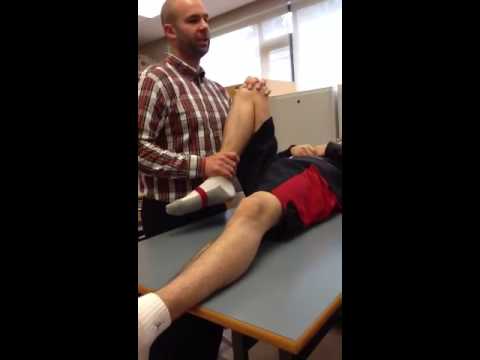
How does the McMurray test work?
- You’ll lay on your back.
- Your provider will bend your knee to 90 degrees perpendicular to the rest of your body (about where it would be if you were in a seated position).
- Your provider will rotate your bent knee in (toward your body) and out (away from your body).
- Your provider will straighten your leg.
What does the McMurray test tell you?
What the McMurray Test Tells Us. It is a procedure by which the knee is systemically rotated to identify where tears in the cartilage (called the meniscus) may have occurred or developed. A torn meniscus is a common injury caused by the forceful twisting of the knee during sport, when running, or during a fall or misstep.
What is the McMurray test for meniscus tear?
How the McMurray Test Is Performed. Any pain or "clicks" serves as a positive diagnosis of a lateral tear of the meniscus. The second half of the test proceeds similarly: The doctor holds the knee in one hand and the sole of the foot in the other. The knee is fully bent and pulled toward outwards in a "bow-legged" position.
How is McMurray's test performed for plantar fasciitis?
Both methods are described by McMurray. 383,399 Nicholas A Piantanida MD, Nicole T Yedlinsky MD, in The Sports Medicine Resource Manual, 2008 McMurray's test is performed with the patient supine and relaxed. The examiner grasps the patient's heel with one hand and the joint line of the knee with the other hand.
How do you perform a varus force test?
Performance: The examiner will hold the knee at the joint line with one hand while holding the foot with the other hand. With the knee fully flexed, the examiner will internally rotate the tibia and extend the knee while applying a varus force at the knee.

When is the McMurray test performed?
When would I need the McMurray test? Your provider will perform the McMurray test if they think you have a torn meniscus. It's one of the most common knee injuries — especially among athletes. Your meniscus is a rubbery wedge of cartilage in your knee between your femur (thigh bone) and tibia (shin bone).
How do you make a McMurray?
0:111:09McMurray's Test - Lateral & Medial Meniscus Damage - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipHold and externally rotate the foot. With the foot still rotated the knee is bent until it reachesMoreHold and externally rotate the foot. With the foot still rotated the knee is bent until it reaches full flexion. The therapist then gradually straightens the knee to full extension.
What is a McMurray's maneuver and what is it used to test for?
The McMurray test, also known as the McMurray circumduction test is used to evaluate individuals for tears in the meniscus of the knee. A tear in the meniscus may cause a pedunculated tag of the meniscus which may become jammed between the joint surfaces.
What do the McMurray test evaluate for?
The eponymous test that is commonly performed as part of the routine knee examination in order to test for the presence of a meniscus tear is McMurray's test, which was described by McMurray in 1942 in the British Journal of Surgery (5).
What is a McMurray test for the knee?
The McMurray test (also known as the McMurray circumduction test) is used to detect internal tears in the knee joint. It is a procedure by which the knee is systemically rotated to identify where tears in the cartilage (called the meniscus) may have occurred or developed.
How do you diagnose a torn meniscus?
DiagnosisX-rays. Because a torn meniscus is made of cartilage, it won't show up on X-rays. But X-rays can help rule out other problems with the knee that cause similar symptoms.MRI . This uses a strong magnetic field to produce detailed images of both hard and soft tissues within your knee.
How accurate is the McMurray test?
Results showed that the McMurray's test had a sensitivity 34.3% and a specificity of 86.4%. Sensitivity of the test for joint-line tenderness was 62.9% and the specificity 50%.
What does medial joint line tenderness mean?
Tenderness to palpation over the medial joint line often signifies two common etiologies: medial meniscal tear and degenerative joint disease. This point is found by first palpating the inferior pole of the patella with the knee in 90 degrees of flexion and then moving medial along the joint line.
