of the valley. Hit the river there and then the contour would come back along the river valley.
How do you identify valleys?
A valley is an elongated depression in the landscape that is formed by the action of water (V-shaped) or carved out by glaciers (U-shaped). Valley bottoms are represented by "U" or "V" shaped contour lines with their closed end pointing towards higher elevation.
How do you find ridges and valleys on a topographic map?
All of the ridges have lower ground in three directions and higher ground in one direction. The closed ends of the U's formed by the contour lines point away from higher ground. To the south lies a valley; the valley slopes downward from east to west.
What's the difference between a valley and a draw?
Draws are similar to valleys on a smaller scale, however while valleys are by nature parallel to a ridgeline, a draw is perpendicular to the ridge, and rises with the surrounding ground, disappearing up-slope.
How do you read elevation contour lines?
0:473:13How to Read Contours on a Topographic Map - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipLet's see a little bit as a PDF we're going to try to find a point that we want to know to find anMoreLet's see a little bit as a PDF we're going to try to find a point that we want to know to find an easy one we're going to look at this little red kind of plus sign right here. And this is the point
What are 3 types of contour lines?
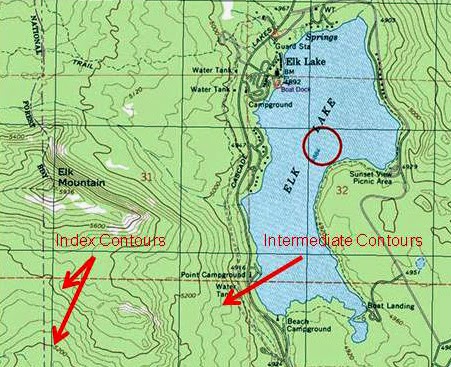
There are 3 kinds of contour lines you'll see on a map: intermediate, index, and supplementary. Index lines are the thickest contour lines and are usually labeled with a number at one point along the line.
How do you read a contour plot?
How to interpret contour plot?Contour plots can indicate peaks or valleys within the range of X and Y at the center of concentric shapes.If the contour lines are spaced close to each other, then the values change rapidly while if the contour lines are spaced far apart then the z values change more slower.More items...
Where can valleys be found?
Valleys are elongate depressions of Earth's surface. Valleys are most commonly drained by rivers and may occur in a relatively flat plain or between ranges of hills or mountains. Those valleys produced by tectonic action are called rift valleys.
What is ridge and valley line?
Ridge & Valley Line Line joining the highest point of a hill across the contours at right angles is called Ridge line. It represent by U-shaped. If the higher values are outside the loop in the contour it indicates a Valley. Line joining the lowest point of a valley across the contours at right is called Valley line.
What are ridges and valleys in fingerprint?
The ridge of a fingerprint usually becomes the dark lines of a fingerprint image which is acquired by the use of the sensor device called fingerprint scanner. Between the ridges are the low lines which are the valleys. The valleys are showed as white lines in a fingerprint image.
What are the physical features of Ridge and Valley?
The Valley & Ridge province consists of elongate parallel ridges and valleys that are underlain by folded Paleozoic sedimentary rocks. The characteristic topography of this region results from differential erosion of linear belts of rocks that are repeated by folding and faulting.
How ridges and valleys are formed?
As erosion began to shape the landscape, the hard layers of sandstone or chert resisted, while the soft areas of shale or limestone eroded more easily. This process slowly developed into the ridges and valleys we see today and greatly influenced the soil composition of the two.
What is ridge and valley line?
Ridge & Valley Line Line joining the highest point of a hill across the contours at right angles is called Ridge line. It represent by U-shaped. If the higher values are outside the loop in the contour it indicates a Valley. Line joining the lowest point of a valley across the contours at right is called Valley line.
How high is the contour interval?
Example: The contour interval is 50 feet according to the map key. You want to find out the elevation of an intermediate line 3 lines above an index line labeled 1,000. For each line above this index line, elevation increases 50 feet. Therefore, the interval line in question is at 1,150 feet above sea level.
How to read elevation on a map?
