Temporal pulse – The temporal pulse (i.e., superficial temporal artery) is palpated on the temple directly in front of the ear with the index finger.
How do you palpate the radial artery pulse?
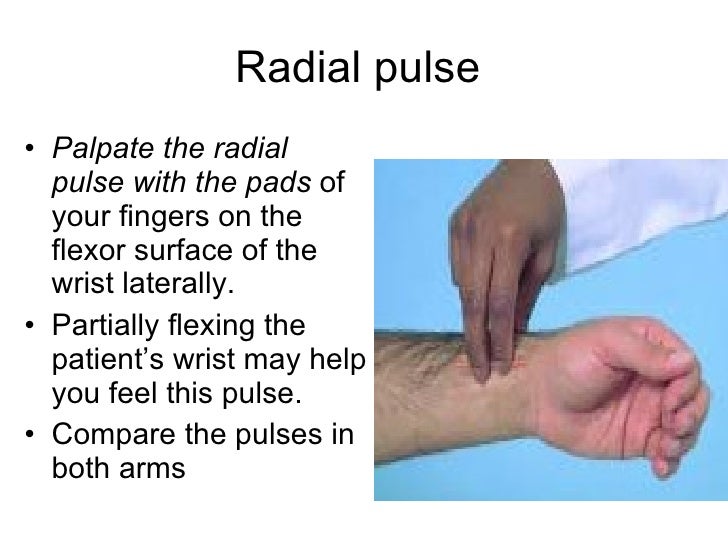
The clinically advised method of palpation of the radial artery pulse is the 3 finger method. Pulse is palpated using this method as follows: Make the subject (or) the person in whom you want to examine the pulse sit comfortably with the forearm placed in mid or semi-prone position, with the wrist slightly flexed.
What does a pulse in the temple feel like?
What does a pulse in your temple feel like? The pulse you feel in your temples is normal and comes from your superficial temporal artery which is a branch of your external carotid artery.
How do you take a pulse with your fingers?
Stand preferably by the right side of the subject. Place the tips of the middle three fingers (index finger, middle finger and ring finger) over the radial artery below the wrist at the base of the thumb. Apply light pressure using the fingers until the pulse is felt. If necessary, move the fingers around till the pulse is felt.
How do I know if I have temporal arteritis?
Your doctor may need to take a biopsy of the artery to diagnose temporal arteritis. The condition is often treated with a steroid, such as prednisone. Feeling a pulse in your temple is normal.

How can we find the temporal pulse site?
The temporal pulse is felt at the temple near the ear. The brachial pulse is felt on the inside of the elbow. The femoral pulse is felt in the groin area. The popliteal pulse is felt behind the knee.
Where do you palpate and feel for temporal artery?
Palpate the temporal arteries immediately in front of the tragus of the ear and up along the temple. Always check these pulses in an elderly patient with headache or unilateral visual changes or when polymyalgia rheumatica, giant-cell arteritis, or temporal arteritis is being considered.
How would the nurse palpate the temporal artery?
Where is the temporal artery palpated? The nurse palpates the temporal artery in the space above the cheek bone near the scalp line. The temporal artery is not found at midline at the base of the neck, between the mandibular joint and the base of the ear, or just left or right of the spine at the base of the skull.
Why do we need to palpate the temporal artery?
IN TEMPORAL ARTERITIS, when the inflamed arteries are painful, tender, enlarged, nodular, and pulseless, cursory examination of the vessels will reveal the diagnosis.
Can you feel temporal artery pulse?
In fact, in temporal arteritis you often can't feel the pulse through this artery at all. You aren't the only person to feel this. People who have heart disease tend to be more aware of their heartbeats than those who don't have heart trouble.
Are temporal arteries palpable?
There may be palpable changes to the temporal artery on examination. An acute phase response is usually seen on laboratory assessment, and a temporal artery biopsy will show inflammation and multinucleated cells with involvement of the internal elastic lamina.
Where can you best feel the pulse of the temporal artery quizlet?
The superficial temporal artery can be palpated anterior to the ear and immediately posterosuperior to the position of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ).
