Step by Step Instructions
- Calculate total roof area. Calculate the total roof area by multiplying its length by width. ...
- Determine leader size. Determine leader or pipe size. ...
- Find rainfall rate. Find the rainfall rate for the building’s location. ...
- Find the area handled by one drain. ...
- Calculate drains needed. ...
How do I size my roof drains?
IPC provides four steps to size the roof drains on a building: Determine 100-year, 1-hour rainfall rate used for location of building Select number of roof drains and calculate the roof area sloped to each drain Size horizontal storm drainage piping Size vertical storm drainage piping
How do you calculate the size of a roof?
Calculate the total roof area by multiplying its length by width. Example: A 200 ft. x 250 ft. = 50,000 sq. ft. area. Determine leader or pipe size. Following are the standard sizes for some of the top manufacturers: Find the rainfall rate for the building’s location.
How do you measure pipe size?
This article has been viewed 106,844 times. Measuring pipe size can be a little confusing at first, but anyone can learn how to do it. To find the right size, first figure out if you need to measure the outside or inside diameter, then measure it with a ruler or tape measure.
How do you determine roof drain flow resistance?
Roof drain flow resistance factors such as roof drain slope, constrictions, elbows, bends (standard plumbing calculations on drain carrying capacity) Local and model code requirements or standards that regulate roof drainage in your area I reviewed several roofing company specifications that discuss drains looking in vain for a good rule of thumb.

How do I calculate pipe drain size?
Divide the pipe's internal diameter by 2. For example, if the pipe has an internal diameter of 0.1 meters: 0.1 ÷ 2 = 0.05 m This is the pipe's radius. Square this radius: 0.05² = 0.0025 m². Multiply the result by pi, which is approximately 3.142: 0.0025 × 3.142 = 0.007855 m².
What is the minimum number of roof drains for any size building?
Not less than two roof drains shall be installed in roof areas 10,000 square feet (929 m2) or less and not less than four roof drains shall be installed in roofs over 10,000 square feet (929 m2) in area.
How do you measure a roof scupper?
To adjust this table for other than a 5-inch design rain fall rate, multiply the square footage on the table by 5 then divide by the local design rain fall rate. Example: For 4 inches of design rainfall rate, a 4-inch long scupper with a 1-inch head would accommodate 287 square feet. (230 x 5) ÷4 = 287.
What are the drains on the roof called?
Many people ask, “What are roof drains called?” and they are simply called roof drainage systems. The drainage system starts at the roof line and then you have roof drainage to ground. The components that you need for a roof drainage system is a gutter system and downspout.
How big are roof drains?
According to the chart, for 1/8” slope per 12” of pipe, for 5,000 square feet of roof area, with a 6” per hour of rainfall, the required pipe size is 8”. To size the vertical roof drain for the same parameters – 5,000 square feet of room area and 6” per hour of rain – consult Table 1106.2(Figure 3).
What size is rainwater pipe?
Rainwater downpipes are most commonly round in section, but may be any shape. They typically have a diameter ranging from 50 - 150 mm, but any size can be used.
How do you size a scupper opening?
The only unconditional guideline for roof scupper sizing provided by the code is that “scupper openings shall be not less than 4 inches (102 mm) in height and have a width that is equal to or greater than the circumference of a roof drain sized for the same roof area.”
What does a scupper look like?
Channel-type scuppers are three sided or are a simple rectangular hole cut in the wall. Some types can be round or a unique, decorative shape using custom sheet metal fabrication. These holes allow any water to drain straight down the sides of your building to prevent standing water and leakage.
Is a scupper a drain?
Definition of Roof Scupper Roof scuppers are not the same as roof drains. Roof drains channel water through the deck of the roof into a piping system that carries water away, while a scupper allows water to drain through an opening in the side of the roof edge.
How much does it cost to install a roof drain?
Installing drainage runs most homeowners between $1,985 and $6,141 with an average cost of $4,053. Small, simpler solutions could be as low as $500 and more complicated projects could get as expensive as $18,000.
Do roof drain pipes need to be insulated?
Storm water piping is also susceptible to condensation and should be insulated from the roof drain bowl to a point where the piping turns from horizontal to vertical. In any event, the storm water piping should be insulated for a minimum of 30 ft. from the roof drain.
Step 1: Calculate total roof area
Calculate the total roof area by multiplying its length by width. Example: A 200 ft. x 250 ft. = 50,000 sq. ft. area.
