
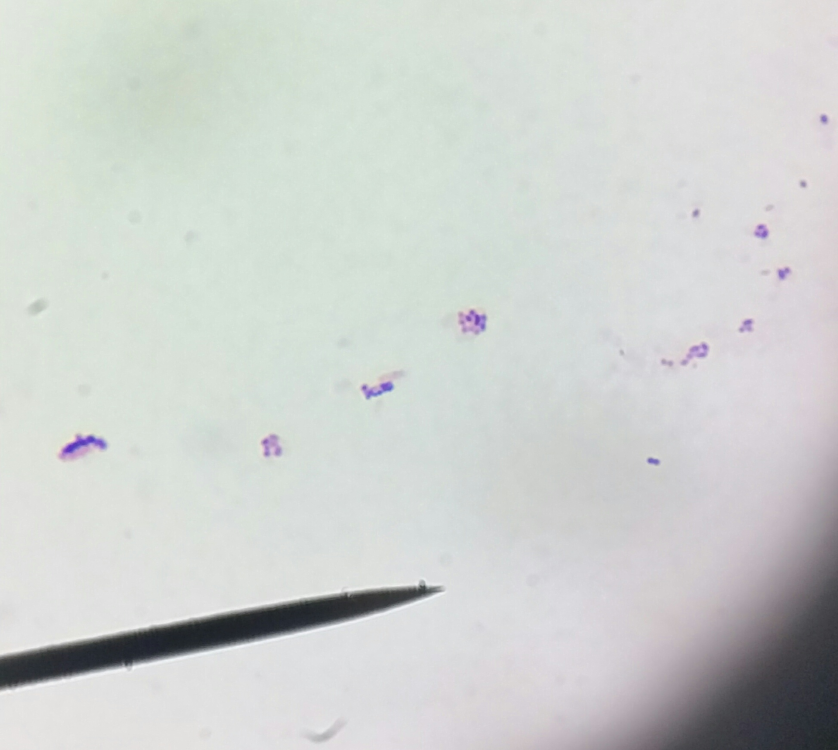
The unknown gram-positive bacterium was identified as Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus aureus is a Gram-positive, round-shaped bacterium that is a member of the Firmicutes, and it is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often positive for catalase and nitrate reduction and is a facultative anaerobe that can grow without the need for oxygen. Although S. aureus usually acts as a commensal of the hum…
How can you tell if a bacteria is Gram positive?
Under a microscope, gram-positive bacteria appear purple-blue because their thick peptidoglycan membrane can hold the dye. The bacteria is called gram-positive due to the positive result. Gram-negative bacteria stain pink-red. Their peptidoglycan layer is thinner, so it doesn’t retain the blue color. The test result is negative.
How to identify unknown bacteria?
Various steps involved in the identification of unknown bacteria are: The importance of this step is to isolate pure colonies of bacteria. The streak plate is a qualitative isolation method; quadrant streaking is mostly done to obtain pure colonies.
Why do Gram positive bacteria appear purple-blue under a microscope?
Under a microscope, gram-positive bacteria appear purple-blue because their thick peptidoglycan membrane can hold the dye. The bacteria is called gram-positive due to the positive result.
What is an example of a Gram negative bacteria?
Gram-negative bacteria’s cell membrane is thin but difficult to penetrate. Because of this nearly “bulletproof” membrane, they are often resistant to antibiotics and other antibacterial interventions. Examples of Gram-negative bacteria include cholera, gonorrhea, and Escherichia coli (E. coli).

How do you identify a Gram positive bacteria?
A Gram stain is colored purple. When the stain combines with bacteria in a sample, the bacteria will either stay purple or turn pink or red. If the bacteria stays purple, they are Gram-positive. If the bacteria turns pink or red, they are Gram-negative.
How would you determine which unknown is Gram positive and which is gram negative?
The Gram stain differentiates organisms by the way the react with colored stains: Gram-negative rods (L) stain pink/red; Gram-positive rods (R) stain blue/purple. ... The amount of blood cell lysis by the bacteria results in a different color in the media.More items...•
Why would you want to identify an unknown bacteria?
