How to plot the position
- Step 1: Start with what we know The first thing we can do is plot our start point on the chart. This should be best practice while monitoring progress on a passage. ...
- Step 2: Allow for wind If the wind is on our beam it will have the effect of pushing the boat sideways. ...
- Step 3: Allow for the tide
Full Answer
How do I plot a 1030 GPS position?
At 1030 you obtain the following position from your GPS: Latitude 41°17.0'N; Longitude 70°26.0'W. Follow the steps below to see how you would plot this 1030 GPS position. Cartographers (chart makers) create a grid-like web on your nautical chart. Latitude lines run in a horizontal direction.
How do you find the latitude and longitude of your boat?
Any GPS receiver will find the latitude and longitude along your sailing routes at any moment. But as a skipper, have you plotted this information onto a navigational chart to check your position?
How do I plot a route using the Breton plotter?
To plot a route from the fairway buoy of your departure harbour to the fairway buoy of your destination you would align North on the Breton Plotter with North on the chart, and then calculate the Variation (this could be 10 degrees or so according to the position of Magnetic North relative to True North – find out in your Nautical Almanac).
How do you find the coordinates of a ship?
To find ship's coordinates one also needs a chronometer (==very precise clock) and a set of pre-calculated tables. 1. To find your latitude you should find today's maximum angle between the Sun and the horizon, e.g. write down that angle when the Sun is at the maximum rise above the horizon.
How to write GPS coordinates?
What are the lines that run up and down on a chart?
How to find the latitude of a compass?
What direction do latitude lines run?
How to find latitude?
What is the name of the grid that runs up and down?
Can GPS find latitude and longitude?
See 2 more
How do you plot a ships position?
To plot the position by visual bearings of two objects, take the bearings of both the objects simultaneously. Now draw the bearing of these objects on the charts. The point where these two bearings (position lines) intersect will be the ship's position.
How do you plot an estimate position?
2:223:38RYA Day Skipper: Plotting an Estimated Position - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipPosition we put a dot and a triangle at the end of our tide line. This is the chart symbol we useMorePosition we put a dot and a triangle at the end of our tide line. This is the chart symbol we use for an estimated. Position. We can now look up the latitude and longitude of our position.
What is plotting in ship?
Plotting. Plotting is the process of keeping track of the position of a vessel over time. This is done by recording the successive positions of the vessel in the nautical chart. The position can be obtained by dead reckoning or by taking bearings from prominent charted landmarks and constructing Lines-of-Position.
What is the most commonly used methods to determine ship's position?
The most commonly used method to determine position is then the classic terrestrial method based on bearings to landmarks (identified characteristic points) with known coordinates. Bearings are determined based on the recorded image of landmarks. Registration can be done using either vision or radar systems.
How do you plot a course at sea?
How to plot a course on a chart:Draw a line from point A to B - using parallel rules, from starting mark to next mark.Check the line for safety - if not, move end mark until you get a safe leg.Measure and mark the heading - transfer the leg to compass.Measure and mark the distance - measure the legs.More items...
What is DR and EP position?
This is the most accurate position that can be obtained by calculation and estimation only. It is derived from the DR position with allowance made for the effects of currents and tidal streams. Again it is an approximate position only.
What are the 4 types of nautical charts?
What are the different types of nautical charts?Navigation charts - contains detailed information about the world's waterways and oceans.Pilot charts - weather routes and time voyages.Small scale charts - general charts, also called Planning charts.Large scale charts - coastal or general approach.More items...
How do you plot a waypoint on a nautical chart?
The first step is to look at the chart, decide on the route, then using a pencil and ruler mark the route from buoy to buoy or chosen position. Each change of course is called a waypoint and its position is marked using a cross with a square around it (the symbol for a waypoint).
What is manual plotting?
Manual Plotting. The Manual Plotter is an object that is designed to work in conjunction with scripts to plot arbitrary data. The functionality is basically the same as the regular data plotter.
What are the 3 primary position fixing methods?
a) Parallel indexing and use of clearing bearings; b) Use of radar to check the accuracy of the charted position by comparing the location of the radar target against the charted symbol; c) Visual cross bearings; Obtaining a three-bearing fix.
What shows the position and direction of a ship?
