How do you measure CMM symmetry? Usually, to measure symmetry, a CMM is set up to calculate the theoretical midpoint datum plane, measure the surfaces of both required surfaces, and then determine where the midpoints lie in reference to the datum plane. This is a complex and sometimes inaccurate method for determining if a part is symmetrical.
How do you measure symmetry?
Usually to measure symmetry, a CMM is setup to calculate the theoretical midpoint datum plane, measure the surfaces of both required surfaces, and then determine where the midpoints lie in reference to the datum plane. This is a complex and sometimes inaccurate method for determining if a part is symmetrical.
What is a CMM used to measure?
A pair of large horizontal arm CMM’s used for car body measurement. This type of CMM is often fully computer-controlled, allowing them to measure, record, and evaluate data without operator intervention. A joystick for manual operation can control some machines.
What is the basic structure of a CMM?
The basic structure of this type of CMM consists of a base with one or more articulating arms or beams. A probe is mounted on a rotating joint at the end of the arm. The arms can be extended or retracted from the base in any direction and will also pivot about the base, allowing for measurements in three axes.
How do you calculate the position of a CMM probe?
From the encoder angle and known member lengths, trigonometry is used to calculate the probe position. Coordinates are adjusted to provide the proper X, Y, Z coordinates for the measurement. CMM probes are often touch-triggered, collecting a measurement point every time they touch a surface.
How do you measure symmetry tolerance?
Using a coordinate measuring machine Initially, the CMM is set up to establish the theoretical center plane. Then, both symmetrical sides are measured using the CMM stylus to calculate where the median points fall. The positions of all the median points along the feature's length are compared with the datum plane.
Which probe is used for measurement of symmetrical geometry?
Using a Caliper or Micrometer.
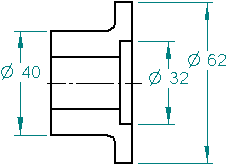
What is a symmetry tolerance?
Symmetry Tolerance is a three-dimensional geometric tolerance that controls how much the median points between two features may deviate from a specified center plane or axis. This tolerance is similar to concentricity, and the verification of symmetry tolerance is likewise time-consuming and difficult.
How do you show symmetry in a drawing?
0:001:14Drawing lines of symmetry - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipGonna cut a figure exactly in half so that whatever's on one side of the line is the same as what'sMoreGonna cut a figure exactly in half so that whatever's on one side of the line is the same as what's on the other side of the line kind of a mirror image so that if you folded the paper.
Can CMM measure angles?
Measurement methodology The CMM was located in a temperature-controlled environment of 20 ± 1 °C. The part used for the study has been a steel angle gauge block with four angles with a nominal value equal to 90° marked with the letters A, B, C, and D (Fig. 2).
What is alignment CMM?
To define a part alignment, the operator must constraint, or lock, all three axes of the coordinate system to the part. This is done though the CMM software and requires establishing the direction of X, Y and Z, as well as their intersection point, origin or XYZ zero point.
What are the 3 types of tolerances?
Three basic tolerances that occur most often on working drawings are: limit dimensions, unilateral, and bilateral tolerances. Three basic tolerances that occur most often on working drawings are: limit dimensions, unilateral, and bilateral tolerances.
How do you describe symmetry?
In geometry, symmetry is defined as a balanced and proportionate similarity that is found in two halves of an object. It means one-half is the mirror image of the other half. The imaginary line or axis along which you can fold a figure to obtain the symmetrical halves is called the line of symmetry.
How do you read position tolerance?
An example of position tolerance is shown below. The top figure shows the position symbol applied to two holes. The boxed symbols can be read "relative to datums A, B, and C, the position of these hole centers shall lie within a cylindrical tolerance zone of diameter 0.3".
How do you calculate line of symmetry?
When a line divides a given figure into two equal halves such that the left and right halves matches exactly then we say that the figure is symmetrical about the line.
How do you find the symmetry of a shape?
Folding Test You can find if a shape has a Line of Symmetry by folding it. When the folded part sits perfectly on top (all edges matching), then the fold line is a Line of Symmetry.
How do you make symmetrical patterns?
3. Making symmetric figures and patterns - Example 1Step 1: Take a piece of paper and fold it.Step 2: Cut out any figure which starts and ends on the fold line such as the one shown below.Step 3: Unfold the figure. You have a symmetric figure where the fold line is the line of symmetry.
Using a Caliper or Micrometer
Measure parts of the target using an analog caliper or micrometer to check the symmetry. It is useful for repeated measurements of single items thanks to its simple, quick usability. Both calipers and micrometers come in various types, which are selectively used depending on the location and form to be measured.
Using a Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM)
The reference element (plane) set-up and the deviation from the target element (plane) can be quickly and accurately measured by anyone just by putting the stylus on each measurement point. The measurement result is recorded in the measuring machine.
How to measure symmetry?
Usually, to measure symmetry, a CMM is set up to calculate the theoretical midpoint datum plane, measure the surfaces of both required surfaces, and then determine where the midpoints lie in reference to the datum plane. This is a complex and sometimes inaccurate method for determining if a part is symmetrical.
What is the symbol for symmetry?
Symmetry is the non-circular version of concentricity . While concentricity really is a focus of symmetry around a datum axis, The Symmetry Symbol is a focus on symmetry over a datum plane. Both symbols focus on the theoretical center datum being constrained within a specific limit to ensure that the entire structure is uniform.
Why should symmetry be avoided?
Symmetry should be avoided in most cases due to its specific functional requirements and measurement difficulty. With flatness, parallelismand true position, you can locate the exact same constraints on the part, albeit with more callouts and measurements required. However since true position can be measured with a gauge (if MMC is used), and flatness is automatically controlled by the size dimension & directly measured off the surfaces, these can be controlled within a process and do not require timely CMM measurements.