Microbiologists must identify bacterial isolates for several practical reasons: • Medical diagnostics — identifying a pathogen isolated from a patient. Food industry — identifying a microbial contaminant responsible for food spoilage. Research setting — identifying a new isolate which carries out an impor tant process.
What are the three main approaches to the identification of unknown bacteria?
What three main approaches can be used by microbiologists to identify microorganisms? -Phenotypic- observing bacterial morphology and staining properties as well as biochemical testing. You just studied 45 terms!
How do you identify unknown bacteria?
If you have an unknown bacteria and you want to identify it, you'll typically perform a gram stain and then observe the colony appearance and the individual features. At that point, you can say you have, for example, a gram-negative, aerobic streptobacilli.
What are the steps to identify an unknown bacteria?
Various steps involved in the identification of unknown bacteria are:Isolation: The importance of this step is to isolate pure colonies of bacteria. ... Staining Reactions: ... Biochemical reactions: ... Indole test: ... Methyl Red Test: ... Voges Proskauer Test: ... Citrate Utilization Test: ... TSI:More items...
How do you identify an unknown culture in microbiology?
1:319:53Identification of unknown bacteria by morphological and biochemical ...YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWe'll begin by inoculating a number of media tubes with our unknown a tsa slant a tryptone broth forMoreWe'll begin by inoculating a number of media tubes with our unknown a tsa slant a tryptone broth for the indole. Test mr vp media a urea slant and fermentation tests for glucose lactose. And sucrose
How do you write an unknown bacteria in a lab report?
For example, instead of writing "I used a TSA agar plate to isolate my unknown," it is customary to write, "A trypticase soy agar (TSA) plate was used to isolate the unknown." It is also customary to write in the past tense for most of the report.
How do you gram stain unknown bacteria?
When Gram staining an unknown, the best method is to make three bacterial smears on the slide. One should be a known Gram positive organism like Staphylococcus aureus. The other should be a known gram negative organism like Escherichia coli . In the middle, make a smear of your unknown organism.
Which test is used for identification of bacteria?
Urease test This test is used to identify bacteria capable of hydrolyzing urea using the enzyme urease. It is commonly used to distinguish the genus Proteus from other enteric bacteria. The hydrolysis of urea forms the weak base, ammonia, as one of its products.
How do biochemical tests identify unknown bacteria?
Identifying bacteria via analyzing their enzymatic profile Each species of bacteria has specific metabolic needs and relies on different enzymes to fuel those unique needs. The presence of catalase, gelatinase, oxidase, urease, for example, can be used to identify the species of bacteria.
What are the important points to remember when identifying different bacteria?
Popular Answers (1) get pure culture of your bacteria for each type (2-3 stable strains); find basic morphologic and biochemical traits (as Mesgor advised), FAME, and establish the group of bacteria. if you have well-nown species, use specific PCR primers developed for them;More items...
What is the color of a streptococci colony?
Alpha hemolytic species produce alpha-hemolysin which reduces hemoglobin (red) to methemoglobin (green) causing a brownish or greenish zone around the colony.
How long does it take for Enterococcus spp. to change its media color?
A negative result is indicated by no growth after 72 hours. Enterococcus spp. typically changes the media color within 24 hours.
How long to incubate a streptolysin O plate?
See page 84 of the Difco/BBL Manual. Incubate the plates at 37°C for 24-48 hours. Strep organisms should be incubated in the CO 2 incubator.
How long to incubate staphylococcus tube?
Incubate the tube overnight at room temperature if you do not get a clot in 4 hours.
How to tell the difference between beta and alpha hemolysis?
There has been total lysis of the red blood cells. Alpha hemolysis is indicated by a small zone of greenish to brownish discoloration of the media.
What are the biofilms that Staphylococcus aureus can colonize?
Many species of Staphylococcus have the ability to form biofilms which can then colonize structures such as medical catheters, stents, heart valves, prostheses, shunts, and valves. The clinically significant species are generally separated into coagulase-positive staphs (S. aureus) and coagulase-negative (CoNS) staphs (S. epidermidis, S.