What does the temporal artery feel like?
Symptoms of temporal arteritis frequent, severe headaches. pain and tenderness over the temples. jaw pain while eating or talking. vision problems, such as double vision or loss of vision in 1 or both eyes.
What is the function of the temporal pulse?
Branching off from the external carotid, it assists in delivering oxygenated blood from the heart to regions within the neck and head.
Where is the temporal artery felt?
It arises from the external carotid artery when it splits into the superficial temporal artery and maxillary artery. Superficial dissection of the right side of the neck, showing the carotid and subclavian arteries. Its pulse can be felt above the zygomatic arch, above and in front of the tragus of the ear.
Which vessel is used for temporal pulse?
The radial artery is most commonly used to check the pulse.
Which side is the temporal artery on?
The temporal artery is a blood vessel on the side of your forehead.
Where is the temporal artery felt?
0:561:29Temporal Pulse Point Palpation, Location, and Nursing AssessmentYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo your pulse site where this X is is found right here this is your temporal artery. And you'll wantMoreSo your pulse site where this X is is found right here this is your temporal artery. And you'll want to feel bilaterally. And see if they are equal.
Can you feel superficial temporal artery?
Superficial temporal artery anatomy The FBSTA is most commonly palpable (if not visible) lateral to the superior orbital rim and anterior to or just within the hairline.
What is the pulse in my temples?
The pulse you feel in your temples is normal and comes from your superficial temporal artery which is a branch of your external carotid artery.
What is temporal arteritis treated with?
Your doctor may need to take a biopsy of the artery to diagnose temporal arteritis. The condition is often treated with a steroid, such as prednisone.
What causes a fast heart rate?
Palpitations. Sometimes stress, anxiety, or physical exertion might cause you to have a fast heart rate or palpitations combined with pain and pressure in your temples. The normal range for your resting heart rate is 60 to 100 beats per minute. Tachycardia, or fast heartbeat, is over 100. Normal physical activity can raise your heart rate up ...
What to do if you have heart palpitations?
If you’re concerned about your heart rate or palpitations, consult with your doctor about an electrocardiogram to detect any heart rhythm disturbances. You doctor will also, among other procedures, check your blood pressure.
Is it normal to feel a pulse in your temple?
Feeling a pulse in your temple is normal. If you feel throbbing pain in your temples, chances are it’s a headache, and is probably nothing to worry about as long as the pain doesn’t last over 15 days a month or interfere with your life. If you experience chronic headaches or feel that the pulsating pain in your temples could be a symptom ...
Can you take a pulse reading with pressure?
So, with gentle pressure you can actually take a pulse reading — like you might do on your wrist. If you feel pain in that area, with or without touching, it could indicate a medical issue.
Can temporal arteritis cause throbbing?
Although you’ll typically feel throbbing with temporal arteritis, the actual pulsations of the artery might decrease to the point where you can’t feel it. Other than pain and throbbing, symptoms may include:
How to palpate a pulse?
So that is the part you should be using. One school prefers dividing palpation between two hand functions. One hand is the palpating hand, while the other one is the hand that applies pressure. Several fingers are placed over the expected location of the pulse. Once the pulse is located, one or two fingers are put over the exact spot. The second hand can be used to apply pressure. This can assess the degree of which the pulse is pounding.
What is Pulse Palpation Good For?
Examining the pulse can offer information about many different conditions. Here are some examples:
What is the scale of a pulse?
The description of pulses is of the degree it bounds. If there is no pulse that is a ‘0’. If there is a normal pulse that is a ‘+2’. Anything in between is a ‘+1’. If pulse palpation reveals an aneurysm than you should just say ‘aneurysmal’. Another system for describing pulses uses a scale of 0-4. In this system ‘+2’ is normal and ‘+4’ is aneurysmal.
Why is pulse palpation important?
It is essential in the evaluation of patients with peripheral artery disease and other vascular conditions. By the way, in Chinese medicine pulse palpation has a very central role. In Chinese Medicine over 20 types of pulses are identified, each with a different meaning.
What does a carotid pulse feel like?
