
How do you increase surplus value? The production of surplus value may be increased by reducing the necessary labor-time and making a corresponding increase in surplus labor-time, without changing the length of the workday. This approach is associated with relative surplus value.
How do you calculate surplus in economics?
It is calculated by analyzing the difference between the consumer’s willingness to pay for a product and the actual price they pay, also known as the equilibrium price. A surplus occurs when the consumer’s willingness to pay for a product is greater than its market price.
How much has the rate of surplus value changed over time?
The Marxian mathematicians Emmanuel Farjoun and Moshé Machover argue that "even if the rate of surplus value has changed by 10–20% over a hundred years, the real problem [to explain] is why it has changed so little" (quoted from The Laws of Chaos: A Probabilistic Approach to Political Economy (1983), p. 192).
Why do sellers increase prices when there is a surplus?
In such an instance, sellers will increase their prices to convert the consumer surplus to a producer surplus. Alternatively, with elastic demand, a small change in price will result in a large change in demand.
What is the theory of surplus value?
…to it “the theory of surplus value ,” which rests on the axiom that human labour alone creates all value and hence constitutes the sole source of profits.… …from him and transformed into surplus value, which the capitalist privately appropriates.

What is meant by surplus value?
SURPLUS-VALUE : The surplus produced over and above what is required to survive, which is translated into profit in capitalism. Since the capitalist pays a laborer for his/her labor, the capitalist claims to own the means of production, the worker's labor-power, and even the product that is thus produced.
What do you mean by surplus value in sociology?
Surplus value. core definition. Surplus value is a concept developed by Karl Marx and it is refers to the new value created by workers in excess of the cost of their own labour, which is appropriated by the capitalist as profit when products are sold.
How surplus value is determined?
Intuitively, surplus value is calculated as the result of subtracting the costs of production from profits. Thus the formula would be as follows: Surplus value (s) = Revenue - production costs (c+v).
What does Karl Marx mean by surplus value?
Surplus value is defined by Marx as the difference between the value that living labor creates in production and value paid by the capitalist to the worker in the form of wages.
What is surplus value?
Surplus value, Marxian economic concept that professed to explain the instability of the capitalist system. Adhering to David Ricardo’s labour theory of value, Karl Marx held that human labour was the source of economic value.
Which theory of value did Karl Marx accept?
To make a profit, Marx argued, the capitalist appropriates this surplus value, thereby exploiting the labourer. Karl Marx accepted Ricardo’s labour theory of value (that the value of a product is based on the quantity of labour that went into producing...
What is surplus value?
In other words, surplus value is the difference between the value paid to the worker and, on the other side, by the total value the worker produces. Surplus value is a ratio, so that even the Uber driver who works a 10-minute shift produces the value of their labor power and surplus value for the capitalist.
How does Marx understand surplus value?
In the first two parts of Capital, Marx builds his logical framework necessary for understanding surplus value. The first step is recognizing that commodities under capitalism have both use values and exchange values. They must have some utility for society and they can be exchanged for one another. More fundamentally, capitalist commodities are produced not for their use value but for their exchange value. If I make a birthday card to give to my friend, it isn’t a commodity; if I make a card in order to exchange it on the market, it is a commodity.
What is Marx's definition of value?
Every commodity is not only the product of labor, not only an exchange value and use value, but also and more fundamentally a value, which Marx defines as socially-necessary labor time. Marx calls value socially-necessary labor time for two reasons.
Who was the first to discover the origins of value?
Marx was the first to discover the origins of value and, therefore, surplus value and the value of labor power. We don’t, however, receive the value of what we produce; we receive a price that is theoretically in line with the value of our own education and training, housing and electricity, transportation and social reproduction, and other costs necessary for the production and reproduction of our commodity.
Why does labor have no value?
If I produce a commodity that no one wants, the labor embodied in it has no value because there is no use value; it’s literally a non-value. Both aspects of value are dynamic; they change over time and in ways that are often unpredictable and hard to pinpoint at the moment.
Consumer Surplus Formula
There is an economic formula that is used to calculate the consumer surplus by taking the difference of the highest consumers would pay and the actual price they pay.
In Practice
Here is an example to illustrate the point. A shopper is determined to buy a laptop with a 1.9GHz CPU and a 15″ screen and is willing to spend up to $1,000.
