How to tell if something is an acid or base?
- ⇒ Acid + Base ⇌ Conjugate Base + Conjugate Acid. ...
- Let’s take another example, CH3COOH reacting with the H2O. ...
- Limitation of Bronsted-Lowry theory: –. ...
- There is no absolute acid and base defined by this theory, the substance can only act as the acid in presence of a base similarly the substance can only act ...
- Also read:-. ...
What is the formula for acid and base?
Write the formula for the conjugate base of each acid HCl,H2SO3,HCHO2,HF. Acids have one more H+ ion than there conjugate base pairs so to write a conjugate base pair, simply remove a H and subtract a charge (-1) *HCl→Cl---Since the charge is 0, when we subtract one charge, the new charge is -1 or -
How do you identify strong acids and bases?
- Strong acids : HCl, HNO 3, H 2 SO 4. - good conductors - large value for current passing
- Weak acids : CH 3 COOH, H 2 CO 3. - poor conductors - low value for current passing
- Strong bases : group 1 hydroxides (ie NaOH etc), or lower group 2 hydroxides Ba (OH) 2. - good conductors
- Weak bases : NH 3, CH 3 CH 2 NH 2. - poor conductors
What are some common household acids and bases?
- Coca-cola/ soft-drinks
- Toilet bowl cleaners
- Lemon juice (or anything citric like oranges etc.)
- Shampoo
- Aspirin
- Phenol
- Milk
- Some vegetables like Spinach
What are the 7 strong acids?
There are only a few (7) strong acids, so many people choose to memorize them. All the other acids are weak. The strong acids are hydrochloric acid, nitric acid, sulfuric acid, hydrobromic acid, hydroiodic acid, perchloric acid, and chloric acid.

What are acids and bases used for?
Acids and bases are used in many chemical reactions. They are responsible for most color change reaction and are used to adjust the pH of chemical solutions. Here are the names of some of the common acids and bases and the formulas associated with them.
Which acid has one less oxygen than the most common form?
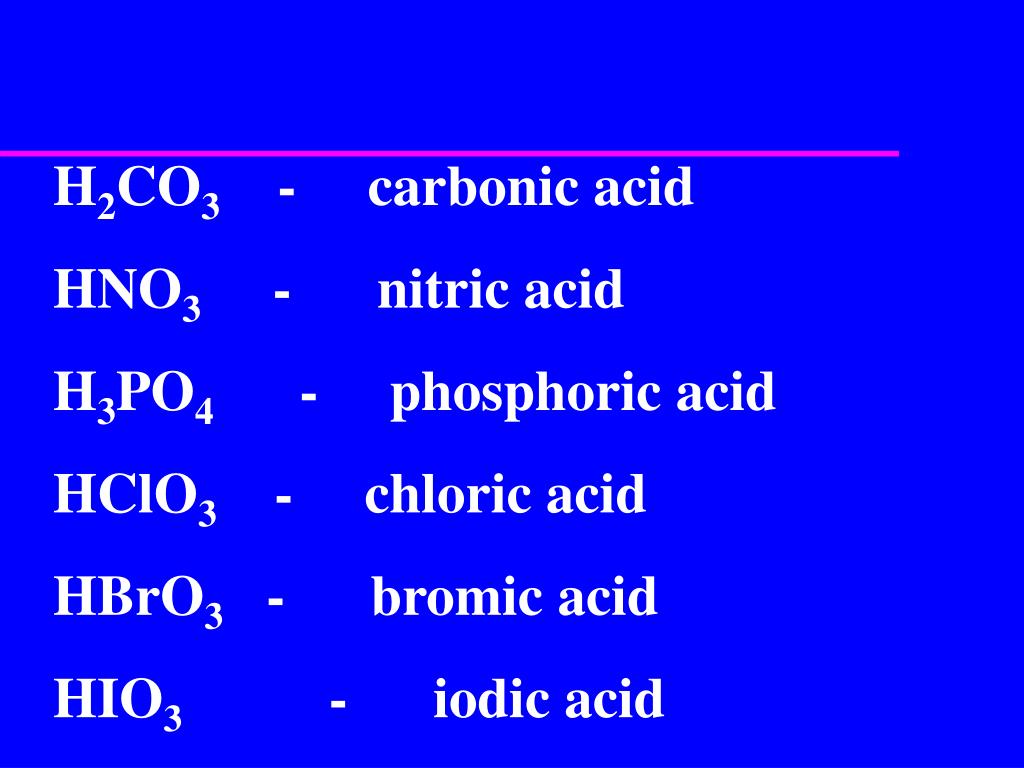
The acid containing one more oxygen than the most common acid has the per- prefix and the -ic ending. Nitric Acid - HNO3.