It is the typical pulse that is palpated distal to a stenosis. For example, this is what the carotid pulse feels like when there is severe aortic stenosis. Another descriptor is ‘water-hammer’. This means the pulse is sharp and strong.
What are the pulse locations?
Basic pulse locations are (from top to bottom): Superficial temporal, carotid, axillary, brachial, radial, femoral, popliteal, posterior tibial and dorsalis pedis arteries. Vascular specialists will also attempt to palpate the aorta.
When describing lower extremity pulses, timing should be included?
When describing lower extremity pulses the timing should be included. The examiner should palpate the radial and femoral pulses simultaneously. The femoral pulse should be simultaneous to the radial pulse. If it is later it may mean that there is coarctation or stenosis of the aorta.
How to feel radial artery pulse?
The radial artery pulse can be felt by gently pressing the radial artery against the underlying bone with the middle and index fingers.
What is the time interval between pulse beats?
Rhythm is the time interval between pulse beats.
What is it called when your pulse is below the normal range?
when the pulse rate is below the normal range (less than 60 in adults) is called Bradycardia. When the pulse rate is above the normal range (more than 100 in adults) is called Tachycardia. Pulse is documented as pulse beats per minute (bpm). To determine pulse rate, you have to count pulse for 60 seconds.
Where is the temporal artery located?
1. Temporal artery pulse. The superficial temporal artery is where you assess temporal pulse with your index and middle fingertips. It can be located over the temple just in front of the tragus of the external ear.
Where are the pulse points on the body?
9 most commonly assessed pulse points on the body by nurses are: Temporal pulse – over the temple. Carotid pulse – at the side of the neck. Apical pulse – over the 5th intercostal space (ICS) at left mid-clavicular line. Brachial pulse – on the antecubital fossa (crook) of the arm.
What is pulse rate?
The pulse rate is the pulsation you feel for one minute. The pulse rate should be within the normal range.
How is the force of a pulse determined?
It is determined by the amount of blood pushed out of the heart into the arteries with every heartbeat. The force will be at normal strength if the client has a normal pulse. Abnormal strengths of the pulse are: A weak or feeble pulse indicates reduced cardiac output and requires immediate action.
Where is the temporal pulse?
Temporal pulse - on superficial temporal artery - over the temple, in front of the ear.
How to palpate or feel the pulse?
The clinically advised method of palpation of the radial artery pulse is the 3 finger method. Pulse is palpated using this method as follows:
What is pulse and pulse rate?
Pulse: When heart contracts, the blood is ejected into the aorta with great force. The forceful ejection of blood into the aorta sets up a pressure wave that travels along the arteries. The pressure wave expands and recoils the arterial walls as it travels. The expansion of the arterial walls is palpable as the pulse at any superficial peripheral artery like the radial artery at the wrist.
Which finger is used to occlude the ulnar artery pulsations?
The distal finger (the finger which is distal to the heart) is used to occlude the ulnar artery pulsations which are entering into the radial artery through the palmar arch.
Where is the Dorsalis Pedis pulse?
Dorsalis pedis pulse - on dorsalis pedis artery - Over the dorsum of the foot
What is the total number of times the pressure waves are transmitted to the arteries during contractions of the heart in?
Pulse rate is the total number of times the pressure waves are transmitted to the arteries during contractions of the heart in a minute.
Where is the brachial pulse located?
Brachial pulse - on brachial artery - in cubital fossa along the medial border of the biceps muscle.
How long do you count pulses?
To save time, you can also count someone's pulse for 30 seconds and multiply that number by two.
How to find someone's pulse?
You can easily find someone's pulse on their neck or wrist, count the beats, and write down that number. While taking someone's pulse can sometimes feel intimidating, it's easy to do with a little dedication and practice. Steps.
What is a pulse of 4?
Write "4" for a quick, bounding pulse. If the pulse is stronger and quicker than usual , this would be a "4.". A pulse in the "4" range should be easy to find. You will likely notice the beats come with more force than the average pulse. A pulse over 100 beats per minute is considered a fast pulse.
What does "0" mean in a pulse?