Consumer Surplus on a Larger Scale
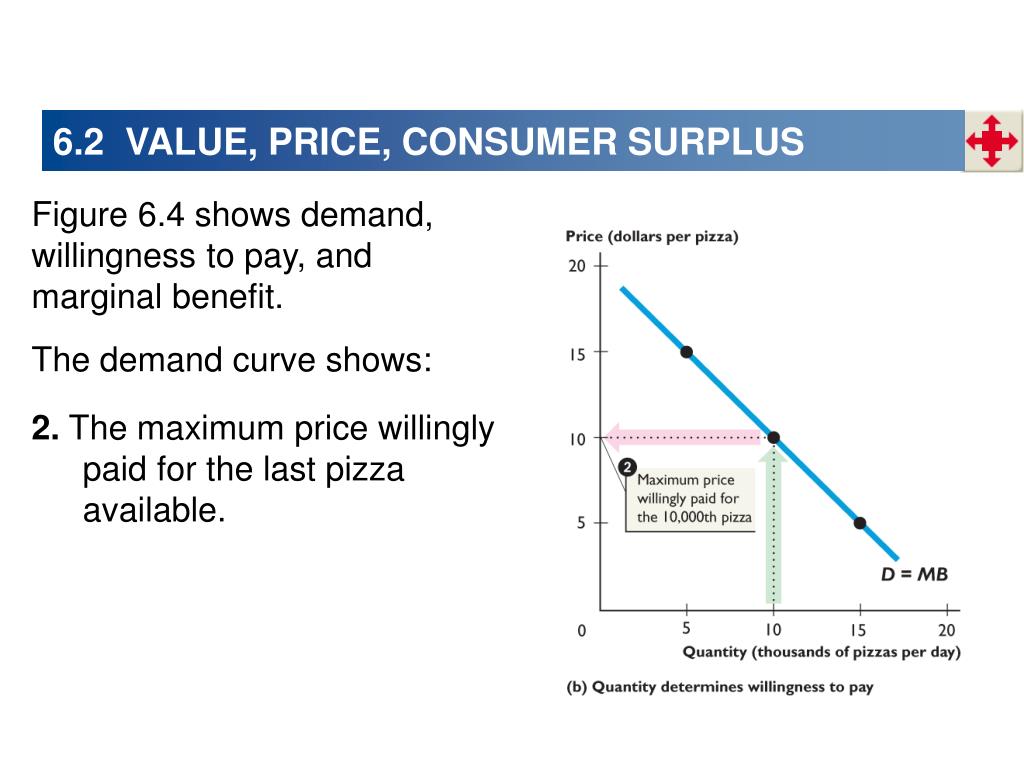
Demand curves are highly valuable in measuring consumer surplus in terms of the market as a whole. A demand curve on a demand-supply graph depicts the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity of the product demanded at that price. Due to the law of diminishing marginal utility, the demand curve is downward sloping.
Producer Surplus
On the other side of the equation is the producer surplus. As you will notice in the chart above, there is another economic metric called the producer surplus which is the difference between the minimum price a producer would accept for goods/services and the price they receive.
Practical Applications
In a theoretical market for bottled water, a customer is willing to pay $10 for the bottled water, which is the highest among other customers. Most customers are only willing to pay $5, which is coincidentally the price that is set when demand meets supply exactly. At $5, 20 bottles are supplied, and the consumer surplus is $50.
More Economic Resources
We hope this has been a helpful guide to the consumer surplus formula. To learn about more important economic principles, please see our related articles and guides below:
What is surplus in economics?
A surplus occurs when the consumer’s willingness to pay for a product is greater than its market price. Consumer surplus is based on the economic theory of marginal utility, which is the additional satisfaction a person derives by consuming one more unit of a product or service. The satisfaction varies by consumer, ...
Why is consumer surplus zero?
Consumer surplus for a product is zero when the demand for the product is perfectly elastic. This is because consumers are willing to match the price of the product. When demand is perfectly inelastic, consumer surplus is infinite because a change in the price of the product does not affect its demand. This includes products that are basic ...
What is the area above the supply level and below the equilibrium price?
The area above the supply level and below the equilibrium price is called product surplus (PS), and the area below the demand level and above the equilibrium price is the consumer surplus (CS).
Why is demand curve downward sloping?
Demand curves are usually downward sloping because the demand for a product is usually affected by its price. With inelastic demand. Inelastic Demand Inelastic demand is when the buyer’s demand does not change as much as the price changes. When price increases by 20% and demand decreases by. , consumer surplus is high because ...
What happens when elastic demand changes?
Alternatively, with elastic demand, a small change in price will result in a large change in demand. It will result in a low consumer surplus as customers are no longer willing to buy as much of the product or service with a change in price.
When price increases by 20% and demand decreases by, what is the consumer surplus?
When price increases by 20% and demand decreases by. , consumer surplus is high because the demand is not affected by a change in the price, and consumers are willing to pay more for a product. In such an instance, sellers will increase their prices to convert the consumer surplus to a producer surplus. Alternatively, with elastic demand, ...
Why is it necessary to measure utility?
It is required because without it, money cannot be used to measure utility.
What is consumer surplus?
Based on the economic theory of marginal utility, consumer surplus is an economic measurement calculating the excess cost that consumers are willing to pay for a product or service in comparison to the actual market price.