What are the most common diseases caused by Staphylococcus species?
They are also important pathogens. Some of the most common diseases caused by Staphylococcus species include: impetigo, toxic shock syndrome, bacteremia, endocarditis, folliculitis furuncle (boils), and osteomyelitis (bone abscesses).
What is the difference between a Gram positive and a Gram negative?
Gram Positive and Gram Negative Bacteria It is a well-known fact that bacterial cells, like plant cells, are surrounded by a cell wall. However, few people know that their cell walls are quite different. Bacterial cell walls are made up of polysaccharide chains linked to amino acids. At the same time, plant cell walls are made up of cellulose, which contains no amino acids. In the same way, ...
Can lactose fermenting bacteria produce endospores?
... are other gram-negative, lactose fermenting bacteria but produce endospores. Thus, they might have tested positive for the endospore stain but if there were coliforms ... (gram reaction and endospore formation) and lactose fermentation reactions. Thus, one can expect sterile water to already be given a negative result ...
What is the difference between Gram positive and Gram negative?
The Gram stain is used to differenciate Gram-positive from Gram-negative bacteria. Gram-positive bacteria have a thicker peptidoglycan layer and therefore retain the primary stain (crystal violet) whereas Gram-negative cells lose it when treated with a decolourizer (absolute alcohol).
How to know what group your bacteria fall into?
In order to know what group your bacteria falls into, you have several methods. You can either inoculate an agar plate and put it in an anaerobic jar or inoculate your bacteria directly into thioglycolate broth or cooked meat medium. The anaerobic jar contains 5% of CO 2, 10% of H 2 and 85% of N 2.
What is the color of acid fast cells?
Cells are treated first with carbol fushin which is heat-fixed, then with acid alcohol which decoulorize all cells except acid fast bacteria and finally with a counterstain (methylene blue). Under the microscope, acid fast cells are red and the others are blue.
What temperature does agar melt?
Both contain agar, which is composed of complex polysaccharides, NaCl and yeast extract or peptone. It melts at 100°C and solidifies at around 40-45°C.
How to tell if a bacteria is aerobic or anaerobic?
In other words, does it need oxygen to grow or can it use fermentation or anaerobic respiration. There are also bacteria that are facultative anaerobes, meaning that in presence of oxygen, they will use it but if they find themselves in anaerobic conditions, they'll be able to grow using fermentation pathways or anaerobic respiration. Another group is called microaerophiles and those grow best when the concentration in oxygen is inferior to 21%.
How to transfer bacteria from one medium to another?
If you use a loop or a needle to transfer bacteria from a medium to another, you must flame the loop or needle in the flame of a Bunsen burner for a few seconds and then wait for the wire to cool down to avoid killing your bacteria. You must always work in the area around our flame since microorganisms are present in the air.
What does it mean when a bacteria is negative?
You place your bacterial strain in a medium containing nitrate and an indicator. If the result is negative, it might mean that the bacteria do not reduce nit rate but it might also mean that the nitrate was reduced to nitrite and then further reduced to ammonia.
What is the difference between Gram positive and Gram negative?
Gram staining is a procedure that allows you to divide bacteria into 2 common types: Gram positive, and Gram negative. Gram positive bacteria have an extra thick cellular wall (made of a polymer called peptidoglycan) that holds a dye stain better than the thinner cell walls of Gram negative bacteria.
How to remove Gram negative bacteria?
Rinse the sample with alcohol or acetone. Alcohol and acetone are decolorizing agents. If your bacteria are a Gram negative strain, these agents will remove the stain from the bacterial cell walls. Allow a few drops of the decolorizing agent to trickle over the sample, and let it sit for no more than 3 seconds.
What to wear to get Gram stain out?
Wear goggles, disposable nitrile gloves, and a lab coat while performing the stain. Put your disposable gloves and any other contaminated waste materials in a biohazard bag when you are done.
How to make a bacterial sample?
To begin the process, place a small drop or piece of your bacterial sample on a sterile slide. Pass the slide through the flame of a Bunsen burner 3 times to heat fix the sample. This will prevent the sample from washing away when you add reagents or rinse the slide.