What injury does Thessaly's test for?
Your provider will perform the Thessaly test if they think you have a torn meniscus. It's one of the most common knee injuries — especially among athletes. Your meniscus is a rubbery wedge of cartilage in your knee between your femur (thigh bone) and tibia (shin bone).
What is the name of a test you would use to determine a tear in the meniscus?
An MRI test can tell whether you have a meniscus tear or other related injuries, and it can help with treatment decisions. Arthroscopy can identify a meniscus tear and treat it at the same time. It can also see if you have other injuries.
What position should a patient be in for a McMurray test?
To perform the McMurray test the patient should be relaxed in a supine position as the examiner firmly supports the knee and the lower leg.
What is the purpose of the McMurray test?
Purpose: The McMurray test is used to assess the integrity of the medial and lateral meniscus, specifically testing for meniscal tears. Meniscal tears are the most common injury to the knee. The McMurray test is commonly performed along with the joint line tenderness test to identify meniscal injury.
How to test for medial meniscus tear?
To test the medial meniscus, the examiner will place the knee into flexion once again, externally rotate the tibia, and extend the knee while applying a valgus force to the knee. Pain or a popping sensation indicates a medial meniscus tear.
What is the McMurray test?
McMurray test of the knee is used to evaluate the injury of the lateral and medial meniscus of the knee joint. It was originally developed to diagnose posterior horn lesions of the medial meniscus.
Who was the first person to describe the McMurray test?
McMurray Test was first described by Thomas Porter McMurray, who was a British orthopedic surgeon.
How to test medial meniscus?
To test the medial meniscus: the clinician rotates the tibia into external rotation, then slowly extends the knee.
When is the McMurray test positive?
McMurray test is Positive when there is a click (or catch) and pain in the extension of the knee.
Is McMurray positive for knees?
The McMurray test is positive in 30% of all children with normal knees.
Does McMurray test have varus valgus stress?
Numerous variations exist for the McM urray test, including the addition of varus / valgus stresses. An examination of the variation seemed to indicate that the McMurray test has some value as a specific test where a positive test would rule in the disease.
What is McMurray's test?
McMurray's test is used to determine the presence of a meniscal tear within the knee.
Which is more accurate, Reiders or McMurrays?
There are several different reported methods of performing McMurrays Test, Reiders method may be the most accurate.
Can IR be tested on posterior horn?
The IR of the tibia followed by extension, the examiner can test the entire posterior horn to the middle segment of the meniscus. The anterior portion of the meniscus is not easily tested because the pressure to that part of the meniscus is not as great.
What is the McMurray test?
McMurray test. The basic premise of the McMurray test is that meniscus tears are trapped during certain knee movements, with resultant pain and clunking. The test is easy to demonstrate but difficult to describe.
What is a pop or click on a McMurray test?
The knee is flexed maximally, with external tibial rotation (medial meniscus) or internal tibial rotation (lateral meniscus). The knee is brought to full extension while maintaining rotation. A positive test produces a pop or click. Pain in a reproducible portion of the range of motion is described as part of McMurray's test.
What is the Apley test?
Apley distraction and grinding (compression) tests. Joint-line tenderness can be associated with meniscus or collateral ligament injury . The concept behind the Apley test is that ligaments usually are painful when stressed in distraction, whereas pain involving the meniscus is felt with compression. With the patient in the prone position, the knee flexed 90°, and the femur stabilized with one hand, distraction is applied with the other hand by pulling upward on the ankle while rotating medially and laterally. A varus and valgus force may also be applied to further delineate whether the MCL or the LCL might be the source of pain (Apley distraction test). Once the distraction portion of the test has been completed, compression is applied to alternately grind the medial and lateral meniscus between the tibia and femur, with gentle varus and valgus force applied, while internally and externally rotating and compressing the ankle downward ( Apley grinding or compression test; Figure 6-38 ).
How to test for a torn meniscus?