Once the individual is under the care of an emergency medical team, document the absences of a pulse as a "0," meaning no pulse. Write "1" for a faint pulse. Sometimes, you can find a pulse, but it is very faint. The beating will be very light and the pulse may also be very slow.
How to measure pulse rate?
Use a watch or a timer on your phone to time yourself for a minute while recording someone's pulse. During that time, count the number of beats. The number you get is the pulse rate, measured in beats per minute.
What is the average pulse?
Mark an average pulse as "3. " If the pulse is steady, easy to detect, and within a normal range, this is considered an average pulse. This would be recorded as "3.". An average pulse is anywhere between 60 and 100 beats per minute.
How fast is a pulse?
A pulse over 100 beats per minute is considered a fast pulse.
How long does it take to treat temporal arteritis?
The mainstay of therapy for temporal arteritis is glucocorticoids, such as oral prednisone. Patients sometimes need to take glucorticoids for up to two years, sometimes longer; the dosage is gradually reduced over this period.
What is the best treatment for temporal arteritis?
Fortunately, a new medication called tocilizumab was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2017 to treat temporal arteritis. This medication is given as a subcutaneous injection.
What causes temporal arteritis?
If not diagnosed and treated quickly, temporal arteritis can cause: 1 Damage to eyesight, including sudden blindness in one or both eyes. 2 Damage to blood vessels, such as an aneurysm (a ballooning blood vessel that may burst). 3 Other disorders, including stroke or transient ischemic attacks (“mini-strokes”).
How long does it take for glucocorticoids to help with temporal arteritis?
The mainstay of therapy for temporal arteritis is glucocorticoids, such as oral prednisone. Patients sometimes need to take glucorticoids for up to two years, sometimes longer; the dosage is gradually reduced over this period.
Is temporal arteritis more common than PMR?
Often, temporal arteritis can be associated with an entity called polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR), which is an inflammatory condition affecting the shoulders, hip girdle and neck. This leads to significant stiffness and pain. PMR is far more common than temporal arteritis, but up to 30 percent of temporal arteritis patients have PMR.
Can temporal arteritis cause blindness?
The vasculitis that causes temporal arteritis can involve other blood vessels, such as the posterior ciliary arteries (leading to blindness), or large blood vessels like the aorta and its branches, which can also lead to serious health problems. If not diagnosed and treated quickly, temporal arteritis can cause:
Can temporal arteritis be reversed?
The outlook for those with temporal arteritis is very good, unless the person has had a loss of vision. If that occurs, the damage generally cannot be reversed. Most complications associated with temporal arteritis are from the use of steroid drugs, not from the disease itself.

Overview
Palpitations
- Sometimes stress, anxiety, or physical exertion might cause you to have a fast heart rate or palp…
The normal range for your resting heart rate is 60 to 100 beats per minute. Tachycardia, or fast heartbeat, is over 100. Normal physical activity can raise your heart rate up to 150 to 170 beats per minute. - Beyond stress, palpitations might be caused by medications, such as decongestants or stimulan…
Rarely, palpitations might indicate an underlying condition, such as:
Tension headaches
- Tension headaches often result from: temporary fatigue, anxiety, stress, or anger. Common sym…
an aching sensation that might feel like a tightening - contracting head and neck muscles
Your doctor might recommend over-the-counter or prescription medications and suggest relaxation training.
Migraine
- M igraine is a sustained throbbing pain that can be felt at your temples, as well as other areas o…
Migraine is believed to be caused by chemical reactions in the brain. Your doctor might recommend treating your migraine with over-the-counter or prescription medications. Your doctor might also suggest biofeedback and relaxation training.
Temporal arteritis
- If the throbbing pain in your temples becomes a constant headache and it’s painful to touch you…
Although you’ll typically feel throbbing with temporal arteritis, the actual pulsations of the artery might decrease to the point where you can’t feel it. Other than pain and throbbing, symptoms may include: - Doctors believe the condition involves antibodies attacking the arterial walls and creating swelli…
Your doctor may need to take a biopsy of the artery to diagnose temporal arteritis. The condition is often treated with a steroid, such as prednisone.