Step 2: Determine leader size
Determine leader or pipe size. Following are the standard sizes for some of the top manufacturers:
Step 3: Find rainfall rate
Find the rainfall rate for the building’s location. The most accurate and up-to-date resource for rainfall rates is going to be your local codes.
Step 4: Find the area handled by one drain
Using the chart below, find the total square footage one drain can handle based on hourly rainfall rate.
Step 5: Calculate drains needed
Take the roof’s total square footage and divide by the total square footage handled by one drain. The result is the number of drains needed.
How to measure pipe size?
To find the right size, first figure out if you need to measure the outside or inside diameter, then measure it with a ruler or tape measure.
How to tell if a pipe has a male or female thread?
1. Determine if your pipe has “male” or “female” threads or no threads. Threads are the little grooves on the ends of some pipes that help them fit together. Male threads are on the outside of the pipe, whereas female threads are on the inside.
How to convert diameter to nominal size?
1. Convert your diameter to nominal size if its smaller than 14 inches (360 mm). If its 14 inches (360 mm) or more, you don’t need to convert it, because the diameter will equal the nominal diameter already. ...
Reader Question: is there a rule of thumb for number of roof drains needed on flat roofs
What is the general area of a flat (1/4"/1'-0" slope) single-ply roof for each roof drain (ratio for the number of roof drains / roof area).
The Roof Drainage Requirements: Calculations
I reviewed several roofing company specifications that discuss drains looking in vain for a good rule of thumb. A calculator (or table as we give below) gives the number of roof drains required to drain the particular roof under design, based on the parameters listed above.
Specifications for Roof Drainage Requirements - Table Approach
The following table, adapted from data from several manufacturers and guided by information posted by J.R. Smith Manufacturing also presumes that you have properly specified the roof drainage design parameters we listed earlier in this article. Smith is basically using U.S.
What color is SDR pipe?
SDR pipe may be white like sched 40PVC or it may also be light green or light blue in color and usually it will have a preformed end bell on one end of the length to permit joining. It may be glued but glueing is not required for storm drains.
Is SDR pipe better than corrugated roll pipe?
SDR pipe has an advantage on long runs because it has a much lower "friction head factor" than corrugated roll pipe. SCHEDULE 40 PVC: Schedule 40 PVC is code approved and it would be perfectly suitable although it would generally be considered overkill and it would be the most expensive. heimert. 13 years ago.
How does stormwater drain?
The methods are: Gravity drainage — Stormwater simply drains off the roof and other areas to the ground. Stormwater flows away from the building naturally to storm drains or, in some cases, to the street.
What is Chapter 11 of the Uniform Plumbing Code?
There are three basic methods covered in Chapter 11 of the Uniform Plumbing Code that are used to deal with stormwater that falls upon the roof or in and around a building. Which method is used will depend on how the building is designed and/or the type of public sewage system used in the area. The methods are:
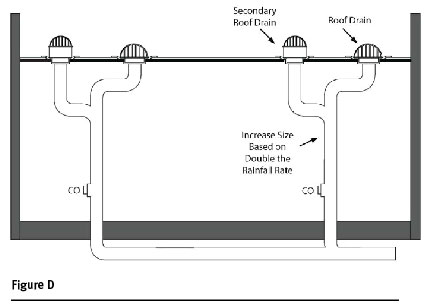
What is secondary drainage?
Secondary drainage. To ensure rainwater accumulation on a roof is drained away, two independent systems of roof drainage are required. They are the primary roof drainage system and the secondary roof drainage system, commonly referred to as an “overflow system.”.
What is the balance between building design and dealing with rain?
When it comes to stormwater, there is a balance that has to be struck between building design and dealing with the rain that lands on the roof. While the building design needs to please a great many people, the roof drainage system also has to be designed to prepare for a rainy day; in this case, a very rainy day.
Can a secondary overflow system be piped to an open area?
The secondary system, basically an emergency overflow system, may be piped to an open area even if it is a walkway or other traveled outside area. The reason for this is the secondary system should seldom be used, and if it is used, it would give a warning that something is wrong with the primary system.
Is it enough to install a drainage system on a roof?
When it comes to design and installing the roof drainage system of a building, it simply is not enough to plan for the average day. In fact, you cannot even gamble that a 100-year rainfall will not happen while you are alive or able to be held responsible for not providing adequate protection.
Is a storm sewer system a sanitary sewer system?
The building and public sewer system is only a sanitary system and may not collect stormwater. There may be a separate storm sewer system, but it is independent of the sanitary system. Combined storm and sanitary systems — Water may accumulate on the roof because of the building design.