What is zeta potential and how is it calculated?
Zeta potential is calculated from electrophoretic mobility with solvent dielectric constant, viscosity and other constants using the Henry Equation. While most zeta measurements will be taken in aqueous systems, any colloids dispersed in a solvent that has an appreciable dielectric constant will exhibit zeta potential.
How well do process trains operate at zeta potentials?
Interestingly many process trains in the water industry appear to operate at zeta potentials (-15< æ <-10 mV) close to the edge of the observed operational windows making them susceptible to small changes in input conditions. The application of zeta potential for the diagnosis and control of water and wastewater treatment processes is not new.
How does Nanocomposix perform zeta potential measurements?
At nanoComposix, we perform zeta potential measurements using a Malvern Zetasizer Nano ZS instrument equipped with a 632 nm HeNe laser operating at a 173 degree detector angle. In a zeta potential measurement, a sample is loaded into a disposable folded capillary cell.
What is the effect of zeta potential on effluent turbidity?
At zeta potentials more negative than -22 mV, the effluent turbidity rises sharply as the suspended particles become effectively stabilized in the water due to mutual repulsion.

How are zeta potentials measured?
In practice, the zeta potential of dispersion is measured by applying an electric field across the dispersion. Particles within the dispersion with a zeta potential will migrate toward the electrode of opposite charge with a velocity proportional to the magnitude of the zeta potential.
What is zeta potential of water?
Raw water particles are typically in a zeta potential range of -15mV to -25mV. A good floc can form in the Zeta potential range of -8mV to +3mV. Adding coagulants (which are positively charged) neutralizes the repulsive (negative) charge of the particles in the raw water and enables a strong floc to form.
What is zeta potential test?
Zeta potential can be measured taking the difference between the potential of the nanoparticle surface and the solution in which the nanoparticle resides, as measured by the change of particle velocity moving toward an electrode while varying the electric field throughout the sample.
How do you read zeta potential results?
zeta potential is a measure of magnitude of charges on nanoparticles . the higher the value (postive or negative), the more stable the colloid dispersion is. Normally, a value of > 30 indicates good stability.
How does pH affect zeta potential?
pH is the most important parameter for zeta potential. For example, if we added acid in nanofluid, pH will decrease, which will increase positive charges on the particle surface. Zeta potential will increase. The point at which zero electrophoretic mobility occurs is called an isoelectric point [34].
How does zeta potential affect flocculation?
Zeta potential affects the size and density of flocs formed. Increases in density cause more rapid flocculation. Low zeta potentials reduce the electrostatic interactions between particles allowing the particles to approach closely and hence produce more compact flocs.
What does negative zeta potential tell you?
Negative zeta potential indicates that the dispersed particles in the suspension that we measure the zeta potential have a negative charge. Therefore, the charge of the dispersed particles is negative.
What is zeta potential and why is it important?
Almost all particulate or macroscopic materials in contact with a liquid acquire an electronic charge on their surfaces. Zeta potential is an important and useful indicator of this charge which can be used to predict and control the stability of colloidal suspensions or emulsions.
What does zeta mean in chemistry?
The zeta potential is a measure of the difference in potential between the bulk fluid in which a particle is dispersed and the layer of fluid containing the oppositely charged ions that is associated with the nanoparticle surface.
What is zeta potential class 12th Chemistry?
Hint: Zeta potential is also known as Electrokinetic. It is used to define or explain the process of preferential adsorption of ions from solution in the electrical charge on colloidal particles. There are two layers: the fixed layer and the diffused layer.
What is zeta potential in pharmaceutics?
The zeta potential indicates the degree of repulsion between adjacent, similarly charged particles (the vitamins) in dispersion. For molecules and particles that are small enough, a high zeta potential will confer stability, i.e., the solution or dispersion will resist aggregation.
What is meant by electrokinetic potential?
Electrokinetic potential is a prime indicator in the stability of colloidal dispersions. From the magnitude of this potential, the degree of electrostatic repulsion between similarly charged adjacent particles in the dispersion can be determined. Electrokinetic potential is also known as zeta potential.
All Answers (3)
Zeta potential is a property of the interface between the solid and the liquid, notably a liquid containing dissolved electrolyte. So, the concept of zeta potential for the dry particles is meaningless.
Similar questions and discussions
What should be the concentration of NPs for an accurate zeta potential measurment?
What is the relationship between zeta potential and effluent?
Figure 3 demonstrates a similar relationship to Figure 1, where an operational zeta potential window exists within which particle concentration in the effluent is both low and stable. A stable effluent concentration is dependant on standard filtration parameters such as media size and filtration rate whereas the operational zeta potential window is unaffected by operational variables and is determined by the chemistry of the system through parameters such as the coagulant type and pH.
Why is Zeta potential used?
The availability of modern methods and improvements in reliability and robustness of the measuring techniques has reinvigorated the application of zeta potential in the diagnosis and operation of physical processes. The regular use of zeta potential as a parameter has become more feasible, especially as improvements in the physical robustness of the technology mean that a system can be taken on site when necessary.
What is low zeta potential?