What is binary compound?
A binary compound consists of two elements. Binary acids have the prefix hydro in front of the full name of the nonmetallic element. They have the ending -ic. Examples include hydrochloric, and hydrofluoric acid includes:
How to determine if a substance is an acid or a base?
To determine whether a substance is an acid or a base, before and after the reaction, count the hydrogens on each substance. If the number of hydrogens decreases this substance is the acid (donates ions of hydrogen). If the number of hydrogen has increased this substance is the basis (accepts ions of hydrogen).
How to tell if a substance is acidic or basic?
Another way to check if a substance is acidic or basic is to use litmus paper. There are two types of litmus paper available that can be used to identify acids and bases – red litmus paper and blue litmus paper. Blue litmus paper turns red under acidic conditions and red litmus paper turns blue under basic or alkaline conditions.
Why do bronsted acids undergo dissociation?
Bronsted acids undergo dissociation to yield protons and therefore increase the concentration of H + ions in the solution.
What are the three theories of acids and bases?
Theories of Acids and Bases. Three different theories have been put forth in order to define acids and bases. These theories include the Arrhenius theory, the Bronsted-Lowry theory, and the Lewis theory of acids and bases. A brief description of each of these theories is provided in this subsection.
What is the difference between acid and base?
Bases, on the other hand, are characterized by a bitter taste and a slippery texture. A base that can be dissolved in water is referred to as an alkali.
What is the color of the base when it reacts with acids?
When these substances chemically react with acids, they yield salts. Bases are known to turn red litmus blue. In our everyday lives, we use many compounds which scientists call acids. The orange or grapefruit juice you drink for breakfast contains citric acid (also known as Vitamin C).
What are acids and bases?
Acids and bases are popular chemicals which interact with each other resulting in the formation of salt and water. The word acid comes from a Latin word ‘acere’ which means ‘sour’. In our everyday lives, we use many compounds which scientists call acids.
What are the names of acids?
Names of acids are typically "something"-acid. As such they are readily identified. Weaks acids are the acids that are not strong. Memorize the strong acids and you'll know everything else is weak. For example, the following are all weak acids: lactic acid, benzoic acid, oxalic acid, trichloroacetic acid, ...The chemical formula for the acids depends on the type of acid (hydroacid, oxoacid, or carboxylic acid). In particular you want to be able to recognize the carboxylic acid group that is found in many organic molecules. It is an oxygen double-bonded to a carbon with an OH group on the same carbon. This is denoted by RCOOH, where the R is a generic representation of the rest of the molecule. For example, formic acid is HCOOH (R = H), acetic acid is CH 3 COOH (R = CH 3 ).
Why are strong acids weak?
Second, there are a number of insoluble hydroxides, like Al (OH) 3 that are weak simply since they don't dissolve in water. They don't really have a conjugate acid. They are weak simply as a result of solubility.
What happens if you neutralize a weak acid?
If we neutralize them with an strong base we will end up with a salt composed of a cation and an anion. The anion is the conjugate base of the acid. This is an important clue to the identity of the species. If the acidic compound is not charged once you remove H + from the compound you will form an anion. Where there is an anion there is always a cation to balance the charge. The cation will be a spectator. Thus the basic salts will be composed of a spectator ion like sodium, Na +, potassium, K + or something like that and an anion that is the conjugate base of the acid. They can be identified as they are the same compound as the weak acid but they are "missing" a H +. Thus F - is the conjugate base of HF. NaF is a basic salt. K (CH 3 COO), potassium acetate, is a basic salt that contains the acetate anion that is the deprotantated form of acetic acid. Their names are also helpful in identification. The names of the anions often end in "ate". The benzoate ion is deprotonated benzoic acid. The formate ion is the conjugate base of formic acid.