When to use center plane symbol?
This symbol only has specific uses for mass balance and form distribution. However, in most cases it is better to avoid using since this is a very difficult callout to measure and can easily be replaced with a Position tolerance.
Can you get UAME from CMM?
In theory – yes it is the center of the Unrelated Actual Mating Envelope from the two surfaces. However the only way to get the UAME would be to scan the surfaces and derive a plane from it. When using a CMM you need to scan the imperfect surface to derive these planes. Great point!
Can you use symmetry control on pitch diameter?
You can, but you need to specify whether the datum is to be taken as the major diameter, the minor diameter or the pitch diameter. I would also caution against using the symmetry control. It’s difficult to machine to and even harder to inspect for. Additionally, other controls such as position or profile can achieve the same results. Lastly, to hammer the point home, the symmetry and concentricity controls have fallen into such disfavor even with ASME that these two controls are likely to be dropped from the standard in the next revision.
How does a CMM work?
The basic structure of this type of CMM consists of a base with one or more articulating arms or beams. A probe is mounted on a rotating joint at the end of the arm. The arms can be extended or retracted from the base in any direction and will also pivot about the base, allowing for measurements in three axes. However, for some configurations, the probe is capable of traversing perpendicular to the base on a horizontal arm, providing a third measurement axis. The photo below shows a portable, rotating, horizontal arm type CMM manufactured by zCAT .
What is a CMM in a car?
A pair of large horizontal arm CMM’s used for car body measurement. This type of CMM is often fully computer-controlled, allowing them to measure, record, and evaluate data without operator intervention. A joystick for manual operation can control some machines.
What is a Coordinate Measuring Machine?
A coordinate measuring machine is an instrument that is used to collect measurements of three-dimensional objects. A CMM consists of a structure that moves in three dimensions, a probe attached to the structure, and a computer control and/or recording system. All coordinate measuring machines operate in the same way: the probe touches points on the object to be measured, and the position of the structure is recorded. Each measurement point is described by X, Y, and Z coordinates. All the measured points for a single object are combined into a 3D CAD file known as a point cloud. The point cloud can be compared to a 3D design drawing to determine if the object has been manufactured to the correct dimensions.
What is the largest CMM?
The largest CMM’s are gantry type. These machines are mounted on custom foundations and installed in bespoke climate-controlled buildings. The layout is similar to bridge machines. Accessibility and the ability to measure very large parts are the primary advantages of a gantry CMM.
Who makes bridge type coordinate measurement machines?
A bridge type coordinate measurement machine manufactured by Mitutoyo.
Is Y14.5M the same as ISO?
No one has addressed yet whether you are working with the ASME Y14.5M or the ISO standard. Symmetry is interpreted differently by the two standards. If you are using Xactmeasure in Pc-Dmis you have a choice between ASME & ISO. The instructor at the Xactmeasure/GD&T class said he had been told the ISO choices worked properly but admitted he himself did not know the ISO Standard well enough to give his personal opinion. That is about where I am. I know enough to know there are differences, but I don't know enough about the ISO standard to say much more than that.
Is ASME symmetry like concentricity?
The other comment I feel compelled to make is that, in ASME symmetry is like concentricity in that it has a unique and complex requirement that is often misunderstood and misapplied.
What is the axis of CMM?
CMM consists of 3-axis namely X-axis, Y-axis, Z-axis. Measurement is done by the prob attached to a third moving axis. This prob could be mechanical, optical, laser or white light.
What is CMM?
CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) is an advanced measurement machine that works to measure complex and large components. CMM is a device for measuring the physical characteristics of an object. The machine is controlled by a computer or an operator. Learn more
How do CMMs gather data?
CMMs generally gather their data by touching the workpiece with a probe ( either a solid probe or an electronic touch-trigger probe) attached the machine's measuring axis. Although the tip of the probe is very accurate, once the probe is attached to the CMM, the location of the tip to the machine's coordinate system must be determined prior to measuring. Since it's the tip's circumference that touches the part, the probe's center and radius are determined by measuring a very accurate sphere (requalification sphere).
What is a CMM probe?
Instead of a finger, the CMM uses a probe to measure points on a workpiece. Each point on the workpiece is unique to the machine's coordinate system. The CMM combines the measured points to form a feature that can now be related to all other features. The Coordinate System: The Machine Coordinate System.
What is CMM software?
With today's CMM software, the CMM measures the workpiece's datums (from the part print), establishes the Part Coordinate System, and mathematically relates it to the Machine Coordinate System.
What is the coordinate system?
The Coordinate System: The Machine Coordinate System. There are two types of coordinate systems in the world of measurement. The first is called the Machine Coordinate System. Here, the X, Y, and Z axes refer to the machine’s motions.
Can CMM errors be corrected?
The majority of the CMM's inaccuracies can be corrected automatically in the CMM’s computer. Once all of the geometric errors of the CMM are measured (called error mapping), they can be minimized or even eliminated by powerful algorithms in the CMM's software. This technique is called volumetric error compensation.
How to measure concentricity of a plane?
Using a Coordinate Measuring Machine ( CMM) Unlike with coaxiality, you measure the circle of the plane. Put the stylus on the measurement point on the datum circle, and then put the stylus on the measurement point on the target circle to measure the concentricity.
What factors affect the measured value of a dial gauge?
Factors such as the angle and strength used to put the dial gauge on the target affect the measured value, which implies that measurements may differ depending on the operator.#N#The friction between the tip of the dial gauge and the surface of the target may also leave scratches on the surface of the target.