Magnetic compass. Important as it is for a ship to know its exact position at any given time, the purpose of a vessel is that it moves between ports. Therefore, it is vital that the ship can head in the correct direction and the chief tool for this is its compass. Modern ships have access to many types of compasses.
Why is it necessary to determine and plot the position of the vessel frequently especially during coastal navigation?
While at sea, accurate position, speed, and heading are needed to ensure the vessel reaches its destination in the safest, most economical and timely fashion that conditions will permit. The need for accurate position information becomes even more critical as the vessel departs from or arrives in port.
How do you present an estimate?
What do I include in an estimate?Job description. Explain the work you'll be doing. ... Materials and labor. Provide a high-level view of the necessary materials and labor and the costs for each. ... Total cost. Clearly and correctly tally up the total costs of the project.This is a big one. ... Sales and company contact info.
How do you prepare an estimate?
Let's consider six primary steps in estimate preparation.Step 1 – Information to bidders' review. ... Step 2 – Bid form review. ... Step 3 – Front end of the specifications review. ... Step 4 – Review specification Divisions 26, 27, 28. ... Step 5 – Installation drawings review. ... Step 6 – Submit RFIs for missing information.
What is an example of an estimate?
An example of an estimate is a list of times and charges that it may cost to complete a construction job. A tentative evaluation or rough calculation, as of worth, quantity, or size. An estimate of the damage caused by the storm.
How do you prepare a building estimate?
How to Write a Construction Estimate in 8 StepsReview The Scope of The Project.Provide a rough timeline.Determine What Work You Need to Subcontract Out.Put Together an Estimate of The Cost of Materials.Check Out The Competition.Outline Your Terms And Conditions.Make Your Estimate Professional.Submit Your Estimate.More items...
Quick and Easy
Here is a quick and easy explanation on how to find your estimated position or your “EP” based on just your course heading and one bearing. This method is used when you are making way on a steady course and you use an un-moving landmark to sight a bearing angle from your ship’s compass (or handheld).
Practice Question
This is typical of what you may find on your coastal navigation portion of your exam. Or if you are taking the ASA105 course. Thank you Tom Tursi at the Maryland School of Sailing for this practice question.
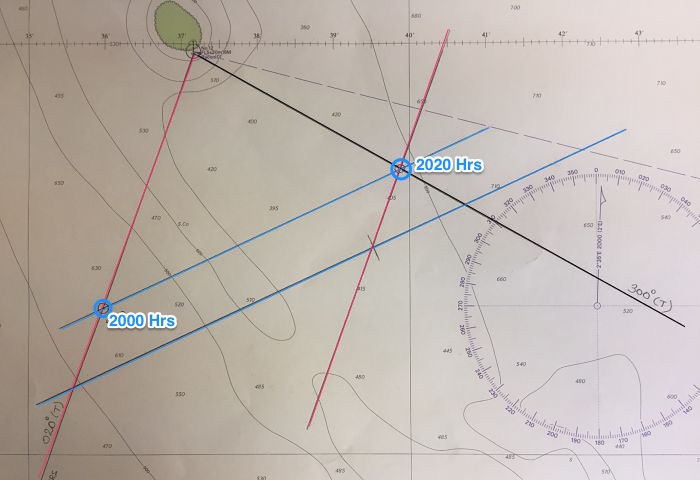
1 - Plot Your Dead Reckoning Positions
Remember we plot all lines on the chart in TRUE! So you need to use your TVMDC conversion table to find the True angles to plot. When labeling the plotted lines, you can use either True values or psc values, you just must stay consistent when writing the exam (and better also in real life practice).
2 - Sight and Plot Your Bearing
At 1000, we take our bearing on the landmark. Again, we choose a non-movable object. In this question, we use a spire. Using the ship’s compass, we sight the spire over our port side at 319° or 299°T.
3 - Never Where You Think You Should Be
Well, we have fallen quite short of where we thought we would end up at 1000! It could be because there is a current, or it could be the tide. Or, maybe, you did not maintain a constant speed of 6.4 knots for the entire hour.
4 - Square And A Dot
Where those two lines meet is your estimated position (EP). Mark it with a square and a dot, then find the latitude and longitude of this dot!
How to write GPS coordinates?