The McMurray test for torn meniscus can provide the clinician with useful information as to the whether a torn medial or lateral meniscus is responsible for the patient's knee pain. To perform the McMurray test for torn meniscus the examiner has the patient assume the supine position on the examination table with the knee maximally flexed. With the affected extremity relaxed the examiner grasps the ankle and palpates the knee while simultaneously rotating the lower leg internally and externally and extending the knee (Fig. 102-14 ). The test is considered positive for a torn meniscus if the examiner appreciates a palpable or auditory click while rotating and extending the knee.
How to remove meniscal fragments?
Loose meniscal fragments are removed with a large-diameter shaver while milking the posterior aspect of the knee to express residual debris.
How to treat horizontal meniscal tear?
Horizontal meniscal tears may be addressed through selective débridement of the lesser-quality upper or lower leaflet of the tear while retaining the more substantial portion with peripheral capsular attachment ( Fig. 5.11 ).
How to excise a bucket handle tear?
Larger, irreparable tears (e.g., chronic irreducible bucket-handle tears) can typically be excised by sharply dissecting the posterior and anterior aspect of the tear with arthroscopic punches or scissors, followed by grasper removal en masse.
What is the purpose of the McMurray test?
The McMurray test (also known as the McMurray circumduction test) is used to detect internal tears in the knee joint. It is a procedure by which the knee is systemically rotated to identify where tears in the cartilage (called the meniscus) may have occurred or developed. 1 . A torn meniscus is a common injury caused by the forceful twisting ...
How does a doctor do a knee flexion?
The procedure itself involves two steps, as follows: The doctor holds the knee in one hand and the sole of the foot in the other. The knee is then fully bent and pulled toward outwards in a "knock-kneed" position. Meanwhile, the doctor will start rotating the foot internally while extending the knee.
Is a McMurray test enough?
While many people assume that an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan would be the first step in diagnosing this type of injury, the McMurray test is often enough to provide a definitive diagnosis.
Can anterior tears be diagnosed?
By contrast, anterior tears (to the front of the knee) are not easily diagnosed and may require an MRI or arthroscopic investigation to pinpoint the damage.
Is meniscal tear easy to diagnose?
Rinonapoli G, Carraro A, Delcogliano A. The clinical diagnosis of meniscal tear is not easy. Reliability of two clinical meniscal tests and magnetic resonance imaging. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2011;24 (1 Suppl 2):39-44. doi:10.1177/03946320110241S208
Purpose of to test
This test is used to determine of to presence of meniscal tear within to knee.
What is Positive findings of this test ?
This test is positive when to patient complain is knee Pain , audible clicking , snapping & locking it is indicate to compromised of meniscus.
Advantages & Disadvantages of this test ?
This test is specially useful for to detect tears in to posterior means back aspect of to knee.

Diagnosis
Symptoms
- LaPrade and Konowalchuk109 described a figure-four test that attempts to replicate symptoms in patients with tears of the lateral meniscus popliteomeniscal attachments. The patient is placed supine, the knee flexed to approximately 90 degrees, the foot placed over the contralateral knee, and the hip externally rotated. A varus loading at the knee joint increases tensile loading in the d…
Signs and symptoms
- The clinical examination may reveal tenderness on palpation at the posterolateral aspect of the joint at the anatomic site of the popliteomeniscal attachments. The McMurray test is performed in maximum flexion, progressing from maximum external rotation to internal rotation and then back to external rotation. This test may produce a lateral palpabl...
Assessment
- Patients complete questionnaires and are interviewed to rate symptoms, functional limitations, sports and occupational activity levels, and patient perception of the overall knee condition according to the Cincinnati Knee Rating System (CKRS).21
Clinical significance
- Injury of the meniscus can occur acutely with a sudden twisting injury on a partially flexed knee. It is a common sports injury, but it can also happen during simple activities that cause rotation of the knee. Meniscal tears can also be due to a prolonged degenerative process, especially in a patient with an ACL-deficient knee. The patient complains of loss of smooth motion, giving out o…
Treatment
- Initial treatment is the control of inflammation with ice, NSAIDs, and rest with the knee immobilized in a comfortable position. As pain subsides, straight leg raises should be done to strengthen the quadriceps. If effusions are present, aspiration is indicated for pain relief. Arthroscopic repair or resection is the preferred treatment for symptomatic patients. Repair of t…