What happens if an acidic compound is not charged?
Where there is an anion there is always a cation to balance the charge. The cation will be a spectator.
Is ammonium an acid or base?
Here the ammonium ion (NH 4+) is an acid and the fluoride ion (F -) is a base. These "mixed" salts are best thought of simply as either acids or bases. There are also compounds with more than one acidic proton (polyprotic species). These will form anions that can be both acids and bases.
Can you identify strong acids and bases?
It will not only allow you to identify the strong acids and bases , but it will help you figure out which ions are simply spectator ions. Second, you should realize that history has played a role in naming compounds. Therefore there are some compounds we typically think of as acids and some compounds we think of bases.
Is NaF a base or compound?
They can be identified as they are the same compound as the weak acid but they are "missing" a H +. Thus F - is the conjugate base of HF. NaF is a basic salt. K (CH 3 COO), potassium acetate, is a basic salt that contains the acetate anion that is the deprotantated form of acetic acid.
What are acids and bases?
Acids and bases are important classes of chemical compounds. They are part of the foods and beverages we ingest, they are present in medicines and other consumer products, and they are prevalent in the world around us. In this chapter, we will focus on acids and bases and their chemistry.
What is the reaction between an acid and a base?
A salt, in chemistry, is any ionic compound made by combining an acid with a base. A reaction between an acid and a base is called a neutralization reaction and can be represented as follows:
What is the chemical reaction between an acid and an Arrhenius base?
An Arrhenius acid is a compound that increases the H + ion concentration in aqueous solution.
What is the active component of a classic acid?
Recall that the active component of a classic acid is the H + ion , while the active part of a classic base is the OH − ion. Both ions are related to water in that all H + ion needs to become a water molecule is an OH − ion, while all an OH − ion needs to become water is an H + ion.
What are the properties of acid?
They react with some metals to give off H 2 gas. They react with carbonate and hydrogen carbonate salts to give off CO 2 gas. Acids that are ingested typically have a sour, sharp taste. (The name acid comes from the Latin word acidus, meaning “sour.”) Bases also have some properties in common. They are slippery to the touch, turn litmus blue, and have a bitter flavor if ingested.
Why does hydrazoic acid not proceed 100% to products?
It does not proceed 100% to products because hydrazoic acid is not a strong acid.
How do you know if a reaction is at its equivalence point?
How does one know if a reaction is at its equivalence point? Usually, the person performing the titration adds a small amount of an indicator a substance that changes color depending on the acidity or basicity of the solution. Because different indicators change colors at different levels of acidity, choosing the correct one is important in performing an accurate titration.

Identifying Acids by Their Chemical Formula Vocabulary and Formula
- Acid:A chemical compound when dissolved in water or react with other compounds gives {eq}H^+{/eq} ions that compound is called acids. For example, hydrochloric acid. $$HCl + NH_3 \rightarrow NH^{4+} +{Cl}^-$$ In this chemical reaction, HCl gives {eq}H^+{/eq} ions. So it is an a…
Identifying Acids by Their Chemical Formula Example 1
- Based on the given chemical formula, which of the following are acids? {eq}NH_3, H_2SO_4, HNO_3, NaCl{/eq} Step 1: Identify the given chemical formulas. $$NH_3, H_2SO_4, HNO_3, NaCl$$ Step 2: Check the chemical formulas that give hydrogen ions, which makes it is an acid. $$NH_3+H^+ \rightarrow NH^{4+}$$ $$H_2SO_4 \rightarrow 2H^+ +{(SO_4)}^{2-}$$ $$HNO_3 \ri…
Identifying Acids by Their Chemical Formula Example 2
- Based on the given chemical formula, which of the following are acids? {eq}KOH, NH_3,H_2CO_3,HCl{/eq} Step 1: Identify the given chemical formulas. $$KOH, NH_3,H_2CO_3,HCl$$ Step 2: Check the chemical formulas that give hydrogen ions, which makes it is an acid. $$KOH \rightarrow K^+ +{OH}^-$$ $$NH_3+H^+ \rightarrow NH^{4+}$$ $$H_2CO_3 …