What is social surplus?
Also referred to as economic surplus or total surplus, a social surplus is the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus. When looking at a demand-supply graph, the social surplus is the total area between the supply curve, the demand curve, and the point of equilibrium. A deadweight loss, which occurs when the economy is producing ...
Why do markets fluctuate?
Markets tend to fluctuate, especially because consumers are able or willing to spend at different price points for any given product or service. This is where a surplus is created.
Why do consumers favor price ceilings?
Basically, money is being disc arded without benefitting anyone. In addition, some of the producer surpluses end up being transferred to consumers, which is why consumers largely favor price ceilings. However, the gain to consumers is less than the loss to producers, aka still a deadweight loss.
What is the selling strategy?
This selling strategy involves charging different prices for the same goods or services based on the business’s estimation of the maximum amount they think the customer is willing to pay.
What Is Excess or Surplus Inventory?
In simple terms, surplus inventory is excess stock. Some companies will hold excess inventory on purpose, as a sort of ‘back up’ supply in case demand is higher than expected. But, more often than not, excess inventory is the result of overstocking due to poor demand forecasting.
What Causes Surplus Inventory?
There are many reasons why a business may end up holding onto surplus items. Sometimes inaccurate demand forecasting is simply a matter of oversight, but in other instances, external factors and socio-economic markers may be at play.
Why having surplus inventory is bad for business
But why is all this spare inventory such a bad thing? Surely it’s good to have extra products to sell?
How to Use Surplus Inventory to Boost Online Sales
We’ve established that too much surplus inventory is less than ideal. It’s eating away at your profit margins and taking up space in the meantime. But there’s no point dwelling on the negatives. We’re here to provide positive, actionable solutions.
How to Avoid Surplus Inventory
We’ve spoken all about what to do with that dreaded extra inventory. But what about avoiding the whole ordeal in the first place? Instead of going into crisis mode every time you’ve got deadstock to shift, how about never having deadstock in the first place.
Wave Goodbye to Surplus Inventory
Don’t let surplus inventory bog you down any longer. With the right strategy, you’ll be able to shift your existing overstock and reduce surplus in the future. With prior planning, and the right tools in tow, you’ll have your business under control from frontend to backend, and make that hard-to-move inventory a thing of the past.
Overview
Theory
The problem of explaining the source of surplus value is expressed by Friedrich Engels as follows:
"Whence comes this surplus-value? It cannot come either from the buyer buying the commodities under their value, or from the seller selling them above their value. For in both cases the gains and the losses of each individual cancel each other, as each individual is in turn buyer and seller. Nor can it come from cheating, for though cheating can enrich one person at the expense of another…
Origin
By the Age of Enlightenment in the 18th century the French physiocrats were already writing on the surplus value that was being extracted from labor by," the employer, the owner, and all exploiters" although they used the term net product. The concept of surplus value continued to be developed under Adam Smith who also used the term "net product" while his successors the Ricardian socialists, began using the term "surplus value" decades later after its coinage by William Thomp…
Definition
Total surplus-value in an economy (Marx refers to the mass or volume of surplus-value) is basically equal to the sum of net distributed and undistributed profit, net interest, net rents, net tax on production and various net receipts associated with royalties, licensing, leasing, certain honorariums etc. (see also value product). Of course, the way generic profit income is grossed and netted in social accounting may differ somewhat from the way an individual business does that …
Interpretations
Surplus-value may be viewed in five ways:
• As a component of the new value product, which Marx himself defines as equal to the sum of labor costs in respect of capitalistically productive labor (variable capital) and surplus-value. In production, he argues, the workers produce a value equal to their wages plus an additional value, the surplus-value. They also transfer part of the value of fixed assets and materials to the new p…
Equalization of rates
Marx believed that the long-term historical tendency would be for differences in rates of surplus value between enterprises and economic sectors to level out, as Marx explains in two places in Capital Vol. 3:
"If capitals that set in motion unequal quantities of living labour produce unequal amounts of surplus-value, this assumes that the level of exploitation of labour, or the rate of surplus-value, i…
Appropriation from production
Both in Das Kapital and in preparatory manuscripts such as the Grundrisse and Results of the immediate process of production, Marx asserts that commerce by stages transforms a non-capitalist production process into a capitalist production process, integrating it fully into markets, so that all inputs and outputs become marketed goods or services. When that process is complete, according to Marx, the whole of production has become simultaneously a labor process
Absolute vs. relative
According to Marx, absolute surplus value is obtained by increasing the amount of time worked per worker in an accounting period. Marx talks mainly about the length of the working day or week, but in modern times the concern is about the number of hours worked per year.
In many parts of the world, as productivity rose, the workweek decreased from 60 hours to 50, 40 or 35 hours.