If you’re looking at an index line, it's easy to read the elevation because it is clearly labeled. However, interval lines are somewhat trickier. To determine their elevation, you’ll need to know the contour intervals. Contour intervals tell you the change in elevation between any two contour lines. You can find the contour interval in the map key, usually located underneath the scale of the map at the bottom center. To understand all map symbols, see the US Gov document.
What are the squiggly lines on a hiking map?
Ever noticed those squiggly lines all over your hiking map? Other than the obvious trails and rivers, these squiggly lines are contour lines.
What is topography in geography?
Topography is the study of geographical features on a landscape. A map with contour lines on it is called a topographic map. Topographic maps use a combination of colors, shading and contour lines to represent changes in elevation and terrain shape. Essentially, topographic maps represent the three-dimensional landscape ...
What does a quick glance at a topographic map give you?
A quick glance at a topographic map will give you a general idea of the landscape. Is it flat or mountainous?
How to turn on topographic view on Google Maps?
Google Maps. You can turn their topographic view (complete with contour lines) by selecting the “Terrain” layer from the options menu.
What is the innermost ring of contour loops?
A. Peak Ring. The innermost ring at the center of several contour loops almost always represents a peak (highest elevation). Sometimes the peak will be represented with a small X and number denoting elevation.
How are hills and mountains shown on a map?
Look for the height and shape of the ground which is shown on 1:25 000 scale maps by brown contour lines. A contour is a line drawn on a map that joins points of equal height above sea level. For 1:25 000 scale maps the interval between contours is usually 5 metres, although in mountainous regions it may be 10 metres.
How do contour lines work?
Now you know how contour lines are created, you can use them to visualise the terrain they show, remembering that: Contours follow points of equal height. If you can't see a number, follow the line to find one. On some maps, not all contours will have labels and are printed slightly lighter, but you can work out the height by looking ...
What is contour on a map?
A contour is a line drawn on a map that joins points of equal height above sea level. For 1:25 000 scale maps the interval between contours is usually 5 metres, although in mountainous regions it may be 10 metres. How contour lines show a pair of small hills.
What does steeper slope mean?
The steeper the slope the closer together the contour lines will be. You can see this in the examples below:
How are hills, slopes and mountains represented on a map?
Hills, slopes and mountains are represented on a map using contour lines. By studying the contour lines you can work out lots about the surrounding terrain including gradients of hills, valleys and steepness of climbs.
How to think about contour lines?
Another way of thinking about contour lines is as a tide mark left by the sea as the tide goes out, leaving a line every 5 metres. Top tip! Remember contour numbering reads up hill – in other words the top of the number is uphill and the bottom is downhill.
Where is the hill peak on the map?
There is a hill peak just over 430m at the top centre of the map. Near the middle of the map, at the 350m contour label, there is a flat area that's a ridge or spur. Now that you have learnt the basics, you can further your knowledge with our advanced guide to reading map contours and relief.
What is a valley in geography?
Valley (Also: Gully, Draw, Couloir) – Long depression in the terrain that has a narrow elevated side and a wide lower opening. A valley can be “V” or “U” shaped and often can be seen as a “negative” to a ridge. On a map, valleys are represented by the same contour shape as ridges with the difference being the the wide openings are at lower elevation. A gully (or draw) is a narrower valley and a couloir is a gully that is formed on the slope of a ridge.
What is the difference between a valley and a couloir?
On a map, valleys are represented by the same contour shape as ridges with the difference being the the wide openings are at lower elevation. A gully (or draw) is a narrower valley and a couloir is a gully that is formed on the slope of a ridge.
What is the difference between a mountain and a hill?
On the map, there will be several contour “rings” leading to a peak. There is no clear difference between a hill and a mountain, but it tends to be subjective to the area – bellow 500 metes (1500ft) will be a hill and above will be a mountain, etc. A mountain tends to be described as having steeper inclines than a hill.
What is a saddle on a map?
Saddle (Also: Col or Pass) – A low point between two distinct peaks (or hills) and forms the shape of a saddle. Saddles are represented on the map by a set of rings of a flatter area with two separate ring sets to represent the two peaks.
What is a mountain ridge?
A mountain tends to be described as having steeper inclines than a hill. Ridge (Also: Arete or Spur) – A continuous elevated terrain with sloping sides. In the map represented by “U” or “V” shaped contour lines where the higher ground is in the wide opening.