1. Write down your GPS Latitude and Longitude into your log.Label each coordinate N or S (for Latitude) and E or W (for Longitud e). In the illustration above, you write down Latitude 41°17.0'N; Longitude 70°26.0'W.
What are the lines that run up and down on a chart?
Those that run left and right (or east and west) are lines or parallels of Latitude. Those that run up and down are lines or meridians of Longitude.
How to find the latitude of a compass?
Find the bottom edge of your "position box". Follow that Latitude line over to the right or left side of the chart. 2. Push the needle point of your compass in that line on the right or left side (latitude scale) of the chart. Notice in illustration B, you stick the needle point in the line marked 41°10.0'N.
What direction do latitude lines run?
Latitude lines run in a horizontal direction. Longitude lines run in a vertical direction. Navigating with Latitude. Imagine the earth, balanced on her axis without a tilt. Wrap a "belt" around the earth, divide it in two and you have the equator--birthplace of Latitude.
How to find latitude?
Latitude lines parallel the equator to the north or to the south. To find latitude, you measure how many degrees you are north or south of the equator. Latitude reaches a maximum of 90 degrees (90°) at both north and south poles. Always label Latitude N, if north of the equator, or S, if south of the equator.
What is the name of the grid that runs up and down?
Those that run up and down are lines or meridians of Longitude. These lines form a series of grids over your nautical chart. At any moment in time, your sailboat will be located in one of those grid boxes--called a "position box". Your first step will be to locate your specific "position box".
Can GPS find latitude and longitude?
Any GPS receiver will find the latitude and longitude along your sailing routes at any moment. But as a skipper, have you plotted this information onto a navigational chart to check your position?
What do we do after we plot our heading and journey distance on the chart?
After we have plotted our heading and journey distance on the chart we have to plot the tidal vector on the end. This will show us what the current has done to our vessels journey over the time we have been travelling.
Why is it important to use recognised plotting symbols when you are doing your chart work?
It is important to use recognised plotting symbols when you are doing your chart work. This is so you can trace back over your work if needs be. It also allows the next sailor who is on watch to understand what you have done. That means they won’t have to wake you up!
Why do we plot an estimate?
On longer passages however, we may not be in sight of charted objects that we could use to gain a more exact position. We may not be in sight of land at all. That’s when we need this tool to estimate where we are.
What happens to the compass heading if the wind is on the starboard side?
If the wind is on the starboard side then the compass heading will decrease. ‘S’ for starboard and ‘S’ for subtract.
What is the final point of a tide vector?
The final point at the end of the tidal vector is our estimated position. This is where we are likely to be after allowing for the effects of the wind and tide. This point is marked by a triangle and it is good practice to note the time of the fix on the chart as well as in the log.
How do we know what our heading is?
We also know what our heading is. We either get this information from the GPS chart plotter or from the magnetic compass. If we were to plot this information onto a chart we could see the heading and distance travelled from a known starting point.
How do we know how fast we are moving through the water?
When we are on a passage we know how fast we are moving through the water. The information is given to us by the ships log. The log is basically a paddle wheel that records distance travelled. A bit like the odometer on a car.
How to zoom in on MarineTraffic?
The main MarineTraffic web platform features a Live Map, showing the positions of vessels. Users can click and drag the map to move around the globe, highlight vessels on the map to find out more information, or use the '+' an '-' symbols to zoom in or out, while the left hand side of the screen has a range of more advanced options.
How Does MarineTraffic Work?
The MarineTraffic service makes use of AIS tracking technology to provide information about the identification, course, speed and current location of vessels. From there, locations can be overlaid onto Google Maps and, as a result, users can use the service to track the movements of ships and other vessels in real-time.
What is MarineTraffic tracking?
The MarineTraffic service makes use of AIS tracking technology to provide information about the identification, course, speed and current location of vessels. From there, locations can be overlaid onto Google Maps and, as a result, users can use the service to track the movements of ships and other vessels in real-time.
How to measure distance on a sailing chart?
To judge the distance of the day’s sailing you will measure off one nautical mile on the latitude scale of the chart with your dividers, and ‘walk’ the dividers along the proposed route. You count the miles and from there gauge how long the day’s sailing will take. A 10 mile route might take a couple of hours while a 20 mile route may take 4-6 depending on the conditions and whether you’re only out to get to the destination or to enjoy the journey itself.