Low zeta potentials reduce the electrostatic interactions between particles allowing the particles to approach closely and hence produce more compact flocs. Figure 1 shows the residual turbidity after sedimentation of a coagulated, highly colored low turbidity raw water. Low and stable effluent turbidity is observed across an operational zeta potential range between +3 mV and - 22 mV. At zeta potentials more negative than -22 mV, the effluent turbidity rises sharply as the suspended particles become effectively stabilized in the water due to mutual repulsion. The size of this operational window can be enhanced by changing the coagulants as seen in Figure 1 where a higher charge density material produces a much wider operational window at positive zeta potentials.
What are the physical processes that are involved in wastewater treatment?
Physical processes such as sedimentation, flotation and filtration remain at the heart of most process trains for the treatment of water and wastewater flows. All these processes depend on the principles relating the size, density and the charge of the particles to be removed.
What is the current challenge of the operational Zeta potential window?
The current challenge is to understand what controls the size of the operational zeta potential window and then how it can be manipulated to improve performance robustness. This may require changes to the chemistry of the water or indeed of the physical processes themselves.
How to determine surface charge?
The surface charge, or more importantly zeta potential (æ), is determined by measuring the particle velocity induced when a potential difference is applied across a capillary cell containing the sample ( Zetasizer, Malvern Panalytical.).
Is Zeta potential a parameter?
The regular use of zeta potential as a parameter has become more feasible, especially as improvements in the physical robustness of the technology mean that a system can be taken on site when necessary.

Zeta Theory
Measurement Mechanics
- At nanoComposix, we perform zeta potential measurements using a Malvern Zetasizer Nano ZS instrument equipped with a 632 nm HeNe laser operating at a 173 degree detector angle. In a zeta potential measurement, a sample is loaded into a disposable folded capillary cell. The cells have two conductive electrodes that make contact with the instrument’s...
Importance of Zeta Potential
- Knowledge of zeta potential can be used to help optimize formulation, resulting in more effective formulation development for suspensions, emulsions or nanoparticle dispersions. Zeta can be used to predict the long-term stability of particles. For example, particles with zeta potentials larger than ±60 mV have excellent stability, where particles with zeta values between -10 mV an…
Ph & Salt Dependence
- A zeta potential value on its own without defining solution conditions is a virtually meaningless number. Zeta potential is strongly pH and salt-dependent and the solution pH needs to be measured and reported with every zeta potential measurement. For example, when a solution containing nanoparticles is titrated with acid to decrease the pH, acidic protons associate with t…
Particle Size and Sedimentation
The Importance of Surface Forces
- However, within the range of sizes normally encountered within water and waste water processes (< 1000 µm), surface forces play a vital role in controlling the removal characteristics of the system.
Zeta Potential
- The surface charge, or more importantly zeta potential (æ), is determined by measuring the particle velocity induced when a potential difference is applied across a capillary cell containing the sample (Zetasizer, Malvern Panalytical.). Zeta potential is known to be a key factor in understanding the performance of physical processes such as floccul...
Zeta Potential, Sedimentation and Flotation
- Zeta potential affects the size and density of flocs formed. Increases in density cause more rapid flocculation. Low zeta potentials reduce the electrostatic interactions between particles allowing the particles to approach closely and hence produce more compact flocs. Figure 1 shows the residual turbidity after sedimentation of a coagulated, highly colored low turbidity raw water. Lo…
Zeta Potential and Flotation Processes
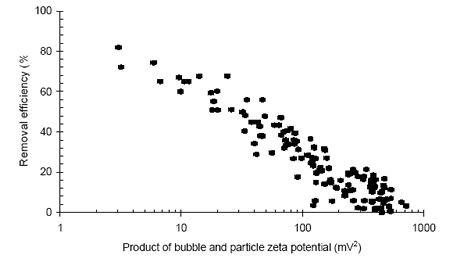
- Flotation processes also function due to density differences but this time because of the reduced densities generated by attaching air bubbles to the solid phase. In such unit operations the importance of zeta potential relates to the ability of the bubbles and particle to adhere and remain attached. It was observed that the process is driven by the combined zeta potentials of both the …
Zeta Potential and Filtration
- Filtration processes function by the attachment of particles on to media grains of materials such as sand and anthracite. The role of zeta potential here is in determining the ability of the particles to be captured. In principle this is the same as for flotation except that, in comparison with the bubbles, the media surfaces are less affected by changes in chemistry. Figure 3 demonstrates …
Conclusions
- The overall picture indicates the existence of operational windows of zeta potential within which treatment efficiencies are high and particle concentrations in the effluent are low. Within these windows, the process has effectively become independent of zeta potential as other factors become performance limiting. Interestingly many process trains in the water industry appear to …
Final Comments
- The application of zeta potential for the diagnosis and control of water and wastewater treatment processes is not new. Research papers regularly cited on this subject date back decades and in fact most of the basic understanding of how zeta potential controls performance remains similar to those early investigations. Early work was limited by the difficulty of the measurement itself a…
Improving Acceptance of Zeta Potential as An Analysis Technique
- The availability of modern methods and improvements in reliability and robustness of the measuring techniques has reinvigorated the application of zeta potential in the diagnosis and operation of physical processes. The regular use of zeta potential as a parameter has become more feasible, especially as improvements in the physical robustness of the technology mean th…
Other Improvements in Water Characterization
- Improvements in associated analytical areas have also been made, enabling much more extensive characterisation of the waters involved. The current challenge is to understand what controls the size of the operational zeta potential window and then how it can be manipulated to improve performance robustness. This may require changes to the chemistry of the water or ind…