What is Gram's iodine?
Gram's Iodine is a solution of iodine, potassium iodide, and sodium bicarbonate. This solution will cause the crystal violet dye to become fused to the cell walls of the bacteria. Add about 5 drops, and let it sit for 1 minute. ...
What is the difference between Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria?
The key to understanding these differences is in the protective membrane, or outer covering, surrounding these bacterial organisms. Gram-negative bacteria have a thin membrane, which is nearly “bulletproof.”. Gram-positive bacteria have a big, thick membrane. Image: Structure of Gram-positive cell wall. Image is copyright free from Wikimedia ...
What are some examples of Gram negative bacteria?
Examples of Gram-negative bacteria include cholera, gonorrhea, and Escherichia coli ( E. coli). The protective covering of these, and other, Gram-negative bacteria make them much more difficult to heal and eradicate.
How thick is the cell membrane of a Gram positive bacteria?
The cell membrane of Gram-positive bacteria can be as much as 20-fold thicker than the protective covering of Gram-negative bacteria. Some examples of Gram-positive bacteria include Streptococcus , Staphylococcus, and Clostridium botulinum (botulism toxin). Gram-positive bacteria have a greater volume of peptidoglycan ...
What makes a Gram positive cell membrane?
Gram-positive bacteria have a greater volume of peptidoglycan (a polymer of amino acids and sugars that create the cell wall of all bacteria in their cell membranes), which is what makes the thick outer covering. This thick outer covering, or membrane, is capable of absorbing a lot of foreign material. Image: Structure of gram-negative cell wall.
Is super bacteria more fireproof than mold proof?
Thus, an individual or a population can experience an outbreak of super bacteria that are more “fireproof,” “mold proof,” and “bulletproof” to antibiotics. Therefore, there is a great need to educate people about the benefits of adopting a healthy, holistic lifestyle.
Do antibiotics work for staph?
Thus, with these analogies, you can quite easily see why some of the “big gun” antibiotics, which work well for serious infections like staph or strep, may have little effect on plaguing Gram-negative bacterium eruptions, such as a cholera outbreak or a mass gonorrheal epidemic.
Can antibiotics damage gram positive bacteria?
The fire-hose or shotgun-bullet antibiotics, which easily damage Gram -positive bacterial membranes , are often unable to blast through or weaken the protective coverings found on Gram-negative bacterium.
What is Gram negative enteric bacilli?
Gram negative enteric bacilli play an important role in the contamination of food. Hence they are the main causative agents of intestinal infection. Gram negative family includes Shigella, Salmonella, Proteus, Klebsiella,Escherichia,Enterobacter etc. Usually four tests are used for differentiation of the various members of Enterobactericeae. They are Indole test,Methyl red test, Voges proskauer test and Citrate test; collectively known as IMViC series of reactions.
What is the principle of identification of bacteria?
Principle: The identification of bacteria is a careful and systematic process that uses many different techniques to narrow down the types of bacteria that are present in an unknown bacterial culture. It produces benefits for many aspects of the research of microorganisms and helps physicians correctly treat patients.
Which bacteria produce coagulase?
This enzyme clots the plasma component of blood. The only significant disease-causing bacteria of humans that produce coagulase are Staphylococcus aureus. Thus this enzyme is a good indicator of the pathogenic potential of S. aureus.
Which enzyme is present in most cytochrome containing aerobic and facultative anaerobic bacteria?
The enzyme catalase is present in most cytochrome containing aerobic and facultative anaerobic bacteria. Catalase has one of the highest turnover numbers of all enzymes such that one molecule of catalase can convert millions of molecules of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen in a second.
Why Identify A Bacteria ?
First Some Basics
Culture Morphology
Cell Morphology
Staining
Respiration
Biochemical Properties
- Another test is whether or not your unknown has an hemolytic reaction. Most bacteria are gamma-hemolytic, which means that they do not have an hemolytic reaction. This test is mostly used on streptococci species: it differentiates non pathogenic streptococci from pathogenic streptococci. This is tested on a blood agar plate: a beta-hemolysis create...
Identifying Your Unknown