How to plot a compass rose?
The compass rose is a plastic circle with 360 degrees marked out around it on an oblong piece of plastic that measurements on it. To plot a route from the fairway buoy of your departure harbour to the fairway buoy of your destination you would align North on the Breton Plotter with North on the chart, and then calculate the Variation (this could be 10 degrees or so according to the position of Magnetic North relative to True North – find out in your Nautical Almanac).
What is a Breton Plotter?
The Breton Plotter has a compass rose and different lines that can be used for navigation on a chart. At its simplest it is a pair of parallel lines so you can slide it around the chart as you do your calculations.
What is the shifting of the magnetic pole?
The shifting of the magnetic pole is known as ‘ Variation ’. Variation is predictable and using your chart’s compass rose you can find the Variation every year for a given location. This might be 7 degrees West for example. In that case, in order to head due North you would have to adjust your course by 7 degrees East.
Where is longitude measured?
Longitude is similar to latitude but it is measured vertically (east - west) from the meridian line that runs through Greenwich, England. The longitude range runs from 0° - 180°. The meridian that is on the opposite side of the globe from Greenwich is known as the International Date Line and is 180° from Greenwich.
Can you use a navigation chart on a tablet?
In most cases these days you will use an electronic chart, whether a Navionics app that runs using the GPS in your tablet or phone, or on the vessel’s electronic navigation system. You will also have paper charts in reserve.
How many lines are needed to plot a posi?
And of course you then have to plot the lines derived from your calculations onto a chart, with a minimum of 3 accurate calculations and lines for a good fix (posi
How long does it take to learn to sail?
Learning the basics takes half an hour, although it takes more skill when the deck of your vessel is moving or you only get a glimpse of your target through cloud.
What is the sextant in physics?
The sextant, if you will, allows you to determine the radius of the circle on earth through which the body would be seen to have that altitude. While it is a circle, it is the line of position of that altitude. Cross the line with another one that represents the same information four hours earlier, and you have a fix!
How to find the range of a vertical height?
Calculating the range of a vertical height is done by making a right-angle triangle between the sea level and the vertical height of the observed object.
How do you measure the angle of an object?
Through the contained telescope you measure the angle of an astronomical object, like a star, with respect to the horizontal direction.
Do you need a reference for navigation?
Very basically, if you know where a star is located in the sky relative to the Earth, you have a reference for navigation. At sea beyond land, all directions look the same, so references are needed.
How to write GPS coordinates?
1. Write down your GPS Latitude and Longitude into your log.Label each coordinate N or S (for Latitude) and E or W (for Longitud e). In the illustration above, you write down Latitude 41°17.0'N; Longitude 70°26.0'W.
What are the lines that run up and down on a chart?
Those that run left and right (or east and west) are lines or parallels of Latitude. Those that run up and down are lines or meridians of Longitude.
How to find the latitude of a compass?
Find the bottom edge of your "position box". Follow that Latitude line over to the right or left side of the chart. 2. Push the needle point of your compass in that line on the right or left side (latitude scale) of the chart. Notice in illustration B, you stick the needle point in the line marked 41°10.0'N.
What direction do latitude lines run?
Latitude lines run in a horizontal direction. Longitude lines run in a vertical direction. Navigating with Latitude. Imagine the earth, balanced on her axis without a tilt. Wrap a "belt" around the earth, divide it in two and you have the equator--birthplace of Latitude.
How to find latitude?
Latitude lines parallel the equator to the north or to the south. To find latitude, you measure how many degrees you are north or south of the equator. Latitude reaches a maximum of 90 degrees (90°) at both north and south poles. Always label Latitude N, if north of the equator, or S, if south of the equator.
What is the name of the grid that runs up and down?
Those that run up and down are lines or meridians of Longitude. These lines form a series of grids over your nautical chart. At any moment in time, your sailboat will be located in one of those grid boxes--called a "position box". Your first step will be to locate your specific "position box".
Can GPS find latitude and longitude?
Any GPS receiver will find the latitude and longitude along your sailing routes at any moment. But as a skipper, have you plotted this information onto a navigational chart to check your position?
